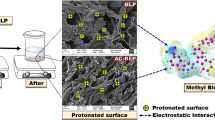
Abstract
Fig leaf, an environmentally friendly byproduct of fruit plants, has been used for the first time to treat of methylene blue dye. The fig leaf-activated carbon (FLAC-3) was prepared successfully and used for the adsorption of methylene blue dye (MB). The adsorbent was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). In the present study, initial concentrations, contact time, temperatures, pH solution, FLAC-3 dose, volume solution, and activation agent were investigated. However, the initial concentration of MB was investigated at different concentrations of 20, 40, 80, 120, and 200 mg/L. pH solution was examined at these values: pH3, pH7, pH8, and pH11. Moreover, adsorption temperatures of 20, 30, 40, and 50 °C were considered to investigate how the FLAC-3 works on MB dye removal. The adsorption capacity of FLAC-3 was determined to be 24.75 mg/g for 0.08 g and 41 mg/g for 0.02 g. The adsorption process has followed the Langmuir isotherm model (R2 = 0.9841), where the adsorption created a monolayer covering the surface of the adsorbent. Additionally, it was discovered that the maximum adsorption capacity (Qm) was 41.7 mg/g and the Langmuir affinity constant (KL) was 0.37 L/mg. The FLAC-3, as low-cost adsorbents for methylene blue dye, has shown good cationic dye adsorption performance.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset utilized/analyzed during the current study will be available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abdulhameed, A. S., Hum, N. N. M. F., Rangabhashiyam, S., Jawad, A. H., Wilson, L. D., Yaseen, Z. M., et al. (2021). Statistical modeling and mechanistic pathway for methylene blue dye removal by high surface area and mesoporous grass-based activated carbon using K2CO3 activator. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 105530.
Abuzerr, S., Darwish, M., & Mahvi, A. H. (2018). Simultaneous removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic reactive red 198 dyes using magnetic activated carbon nanoparticles: Equilibrium, and kinetics analysis. Water Science and Technology, 2017(2), 534–545.
Alam, M. Z., Bari, M. N., & Kawsari, S. (2022). Statistical optimization of methylene blue dye removal from a synthetic textile wastewater using indigenous adsorbents. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators, 14, 100176.
Al-Ghouti, M. A., & Al-Absi, R. S. (2020). Mechanistic understanding of the adsorption and thermodynamic aspects of cationic methylene blue dye onto cellulosic olive stones biomass from wastewater. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–18.
Bencheikh, I., Azoulay, K., Mabrouki, J., El Hajjaji, S., Dahchour, A., Moufti, A., & Dhiba, D. (2020). The adsorptive removal of MB using chemically treated artichoke leaves: Parametric, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic study. Scientific African, 9, e00509.
Bharathi, K. S., & Ramesh, S. T. (2013). Removal of dyes using agricultural waste as low-cost adsorbents: A review. Applied Water Science, 3(4), 773–790.
Blaga, A. C., Tanasă, A. M., Cimpoesu, R., Tataru-Farmus, R.-E., & Suteu, D. (2022). Biosorbents based on biopolymers from natural sources and food waste to retain the methylene blue dye from the aqueous medium. Polymers, 14(13), 2728.
Canales-Flores, R. A., & Prieto-García, F. (2020). Taguchi optimization for production of activated carbon from phosphoric acid impregnated agricultural waste by microwave heating for the removal of methylene blue. Diamond and Related Materials, 109, 108027.
Choma, J., Osuchowski, Ł, Dziura, A., Marszewski, M., & Jaroniec, M. (2015). Benzene and methane adsorption on ultrahigh surface area carbons prepared from sulphonated styrene divinylbenzene resin by KOH activation. Adsorption Science & Technology, 33(6–8), 587–594.
Choudhry, A., Sharma, A., Khan, T. A., & Chaudhry, S. A. (2021). Flax seeds based magnetic hybrid nanocomposite: An advance and sustainable material for water cleansing. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 42, 102150.
Dural, M. U., Cavas, L., Papageorgiou, S. K., & Katsaros, F. K. (2011). Methylene blue adsorption on activated carbon prepared from Posidonia oceanica (L.) dead leaves: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168(1), 77–85.
El Messaoudi, N., El Mouden, A., El Khomri, M., Bouich, A., Fernine, Y., Ciğeroğlu, Z., et al. (2022). Experimental study and theoretical statistical modeling of acid blue 25 remediation using activated carbon from Citrus sinensis leaf. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 563, 113585.
Guo, D., Li, Y., Cui, B., Hu, M., Luo, S., Ji, B., & Liu, Y. (2020). Natural adsorption of methylene blue by waste fallen leaves of Magnoliaceae and its repeated thermal regeneration for reuse. Journal of Cleaner Production, 267, 121903.
Gutub, S. A., Bassyouni, M., & Abdel-Hamid, S. M. S. (2013). Dissolved solids adsorption of freshwater using synthesized bio-foam composite. Life Science Journal, 10(2), 464–471.
Haghbin, M. R., & Shahrak, M. N. (2021). Process conditions optimization for the fabrication of highly porous activated carbon from date palm bark wastes for removing pollutants from water. Powder Technology, 377, 890–899.
Halysh, V., Sevastyanova, O., Pikus, S., Dobele, G., Pasalskiy, B., Gun’ko, V. M., & Kartel, M. (2020). Sugarcane bagasse and straw as low-cost lignocellulosic sorbents for the removal of dyes and metal ions from water. Cellulose, 27(14), 8181–8197.
Hasan, R., Ying, W. J., Cheng, C. C., Jaafar, N. F., Jusoh, R., Jalil, A. A., & Setiabudi, H. D. (2020). Methylene blue adsorption onto cockle shells-treated banana pith: Optimization, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, 20(2), 368–378.
Hu, X.-S., Liang, R., & Sun, G. (2018). Super-adsorbent hydrogel for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6(36), 17612–17624.
Huang, S., & Shi, J. (2014). Monolithic macroporous carbon materials as high-performance and ultralow-cost sorbents for efficiently solving organic pollution. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 53(12), 4888–4893.
Islam, M. A., Ahmed, M. J., Khanday, W. A., Asif, M., & Hameed, B. H. (2017). Mesoporous activated coconut shell-derived hydrochar prepared via hydrothermal carbonization-NaOH activation for methylene blue adsorption. Journal of Environmental Management, 203, 237–244.
Izan, N. R., Zainol, M. M., Nordin, A. H., Asmadi, M., Wong, S. L., Azhar, M. A. I., & Alias, N. H. (2020). Removal of methylene blue via adsorption using magnetic char derived from food waste. Malaysian Journal of Chemistry, 24(2) 283–292.
Jawad, A. H., Rashid, R. A., Ishak, M. A. M., & Wilson, L. D. (2016). Adsorption of methylene blue onto activated carbon developed from biomass waste by H2SO4 activation: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(52), 25194–25206.
Jawad, A. H., Ramlah, A. R., Khudzir, I., & Sabar, S. (2017). High surface area mesoporous activated carbon developed from coconut leaf by chemical activation with H3PO4 for adsorption of methylene blue. Desalination and Water Treatment, 74, 326–335.
Jawad, A. H., Bardhan, M., Islam, M. A., Islam, M. A., Syed-Hassan, S. S. A., Surip, S. N., et al. (2020). Insights into the modeling, characterization and adsorption performance of mesoporous activated carbon from corn cob residue via microwave-assisted H3PO4 activation. Surfaces and Interfaces, 21, 100688.
Jiang, W., Zhang, L., Guo, X., Yang, M., Lu, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Adsorption of cationic dye from water using an iron oxide/activated carbon magnetic composites prepared from sugarcane bagasse by microwave method. Environmental Technology, 42(3), 337–350.
Kadhom, M., Albayati, N., Alalwan, H., & Al-Furaiji, M. (2020). Removal of dyes by agricultural waste. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 16, 100259.
Khangwichian, W., Pattamasewe, S., Leesing, R., Knijnenburg, J. T. N., & Ngernyen, Y. (2022). Adsorption of cationic dye on activated carbon from hydrolyzed Dipterocarpus alatus leaves: Waste from biodiesel production. Engineering and Applied Science Research, 49(4), 531–544.
Khomri, M. E., Messaoudi, N. E., Dbik, A., Bentahar, S., Fernine, Y., Bouich, A., et al. (2022). Modification of low-cost adsorbent prepared from agricultural solid waste for the adsorption and desorption of cationic dye. Emergent Materials, 5(6), 1679–1688.
Kılıç, M., Apaydın-Varol, E., & Pütün, A. E. (2012). Preparation and surface characterization of activated carbons from Euphorbia rigida by chemical activation with ZnCl2, K2CO3, NaOH and H3PO4. Applied Surface Science, 261, 247–254.
Kushwaha, A. K., Gupta, N., & Chattopadhyaya, M. C. (2014). Removal of cationic methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous solution by waste materials of Daucus carota. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 18(3), 200–207.
Li, Z., Gao, X., Wu, L., Wang, K., & Kobayashi, N. (2017). Preparation of activated carbons from poplar wood by chemical activation with KOH. Journal of Porous Materials, 24(1), 193–202.
Liu, L., Li, Y., & Fan, S. (2019). Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 modified biochar and its application in methylene blue removal from aqueous solution. Processes, 7(12), 891.
Liu, Z., Sun, Y., Xu, X., Qu, J., & Qu, B. (2020). Adsorption of Hg (II) in an aqueous solution by activated carbon prepared from rice husk using KOH activation. ACS Omega, 5(45), 29231–29242.
Mahamad, M. N., Zaini, M. A. A., & Zakaria, Z. A. (2015). Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from pineapple waste biomass for dye removal. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 102, 274–280.
Mangla, D., Sharma, A., & Ikram, S. (2022). Synthesis of ecological chitosan/PVP magnetic composite: Remediation of amoxicillin trihydrate from its aqueous solution, isotherm modelling, thermodynamic, and kinetic studies. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 175, 105261.
Martín-González, M. A., Susial, P., Pérez-Peña, J., & Doña-Rodríguez, J. M. (2013). Preparation of activated carbons from banana leaves by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Adsorption of methylene blue. Revista mexicana de ingeniería química, 12(3), 595–608.
Mekuria, D., Diro, A., Melak, F., & Asere, T. G. (2022). Adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye using biowaste materials: Barley Bran and enset midrib leaf. Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4849758
El Messaoudi, N., El Khomri, M., Goodarzvand Chegini, Z., Chlif, N., Dbik, A., & Bentahar, S., et al. (2021). Desorption study and reusability of raw and H2SO4 modified jujube shells (Zizyphus lotus) for the methylene blue adsorption. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1–17.
Mousavi, S. A., Mahmoudi, A., Amiri, S., Darvishi, P., & Noori, E. (2022). Methylene blue removal using grape leaves waste: Optimization and modeling. Applied Water Science, 12(5), 1–11.
Murthy, T. P. K., Gowrishankar, B. S., Krishna, R. H., Chandraprabha, M. N., & Mathew, B. B. (2020). Magnetic modification of coffee husk hydrochar for adsorptive removal of methylene blue: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 2, 205–212.
Mustikaningrum, M., Cahyono, R. B., & Yuliansyah, A. T. (n.d.). Adsorption of methylene blue on nano-crystal cellulose of oil palm trunk: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, 22(4), 953–964.
Nordin, A. H., Wong, S., Ngadi, N., Zainol, M. M., Abd Latif, N. A. F., & Nabgan, W. (2021). Surface functionalization of cellulose with polyethyleneimine and magnetic nanoparticles for efficient removal of anionic dye in wastewater. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(1), 104639.
Omer, O. S., Hussein, M. A., Hussein, B. H. M., & Mgaidi, A. (2018). Adsorption thermodynamics of cationic dyes (methylene blue and crystal violet) to a natural clay mineral from aqueous solution between 293.15 and 323.15 K. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 11(5), 615–623.
Patra, B. R., Mukherjee, A., Nanda, S., & Dalai, A. K. (2021a). Biochar production, activation and adsorptive applications: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19(3), 2237–2259.
Patra, B. R., Nanda, S., Dalai, A. K., & Meda, V. (2021b). Slow pyrolysis of agro-food wastes and physicochemical characterization of biofuel products. Chemosphere, 285, 131431.
Patra, B. R., Nanda, S., Dalai, A. K., & Meda, V. (2021c). Taguchi-based process optimization for activation of agro-food waste biochar and performance test for dye adsorption. Chemosphere, 285, 131531.
Prashanthakumar, T. K. M., Kumar, S. K. A., & Sahoo, S. K. (2018). A quick removal of toxic phenolic compounds using porous carbon prepared from renewable biomass coconut spathe and exploration of new source for porous carbon materials. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(1), 1434–1442.
Rashid, R. A., Jawad, A. H., Ishak, M. A. M., & Kasim, N. N. (2016). KOH-activated carbon developed from biomass waste: Adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene blue uptake. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(56), 27226–27236.
Shakoor, S., & Nasar, A. (2017). Adsorptive treatment of hazardous methylene blue dye from artificially contaminated water using cucumis sativus peel waste as a low-cost adsorbent. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 5, 152–159.
Shannon, M. A., Bohn, P. W., Elimelech, M., Georgiadis, J. G., Mariñas, B. J., & Mayes, A. M. (2008). Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature, 452(7185), 301–310.
Sharma, A., Mangla, D., & Chaudhry, S. A. (2022). Recent advances in magnetic composites as adsorbents for wastewater remediation. Journal of Environmental Management, 306, 114483.
Sharma, A., Rasheed, S., Mangla, D., Choudhry, A., Shukla, S., & Chaudhry, S. A. (2023). Cobalt ferrite incorporated ocimum sanctum nanocomposite matrix as an interface for adsorption of organic dyes: A sustainable alternative. ChemistrySelect, 8(5), e202203709.
Shelke, B. N., Jopale, M. K., & Kategaonkar, A. H. (2022). Exploration of biomass waste as low cost adsorbents for removal of methylene blue dye: A review. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 99(7), 100530.
Singh, A., Nanda, S., Guayaquil-Sosa, J. F., & Berruti, F. (2021). Pyrolysis of Miscanthus and characterization of value-added bio-oil and biochar products. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 99, S55–S68.
Stewart, G. G. (2016). Saccharomyces species in the Production of Beer. Beverages, 2(4), 34.
Tran, H. N., You, S.-J., & Chao, H.-P. (2017a). Fast and efficient adsorption of methylene green 5 on activated carbon prepared from new chemical activation method. Journal of Environmental Management, 188, 322–336.
Tran, H. N., You, S.-J., Nguyen, T. V., & Chao, H.-P. (2017b). Insight into the adsorption mechanism of cationic dye onto biosorbents derived from agricultural wastes. Chemical Engineering Communications, 204(9), 1020–1036.
Wang, J., & Guo, X. (2020). Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 390, 122156.
Wu, H.-Y., Chen, S. S., Liao, W., Wang, W., Jang, M.-F., Chen, W.-H., et al. (2020). Assessment of agricultural waste-derived activated carbon in multiple applications. Environmental Research, 191, 110176.
Yağmur, H. K., & Kaya, İ. (2021). Synthesis and characterization of magnetic ZnCl2-activated carbon produced from coconut shell for the adsorption of methylene blue. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1232, 130071.
Zhu, R., Yu, Q., Li, M., Zhao, H., Jin, S., Huang, Y., et al. (2021). Analysis of factors influencing pore structure development of agricultural and forestry waste-derived activated carbon for adsorption application in gas and liquid phases: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(5), 105905.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the College of Sciences for Women, University of Babylon, for facilitating this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Safaa Talib Al-Asadi: wrote the first draft of the manuscript, did the experiments and organized the structure of the manuscript.
Fouad Fadhil Al-Qaim: analyzed the data and edited the final draft of the manuscript.
Haider Falih SHamikh Al-Saedi: collected the references and improved the final revised draft.
Issa Farhan Deyab: revised the whole manuscript and improved the structure of the final draft.
Hesam Kamyab: revised the whole manuscript and improvement the English language.
Shreeshivadasan Chelliapan: revised the whole manuscript and improvement the English language.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Asadi, S.T., Al-Qaim, F.F., Al-Saedi, H.F.S. et al. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using low-cost adsorbent: kinetic, isotherm adsorption, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Monit Assess 195, 676 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11334-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11334-2