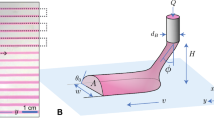
Abstract
We present a two-dimensional large-aspect-ratio model for the off-contact screen printing of a power-law fluid. We extend the work of White et al. (J Eng Math 54:49–70, 2005) by explicitly including the fluid/air free surface that is present beneath the screen ahead of the squeegee. In the distinguished parameter limit of greatest interest to industry, the process is quasi-steady on the time-scale of a print and can be analysed in three separate regions using the method of matched asymptotic expansions. This allows us to predict where the fluid transfers through the screen, the point at which it first makes contact with the substrate, and the amount of fluid deposited on the substrate during a print stroke. Finally, we show that using a shear-thinning fluid will decrease the amount of fluid transferred ahead of the squeegee, but increase the amount of fluid deposited on the substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobs DR, Voigt DR (1970) Parametric dependencies in thick film screening. Proc ISHM 18: 1–10
Riemer DE (1988) Analytical model of the screen printing process: part 1. Solid State Technol 8: 107–111
Riemer DE (1988) Analytical model of the screen printing process: part 2. Solid State Technol 9: 85–90
Riemer DE (1989) The theoretical fundamentals of the screen printing process. Hybrid Circuits 18: 8–17
Taylor GI (1962) On scraping viscous fluid from a plane surface. In: Schäfer M (eds) Miszellaneen der Angewandten Mechanik. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin, pp 313–315
Hunter B (1994) A Stokes flow analysis of the screen printing process. Int J Microcircuits Electron Pack 17: 21–26
Riedler J (1983) Viscous flow in corner regions with a moving wall and leakage of fluid. Acta Mech 48(1–2): 95–102
Jeong J, Kim M (1985) Slow viscous flow due to sliding of a semi-infinite plate over a plane. J Phys Soc Jpn 54: 1789–1799
Owczarek JA, Howland FL (1990) A study of the off-contact screen printing process - Part I: model of the printing process and some results derived from experiments. IEEE Trans Comp Hybrids Manuf Technol 13(2): 358–367
Owczarek JA, Howland FL (1990) A study of the off-contact screen printing process - Part II: analysis of the model of the printing process. IEEE Trans Comp Hybrids Manuf Technol 13(2): 368–375
Clements DJ, Desmulliez MPY, Abraham E (2007) The evolution of paste pressure during stencil printing. Solder Surf Mt Tech 19: 9–14
Anderson JT, Gethin DT, Claypole TC, Jewell EH, Bohan MFJ, Korochkina TV (2000) Hydrodynamic interactions in the screen-printing process. J Prepress Print Technol 3: 10–17
White G, Breward C, Howell P, Young R (2005) A model for the screen-printing of Newtonian fluids. J Eng Math 54: 49–70
Chapman SJ, Fitt AD, Please CP (1997) Extrusion of power-law shear thinning fluids with small exponent. Int J Non-linear Mech 32(1): 187–199
Ross AB, Wilson SK, Duffy BR (1999) Blade coating of a power-law fluid. Phys Fluids 11(5): 958–970
Ostwald W (1925) Ueber die Geschwindigkeitsfunktion der Viskosität disperser Systeme. I. Colloid Polym Sci 36(2): 99–117
Bird R, Armstrong RC, Hassager O (1987) Dynamics of polymeric liquids, vol 1, 2 edn. Fluid mechanics. Wiley, New York
Beavers GS, Joseph DD (1967) Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J Fluid Mech 30(1): 197–207
Pozdrikidis C (2001) Shear flow over a particulate or fibrous plate. J Eng Math 39: 3–24
Pozdrikidis C (2004) Boundary conditions for shear flow past a permeable interface modelled as an array of cylinders. Comput Fluids 33: 1–17
Pozdrikidis C (2005) Effect of membrane thickness on the slip and drip velocity in parallel shear flow. J Fluids Struct 20: 177–187
Tio KK, Sadhal SS (1994) Boundary conditions for Stokes flow near a porous membrane. Appl Sci Res 52(1): 1–20
Taroni M (2010) Thin film models of the screen-printing process. D.Phil thesis, Oxford
White G (2006) Mathematical modelling of the screen-printing process. D.Phil thesis, Oxford
McEwan AD, Taylor GI (1966) The peeling of a flexible strip attached by a viscous adhesive. J Fluid Mech 26: 1–15
Taylor GI (1963) Cavitation of a viscous fluid in narrow passages. J Fluid Mech 16(4): 595–619
Coyne JC, Elrod HG (1970) Conditions for the rupture of a lubrication film. Part 1. Theoretical model. J Lubr Technol 92: 451–456
Savage MD (1977) Cavitation in lubrication. Part 1. On boundary conditions and cavity-fluid interfaces. J Fluid Mech 80: 743–755
Ruschak KJ (1982) Boundary conditions at a liquid/air interface in lubrication flows. J Fluid Mech 119: 107–120
Coyle DJ, Macosko CW, Scriven LE (1986) Film-splitting flows in forward roll coating. J Fluid Mech 171: 183–207
Dussan V, EB, Davis SH (1974) On the motion of a fluid-fluid interface along a solid surface. J Fluid Mech 65: 71–95
Hocking LM, Rivers AD (1982) The spreading of a drop by capillary action. J Fluid Mech 121: 425–442
Moriarty JA, Terrill EL (1996) Mathematical modelling of the motion of hard contact lenses. Euro J Appl Math 7: 117–575
Keller HB (1985) Numerical methods for two point boundary value problems. Dover publications, New York
Boyd JP (2001) Chebyshev and Fourier spectral methods. Dover publications, New York
Shampine LF, Kierzenka J, Reichelt MW (2000) Solving boundary value problems for ordinary differential equations in Matlab with bvp4c. ftp://ftp.mathworks.com/pub/doc/papers/bvp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taroni, M., Breward, C.J.W., Howell, P.D. et al. The screen printing of a power-law fluid. J Eng Math 73, 93–119 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-011-9500-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-011-9500-6