Abstract
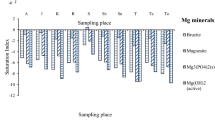
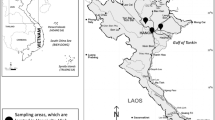
In this study, an investigation of important properties, including moisture content, pH, plant nutrients, organic matter, mineral oil, and the contents of heavy metals (HMs) in sewage sludge (SS) collected from 32 urban treatment plants in Shaanxi Province, China, was carried out. The test results showed that the pH and the moisture, organic matter, total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and mineral oil contents of the SS varied over different rainfall periods, and most of the indicators met the standard criteria for SS agricultural reuse in China. Principal component analysis (PCA) and correlation analysis indicated that the pollutant characteristics of the SS depended on time span and geographical distribution. The mean contents of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, Ni, Cr, Hg, and As in SS were 3.95, 16.38, 5.43, 7.70, 1.31, 1.53, 32.77, and 1.40 times higher than the soil background values, respectively. Speciation analysis showed that the forms of HMs in the SS were significantly different. Assessments based on the geoaccumulation index (Igeo), Nemerow integrated pollution index (NIPI), and potential ecological risk index (RI) suggested that HM pollution risk levels were either uncontaminated or moderately contaminated in some regions and that SS recycled for agricultural applications carried a low risk. In conclusion, certain potential ecological risks exist for SS agricultural utilization in Shaanxi Province, and it is necessary to reduce the HM content before SS resource utilization for land application.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on request from the authors.
References
Badza, T., Tesfamariam, E. H., & Cogger, C. G. (2020). Agricultural use suitability assessment and characterization of municipal liquid sludge: Based on South Africa survey. Science of the Total Environment, 721, 137658.
Brown, J. N., & Peake, B. M. (2006). Sources of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban stormwater runoff. Science of the Total Environment, 359(1), 145–155.
Carbonell-Barrachina, A., Jugsujinda, A., DeLaune, R. D., Patrick, W. H., Burló, F., Sirisukhodom, S., & Anurakpongsatorn, P. (1999). The influence of redox chemistry and pH on chemically active forms of arsenic in sewage sludge-amended soil. Environment International, 25(5), 613–618.
Chen, J., Wei, F., Zheng, C., Wu, Y., & Adriano, D. C. (1991). Background concentrations of elements in soils of China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 57(1), 699–712.
Gherghel, A., Teodosiu, C., & De Gisi, S. (2019). A review on wastewater sludge valorisation and its challenges in the context of circular economy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 228, 244–263.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Huang, H., Yuan, X., Zeng, G., Zhu, H., Li, H., Liu, Z., Jiang, H., Leng, L., & Bi, W. (2011). Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 102(22), 10346–10351.
Kacprzak, M., Neczaj, E., Fijałkowski, K., Grobelak, A., Grosser, A., Worwag, M., Rorat, A., Brattebo, H., Almås, Å., & Singh, B. R. (2017). Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environmental Research, 156, 39–46.
Kim, J.-H., Oh, J.-I., Lee, J., & Kwon, E. E. (2019). Valorization of sewage sludge via a pyrolytic platform using carbon dioxide as a reactive gas medium. Energy, 179, 163–172.
Kowalik, R., Latosińska, J., & Gawdzik, J. (2021). Risk analysis of heavy metal accumulation from sewage sludge of selected wastewater treatment plants in Poland. Water, 13(15), 2070.
Latosińska, J. (2020). Risk assessment of soil contamination with heavy metals from sewage sludge and ash after its incineration. Desalination and Water Treatment, 199, 297–306.
Lu, J.-Y., Wang, X.-M., Liu, H.-Q., Yu, H.-Q., & Li, W.-W. (2019). Optimizing operation of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: The remaining barriers and future implications. Environment International, 129, 273–278.
Ma, L., Yang, Z., Li, L., & Wang, L. (2016). Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils of Changsha, a mine-impacted city in Southern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(17), 17058–17066.
Markiewicz, A., Björklund, K., Eriksson, E., Kalmykova, Y., Strömvall, A.-M., & Siopi, A. (2017). Emissions of organic pollutants from traffic and roads: Priority pollutants selection and substance flow analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 580, 1162–1174.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
Natal-da-Luz, T., Tidona, S., Jesus, B., Morais, P. V., & Sousa, J. P. (2009). The use of sewage sludge as soil amendment. The need for an ecotoxicological evaluation. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 9(3), 246–260.
Pathak, A., Dastidar, M., & Sreekrishnan, T. (2009). Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(8), 2343–2353.
Piekutin, J. (2015). Assessment of ground water pollution in parking areas. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 16(1), 153–158.
Qian, L., Wang, S., Xu, D., Guo, Y., Tang, X., & Wang, L. (2016). Treatment of municipal sewage sludge in supercritical water: A review. Water Research, 89, 118–131.
Qiu, H. (2010). Studies on the potential ecological risk and homology correlation of heavy metal in the surface soil. Journal of Agricultural Science, 2(2), 194.
Qu, J., Wang, H., Wang, K., Yu, G., Ke, B., Yu, H.-Q., Ren, H., Zheng, X., Li, J., Li, W.-W., Gao, S., & Gong, H. (2019). Municipal wastewater treatment in China: Development history and future perspectives. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 13(6), 88.
Simões-Mota, A., Virto, I., & Poch, R. M. (2022). Effects of long-term sewage sludge application to a calcareous soil structure. Soil Use and Management, 38(4), 1693–1704.
Singh, R. P., & Agrawal, M. (2008). Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Management, 28(2), 347–358.
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Xie, X., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1–3), 455–462.
Sundaray, S. K., Nayak, B. B., Lin, S., & Bhatta, D. (2011). Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—A case study: Mahanadi basin, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2–3), 1837–1846.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1), 566–575.
Tuo, S., & He, H. (2021). A study of multiregional economic correlation analysis based on big data—Taking the regional economy of cities in Shaanxi Province, China, as an example. Sustainability, 13(9), 5121.
Tytła, M., Widziewicz, K., & Zielewicz, E. (2016). Heavy metals and its chemical speciation in sewage sludge at different stages of processing. Environmental Technology, 37(7), 899–908.
Viau, E., Bibby, K., Paez-Rubio, T., & Peccia, J. (2011). Toward a consensus view on the infectious risks associated with land application of sewage sludge. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(13), 5459–5469.
Wang, Y., Yang, L., Kong, L., Liu, E., Wang, L., & Zhu, J. (2015). Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. CATENA, 125, 200–205.
Wang, H., Cao, J., Wu, J., & Chen, Y. (2021). Spatial and temporal variability in soil pH of Shaanxi Province over the last 40 years. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29(6), 10.
Wilding, L. P. (1985). Spatial variability: Its documentation, accomodation and implication to soil surveys. In D. R. Nielson & J. Bouma (Eds.), Soil spatial variability (pp. 166–193). Pudoc.
Yakamercan, E., Ari, A., & Aygün, A. (2021). Land application of municipal sewage sludge: Human health risk assessment of heavy metals. Journal of Cleaner Production, 319, 128568.
Zhang, X., Wang, X.-Q., & Wang, D.-F. (2017). Immobilization of heavy metals in sewage sludge during land application process in China: A review. Sustainability, 9(11), 2020.
Zhao, S., Feng, C., Yang, Y., Niu, J., & Shen, Z. (2012). Risk assessment of sedimentary metals in the Yangtze Estuary: New evidence of the relationships between two typical index methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 241, 164–172.
Zhu, Y., Zhang, Y., Luo, D., Chong, Z., Li, E., & Kong, X. (2021). A review of municipal solid waste in China: Characteristics, compositions, influential factors and treatment technologies. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(5), 6603–6622.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Science and Technology Innovation Team of Shaanxi Province (No 2022TD-34), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuan Chen: Investigation, analysis, writing—original draft. Jian-feng Zhang: Conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—review and editing. Chang-shun Sun: Investigation, software, validation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xuan, C., Jianfeng, Z. & Changshun, S. Characteristics and risk assessment of sewage sludge from urban wastewater treatment plants in Shaanxi Province, China. Environ Monit Assess 195, 799 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11420-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11420-5