Abstract
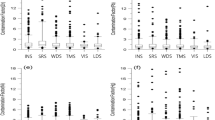
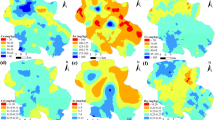
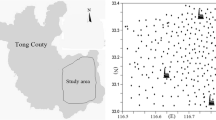
The urban soils suffered seriously from heavy metal pollutions with rapid industrialization and urbanization in China. In this study, 54 urban soil samples were collected from Changsha, a mine-impacted city located in Southern China. The concentrations of heavy metals (As, Cd, Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) were determined by ICP-MS. The pollution sources of heavy metals were discriminated and identified by the combination of multivariate statistical and geostatistical methods. Four main sources were identified according to the results of hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), principal component analysis (PCA), and spatial distribution patterns. Co and Mn were primarily derived from soil parent material. Cu, Pb, and Zn with significant positive relationships were associated with mining activities and traffic emissions. Cd and Ni might be affected by commercial activities and industrial discharges. As isolated into a single group was considered to have correlation with coal combustion and waste incineration. Risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils indicated an overall moderate potential ecological risk in the urban region of Changsha.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burt R, Hernandez L, Shaw R, Tunstead R, Ferguson R, Peaslee S (2014) Trace element concentration and speciation in selected urban soils in New York City. Environ Monit Assess 186:195–215
Chen T, Liu X, Zhu M, Zhao K, Wu J, Xu J, Huang P (2008) Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban–rural transitional area of Hangzhou. China Environ Pollut 151:67–78
Chen X, Lu X, Yang G (2012) Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. CATENA 98:73–78
Chen H, Lu X, Li LY, Gao T, Chang Y (2014) Metal contamination in campus dust of Xi’an, China: a study based on multivariate statistics and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 484:27–35
CNEMC NEMCC (1990) The background values of elements in Chinese soils. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing, pp 330–445
Cui Y, Zhu Y-G, Zhai R, Huang Y, Qiu Y, Liang J (2005) Exposure to metal mixtures and human health impacts in a contaminated area in Nanning. China Environ Int 31:784–790
Ding Z, Hu X (2014) Ecological and human health risks from metal(loid)s in peri-urban soil in Nanjing. China Environ Geochem Health 36:399–408
Fu J, Zhao CP, Luo YP, Liu CS, Kyzas GZ, Luo Y, Zhao DY, An SQ, Zhu HL (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: their relations to environmental factors. J Hazard Mater 270:102–109
Gallagher FJ, Pechmann I, Bogden JD, Grabosky J, Weis P (2008) Soil metal concentrations and vegetative assemblage structure in an urban brownfield. Environ Pollut 153:351–361
Guo G, Wu F, Xie F, Zhang R (2012) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. J Environ Sci 24:410–418
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hu Y, Cheng H (2013) Application of stochastic models in identification and apportionment of heavy metal pollution sources in the Surface Soils of a large-scale region. Environ Sci Technol 47:3752–3760
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Lee CS, Li XD, Shi WZ, Cheung SC, Thornton I (2006) Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci Total Environ 356:45–61
Li PY, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu JH (2015) Heavy metal contamination of Yellow River alluvial sediments, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 73:3403–3415
Liao X-Y, Chen T-B, Xie H, Liu Y-R (2005) Soil As contamination and its risk assessment in areas near the industrial districts of Chenzhou City, Southern China. Environ Int 31:791–798
Liu H, Probst A, Liao B (2005) Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci Total Environ 339:153–166
Lu X, Wang L, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Luo W, Wang T, Lu Y, Giesy JP, Shi Y, Zheng Y, Xing Y, Wu G (2007) Landscape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in soils. Environ Pollut 146:567–576
Luo X-S, Xue Y, Wang Y-L, Cang L, Xu B, Ding J (2015) Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 127:152–157
Ma L, Sun J, Yang Z, Wang L (2015) Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils affected by mining activities around the Ganxi River in Chenzhou, Southern China. Environ Monit Assess 187:731
Madiseh SD, Savary A, Parham H, Sabzalizadeh S (2009) Determination of the level of contamination in Khuzestan coastal waters (Northern Persian Gulf) by using an ecological risk index. Environ Monit Assess 159:521–530
Mihailović A, Budinski-Petković L, Popov S, Ninkov J, Vasin J, Ralević NM, Vučinić Vasić M (2015) Spatial distribution of metals in urban soil of Novi Sad, Serbia: GIS based approach. J Geochem Explor 150:104–114
Nanos N, Rodríguez Martín JA (2012) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in soils: spatial variability in the Duero river basin (Spain). Geoderma 189–190:554–562
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V, Venkatachalapathy R (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments. India Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
USEPA (2007) Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils, Revision 1. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Wang Z, Chai L, Yang Z, Wang Y, Wang H (2010) Identifying sources and assessing potential risk of heavy metals in soils from direct exposure to children in a mine-impacted city, Changsha. China J Environ Qual 39:1616–1623
Wang M, Markert B, Chen W, Peng C, Ouyang Z (2012) Identification of heavy metal pollutants using multivariate analysis and effects of land uses on their accumulation in urban soils in Beijing. China Environ Monit Assess 184:5889–5897
Wei B, Jiang F, Li X, Mu S (2009) Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban road dusts from Urumqi, NW China. Microchem J 93:147–152
Wu Q, Leung JYS, Geng X, Chen S, Huang X, Li H, Huang Z, Zhu L, Chen J, Lu Y (2015) Heavy metal contamination of soil and water in the vicinity of an abandoned e-waste recycling site: implications for dissemination of heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 506–507:217–225
Yang Z, Lu W, Long Y, Bao X, Yang Q (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City. China J Geochem Explor 108:27–38
Zhou LL, Yang B, Xue ND, Li FS, Seip HM, Cong X, Yan YZ, Liu B, Han BL, Li HY (2014) Ecological risks and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils from Huanghuai Plain. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1360–1369
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (No. 201503108) and National Science and Technology Major Project of China—Water Pollution Control and Treatment (No. 2013ZX07504-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Yang, Z., Li, L. et al. Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils of Changsha, a mine-impacted city in Southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 17058–17066 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6890-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6890-z