Abstract
Groundwater contamination becomes an alarming threat to the provision of ecosystem services and natural resources. A very high level of groundwater contamination has been observed in the northeastern states particularly in North Tripura district. Therefore, the present study considered the region as a case study to evaluate the hydrogeochemical facies, heavy metal pollution and irrigation indices, and their impact on human health. For the investigation, we have collected a total of 35 groundwater samples from North Tripura district. Hydrogeochemical facies through Piper plot reflect Ca2+–Mg2+–HCO3− and Na+–HCO3− as dominant water types. Gibbs plot identifies the dominance of rock-water interaction process in groundwater hydrochemistry. Geochemical plots indicate the dominance of silicate weathering, ion exchange and carbonate dissolution processes in groundwater mineralisation. The order of trace metal contaminations follows Fe > As > Zn > Mn > Cu > Pb. Results of heavy metal indices suggest above 80% samples are at high risk due to high Fe contamination. The risk of the heavy metal indices is associated with rising elevation in southern part of North Tripura. Findings of health risk assessment study imply that children face much carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks than adults because of unsafe levels of Fe and As. Multivariate statistical tools are applied to unravel interrelationships among all ions and trace metals as well as probable hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater. Results of Wilcox and USSL plots suggest 77% samples meet irrigation suitability criteria. Besides, the analysis suggests a better insight to identify hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater chemistry and the suitability of groundwater for irrigation and drinking purposes. The study also suggests treatment and sustainable management of groundwater resources is compulsory to reduce trace metal contaminations before public use.
Graphical abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that no external data has been used in this study.
References
APHA. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (22nd ed.). APHA- AWWA- WEF.
Adimalla, N., & Qian, H. (2019). Hydrogeochemistry and fluoride contamination in the hard rock terrain of central Telangana, India: Analyses of its spatial distribution and health risk. SN Applied Sciences, 1(3), 202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0219-8
Aly, A. A., Al-Omran, A. M., & Alharby, M. M. (2015). The water quality index and hydrochemical characterization of groundwater resources in Hafar Albatin Saudi Arabia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(6), 4177–4190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1463-2
Backman, B., Bodiš, D., Lahermo, P., Rapant, S., & Tarvainen, T. (1998). Application of a groundwater contamination index in Finland and Slovakia. Environmental Geology, 36(1–2), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050320
Banerjee, S., Das, B., Umlong, I. M., Devi, R. R., Kalita, H., Saikia, L. B., et al. (2011). Heavy metal contaminants of underground water in Indo Bangla border districts of. International Journal of ChemTech Research, 3(1), 516–522.
Barzegar, R., AsghariMoghaddam, A., Soltani, S., Fijani, E., Tziritis, E., & Kazemian, N. (2019). Heavy metal(loid)s in the groundwater of Shabestar Area (NW Iran): Source identification and health risk assessment. Exposure and Health, 11(4), 251–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0267-5
Bhattacharya, P., Adhikari, S., Samal, A. C., Das, R., Dey, D., Deb, A., et al. (2020). Health risk assessment of co-occurrence of toxic fluoride and arsenic in groundwater of Dharmanagar region, North Tripura (India). Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 11, 100430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100430
Bhutiani, R., Kulkarni, D. B., Khanna, D. R., & Gautam, A. (2016). Water quality, pollution source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of an industrial area in North India. Exposure and Health, 8(1), 3–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0178-2
Bodrud-Doza, M., Islam, S. M. D. U., Rume, T., Quraishi, S. B., Rahman, M. S., & Bhuiyan, M. A. H. (2020). Groundwater quality and human health risk assessment for safe and sustainable water supply of Dhaka City dwellers in Bangladesh. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100374
Brindha, K., Paul, R., Walter, J., Tan, M. L., & Singh, M. K. (2020). Trace metals contamination in groundwater and implications on human health: Comprehensive assessment using hydrogeochemical and geostatistical methods. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(11), 3819–3839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00637-9
CGWB. (2012). Ground water information booklet North Tripura District, Tripura (p. 16). Central Ground Water Board, North Eastern Region, Ministry of Water Resources, Guwahati, India.
Chacha, N., Naju, K. N., Lugomela, G. V., & Muzuka, A. N. N. (2018). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and spatial distribution of groundwater quality in Arusha well fields Northern Tanzania. Applied Water Science, 8(4), 118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0760-4
Chakraborti, D., Rahman, M. M., Das, B., Chatterjee, A., Das, D., Nayak, B., et al. (2017). Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in India. Hydrogeology Journal, 25(4), 1165–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1556-6
Chaturvedi, A., Bhattacharjee, S., Singh, A. K., & Kumar, V. (2018). A new approach for indexing groundwater heavy metal pollution. Ecological Indicators, 87, 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.12.052
Dohare, D., Deshpande, S., & Kotiya, A. (2014). Analysis of ground water quality parameters: A review. Research Journal of Engineering Sciences, 3(5), 2278–9472.
Doneen, L. D. (1964). Notes on water quality in agriculture. Published as a water science and engineering paper 4001: Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California.
Durov, S. A. (1948). Natural waters and graphic representation of their compositions. Doklady Akademii Nauk, 59(59), 87–90.
Edet, A. E., & Offiong, O. E. (2002). Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring. A study case from Akpabuyo-Odukpani area, Lower Cross River Basin (southeastern Nigeria). GeoJournal, 57(4), 295–304. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GEJO.0000007250.92458.de
Edokpayi, J. N., Enitan, A. M., Mutileni, N., & Odiyo, J. O. (2018). Evaluation of water quality and human risk assessment due to heavy metals in groundwater around Muledane area of Vhembe District, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Chemistry Central Journal, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-017-0369-y
Elumalai, V., Nethononda, V. G., Manivannan, V., Rajmohan, N., Li, P., & Elango, L. (2020). Groundwater quality assessment and application of multivariate statistical analysis in Luvuvhu catchment, Limpopo, South Africa. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 171, 103967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103967
Fianko, J. R., Adomako, D., Osae, S., Ganyaglo, S., Kortatsi, B. K., Tay, C. K., & Glover, E. T. (2010). The hydrochemistry of groundwater in the Densu River Basin Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 167(1–4), 663–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1082-7
Gaikwad, S., Gaikwad, S., Meshram, D., Wagh, V., Kandekar, A., & Kadam, A. (2020). Geochemical mobility of ions in groundwater from the tropical western coast of Maharashtra, India: Implication to groundwater quality. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(3), 2591–2624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00312-9
Gao, Z., Han, C., Yuan, S., Liu, J., Peng, Y., & Li, C. (2021). Assessment of the hydrochemistry, water quality, and human health risk of groundwater in the northwest of Nansi Lake Catchment, north China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01011-z
Gong, G., Mattevada, S., & O’Bryant, S. E. (2014). Comparison of the accuracy of kriging and IDW interpolations in estimating groundwater arsenic concentrations in Texas. Environmental Research, 130, 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2013.12.005
He, S., & Li, P. (2020). A MATLAB based graphical user interface (GUI) for quickly producing widely used hydrogeochemical diagrams. Geochemistry, 80(4), 125550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.125550
ICMR. (2009). Nutrient requirements and recommended dietary allowances for Indians (p. 334) Indian Council Medical Research, Hyderabad, India.
Jahanshahi, R., & Zare, M. (2015). Assessment of heavy metals pollution in groundwater of Golgohar iron ore mine area Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(1), 505–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4057-8
Jampani, M., Huelsmann, S., Liedl, R., Sonkamble, S., Ahmed, S., & Amerasinghe, P. (2018). Spatio-temporal distribution and chemical characterization of groundwater quality of a wastewater irrigated system: A case study. Science of the Total Environment, 636, 1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.347
Jerome, C., & Pius, A. (2010). Evaluation of water quality index and its impact on the quality of life in an industrial area in Bangalore, South India. American Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1(3), 595–603. https://doi.org/10.5251/ajsir.2010.1.3.595.603
Joardar, M., Das, A., Chowdhury, N. R., Mridha, D., De, A., Majumdar, K. K., & Roychowdhury, T. (2021). Health effect and risk assessment of the populations exposed to different arsenic levels in drinking water and foodstuffs from four villages in arsenic endemic Gaighata block, West Bengal India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(8), 3027–3053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00823-3
Kaiser, H. F. (1958). The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 23(3), 187–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02289233
Kanagaraj, G., & Elango, L. (2019). Chromium and fluoride contamination in groundwater around leather tanning industries in southern India: Implications from stable isotopic ratio Δ53Cr/Δ52Cr, geochemical and geostatistical modelling. Chemosphere, 220, 943–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.105
Kelly, W. P. (1940). Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. Proceedings of American Society of Civil Engineers, 66, 607–613.
Kshetrimayum, K. S., & Hegeu, H. (2016). The state of toxicity and cause of elevated Iron and Manganese concentrations in surface water and groundwater around Naga Thrust of Assam-Arakan basin Northeastern India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(7), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5372-4
Lermi, A., & Ertan, G. (2019). Hydrochemical and isotopic studies to understand quality problems in groundwater of the Niğde Province Central Turkey. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(12), 365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8365-2
Li, J., Wang, G., Liu, F., Cui, L., & Jiao, Y. (2021). Source apportionment and ecological-health risks assessment of heavy metals in topsoil near a factory Central China. Exposure and Health, 13(1), 79–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00363-8
Li, P., Li, X., Meng, X., Li, M., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Exposure and Health, 8(3), 361–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y
Liang, C. P., Wang, S. W., Kao, Y. H., & Chen, J. S. (2016). Health risk assessment of groundwater arsenic pollution in southern Taiwan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38(6), 1271–1281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9794-4
Lloyd, J. A., & Heathcote, J. A. (1985). Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater: An introduction. Oxford Uni. Press, New York (p. 296).
Maanan, M., Saddik, M., Maanan, M., Chaibi, M., Assobhei, O., & Zourarah, B. (2015). Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon Morocco. Ecological Indicators, 48(July 2015), 616–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.09.034
Mallick, S. K., Pramanik, M., Maity, B., Das, P., & Sahana, M. (2021). Plastic waste footprint in the context of COVID-19: Reduction challenges and policy recommendations towards sustainable development goals. Science of the Total Environment, 796, 148951. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.148951
Marandi, A., & Shand, P. (2018). Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Applied Geochemistry. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.07.009
Masoud, A. A., El-Horiny, M. M., Atwia, M. G., Gemail, K. S., & Koike, K. (2018). Assessment of groundwater and soil quality degradation using multivariate and geostatistical analyses, Dakhla Oasis Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 142, 64–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.03.009
Mohan, S. V., Nithila, P., & Jayarama Reddy, S. (1996). Estimation of heavy metals in drinking water and development of heavy metal pollution index. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A Toxic/hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 31(2), 283–289. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529609376357
Mukherjee, A., & Fryar, A. E. (2008). Deeper groundwater chemistry and geochemical modeling of the arsenic affected western Bengal basin, West Bengal India. Applied Geochemistry, 23(4), 863–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.07.011
Nag, S. K., & Das, S. (2017). Assessment of groundwater quality from Bankura I and II Blocks, Bankura District, West Bengal India. Applied Water Science, 7(6), 2787–2802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0530-8
Omonona, O. V., Amah, J. O., Olorunju, S. B., Waziri, S. H., Ekwe, A. C., Umar, D. N., & Olofinlade, S. W. (2019). Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater from fractured Albian carbonaceous shale aquifers around Enyigba-Ameri, southeastern Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7236-3
Palmucci, W., Rusi, S., & Di Curzio, D. (2016). Mobilisation processes responsible for iron and manganese contamination of groundwater in Central Adriatic Italy. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(12), 11790–11805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6371-4
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259.https://doi.org/10.3133/wri994259
Paul, R., Prasanna, M. V., Gantayat, R. R., & Singh, M. K. (2019a). Groundwater quality assessment in Jirania Block, west district of Tripura, India, using hydrogeochemical fingerprints. SN Applied Sciences, 1(9), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1092-1
Paul, R., Brindha, K., Gowrisankar, G., Tan, M. L., & Singh, M. K. (2019b). Identification of hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater quality in Tripura, Northeast India using evaluation indices, GIS, and multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(15). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8479-6
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Transactions- American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Planning Commission. (2011). Report of the working group on rural domestic water and sanitation, Twelfth five year plan—2012–2017 (p. 220). Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Government of India, New Delhi.
Pramanik, M., Singh, P., Kumar, G., Ojha, V. P., & Dhiman, R. C. (2020). El Niño Southern Oscillation as an early warning tool for dengue outbreak in India. BMC Public Health, 20(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09609-1
Prasad, B., Kumari, P., Bano, S., & Kumari, S. (2014). Ground water quality evaluation near mining area and development of heavy metal pollution index. Applied Water Science, 4(1), 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0126-x
Prasad, B., & Mondal, K. K. (2008). The impact of filling an abandoned open cast mine with fly ash on ground water quality: A case study. Mine Water and the Environment, 27(1), 40–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-007-0021-5
Prasanna, M. V., Chidambaram, S., Gireesh, T. V., & Ali, T. V. J. (2011). A study on hydrochemical characteristics of surface and sub-surface water in and around Perumal Lake, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu South India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 63(1), 31–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0664-6
Qian, C., Wu, X., Mu, W. P., Fu, R. Z., Zhu, G., Wang, Z. R., & dan Wang, D. (2016). Hydrogeochemical characterization and suitability assessment of groundwater in an agro-pastoral area, Ordos Basin NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(20), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6123-2
Rawat, K., Pradhan, S., Tripathi, V., Jeyakumar, L., & Singh, S. K. (2019). Statistical approach to evaluate groundwater contamination for drinking and irrigation suitability. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 9(July), 100251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100251
Rezaei, A., Hassani, H., Hassani, S., Jabbari, N., Fard Mousavi, S. B., & Rezaei, S. (2019). Evaluation of groundwater quality and heavy metal pollution indices in Bazman basin, southeastern Iran. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 9(July), 100245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100245
Richard, L. A. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Science, 78(2), 154.
Roy, B., Roy, S., Mitra, S., & Manna, A. K. (2021). Evaluation of groundwater quality in West Tripura Northeast India through combined application of water quality index and multivariate statistical techniques. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14(19), 2037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08384-6
Rufino, F., Busico, G., Cuoco, E., Muscariello, L., Calabrese, S., & Tedesco, D. (2021). Geochemical characterization and health risk assessment in two diversified environmental settings (Southern Italy). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00930-1
Saleh, H. N., Panahande, M., Yousefi, M., Asghari, F. B., Oliveri Conti, G., Talaee, E., & Mohammadi, A. A. (2019). Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater wells in Neyshabur Plain Iran. Biological Trace Element Research, 190(1), 251–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1516-6
Sathe, S. S., Mahanta, C., & Subbiah, S. (2021). Hydrogeochemical evaluation of intermittent alluvial aquifers controlling arsenic and fluoride contamination and corresponding health risk assessment. Exposure and Health, (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-021-00411-x
Sawyer, C., & McCarthy, P. (1967). Chemical and sanitary engineering (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Schoeller, H. (1977). Geochemistry of groundwater. In Groundwater studies-An international guide for research and practice, Chap. 15, pp. 1–18, UNESCO, Paris.
Shemsanga, C., Muzuka, A. N. N., Martz, L., Komakech, H. C., Elisante, E., Kisaka, M., & Ntuza, C. (2017). Origin and mechanisms of high salinity in Hombolo Dam and groundwater in Dodoma municipality Tanzania, revealed. Applied Water Science, 7(6), 2883–2905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0569-6
Shepard, D. (1968). A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In Proceedings of the 168 ACM National Conference, New York (pp. 517–524). https://doi.org/10.1145/800186.810616
Singh, A. K., & Kumar, S. R. (2015). Quality assessment of groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in semi-urban area of Tripura, India. Ecology, Environment and Conservation, 21(1), 97–108.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., & Sinha, S. (2005). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques - A case study. Analytica Chimica Acta, 538(1–2), 355–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.02.006
Sirajudeen, J., Arulmanikandan, S., & Manivel, V. (2015). Heavy metal pollution index of groundwater of Fathima Nagar area near Uyyakondan Channel Tiruchirappalli District, Tamil Nadu, India. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 4(1), 967–975. http://www.wjpps.com/download/article/1420091686.pdf. Accessed 17 May 2021
Sunkari, E. D., Abu, M., Zango, M. S., & LomoroWani, A. M. (2020). Hydrogeochemical characterization and assessment of groundwater quality in the Kwahu-Bombouaka Group of the Voltaian Supergroup Ghana. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 169, 103899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103899
Szabolcs, I., & Darab, C. (1964). The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate Content on soils. In I. Szabolics (Ed.) Proceeding of 8th International Congress Soil Science Sodics, 2, 803–812.
Thilagavathi, R., Chidambaram, S., Thivya, C., Prasanna, M. V., Singaraja, C., Tirumalesh, K., & Pethaperumal, S. (2014). Delineation of natural and anthropogenic process controlling hydrogeochemistry of layered aquifer sequence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences India Section A - Physical Sciences, 84(1), 95–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-013-0114-4
UNDESA. (2013). World population prospects, Population Division Database. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. New York, Washington, DC.
Wagh, V. M., Panaskar, D. B., Muley, A. A., & Mukate, S. V. (2017). Groundwater suitability evaluation by CCME WQI model for Kadava River Basin, Nashik, Maharashtra India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 3(2), 557–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0316-x
Wei, M., Wu, J., Li, W., Zhang, Q., Su, F., & Wang, Y. (2021). Groundwater geochemistry and its impacts on groundwater arsenic enrichment, variation, and health risks in Yongning County, Yinchuan Plain of Northwest China. Exposure and Health, (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-021-00391-y
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking water quality (4th edn.). World Health Organization, Geneva.
Wilcox, L.V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters. U.S. Geological Survey, Department of Agriculture, Washington D.C. Circular No. 969, 19.
Wu, J., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, H. (2020). Groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality index incorporating health risk weighting in Dingbian County Ordos Basin of Northwest China. Geochemistry, 80(4), 125607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125607
Xu, P., Feng, W., Qian, H., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Hydrogeochemical characterization and irrigation quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the central-Western Guanzhong basin, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16091492
Yetiş, R., Atasoy, A. D., Demir Yetiş, A., & Yeşilnacar, M. İ. (2019). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater in Balikligol Basin, Sanliurfa, Turkey. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8330-0
Yidana, S. M., & Yidana, A. (2010). An assessment of the origin and variation of groundwater salinity in southeastern Ghana. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(6), 1259–1273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0449-y
Zechmeister, H. G. (1995). Correlation between altitude and heavy metal deposition in the Alps. Environmental Pollution, 89(1), 73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(94)00042-C
Zhang, Q., Xu, P., & Qian, H. (2020). Groundwater quality assessment using improved water quality index (WQI) and human health risk (HHR) evaluation in a semi-arid region of Northwest China. Exposure and Health, 12(3), 487–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00345-w
Zhou, Y., Li, P., Xue, L., Dong, Z., & Li, D. (2020). Solute geochemistry and groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study in Xinle City North China. Geochemistry, 80(4), 125609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125609
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Department of Chemical Engineering and Department of Bio Engineering, National Institute of Technology (NIT) Agartala, for supporting all facility for carrying out experiment and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Biplab Roy: conceptualisation; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; resources; software; validation; visualisation; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Malay Pramanik: data curation; formal analysis; methodology; software; visualisation; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Ajay Kumar Manna: conceptualisation; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; resources; software; supervision; validation; visualisation; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Silicate weathering and carbonate dissolution processes dominate groundwater chemistry.
• Metal contaminations assessed using heavy metal indices and health risk evaluations.
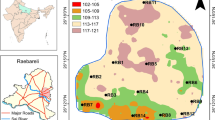
• Most influencing metals Fe and As exceed WHO limit in 80% and 20% samples.
• Higher carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks for children than adults due to Fe and As.
• Wilcox and USSL plots reveal about 77% samples have irrigation suitability criteria.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, B., Pramanik, M. & Manna, A.K. Hydrogeochemistry and quality evaluation of groundwater and its impact on human health in North Tripura, India. Environ Monit Assess 195, 39 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10642-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10642-3