Abstract
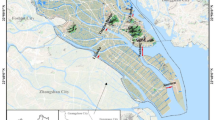
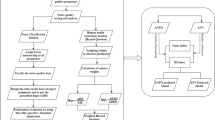
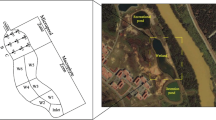
Keeping purpose and targeted end-users in perspective, several water quality indices have been developed over the past decades to summarily convey water quality information to decision-makers and the general public. Industrial water quality is often analyzed based on the corrosion and scaling potentials (CSPs) of water. The commonly used CSP index parameters are chloride–sulfate mass ratio, Langelier index, Larson-Skold index, aggressive index, Ryznar stability index, and Puckorius scaling index. Simultaneous application of these index parameters often classifies a sample into multiple water quality categories, thereby introducing bias in assessment and decision-making. No previous numerical model integrated the CSP indices to provide a single, composite index value for a more unbiased interpretation of industrial water quality. Therefore, this paper proposes an integrated industrial water quality index (IIWQI) that integrates the six CSP index parameters for direct and concise assessment of industrial water resources. To achieve its aim, this research incorporated information entropy theory and soft computing techniques. The developed IIWQI was applied to water samples from southeastern Nigeria. Different classification groups were observed based on the six CSP indices. However, the IIWQI summarized the classifications of the water samples into three categories: Class 1 (28.57%, slight-medium corrosivity, significant scaling potential); Class 2 (46.43%, medium–high corrosivity, no scaling); and Class 3 (25.00%, high-very high corrosion, no scaling). Correlation analysis revealed the relationships between the physicochemical variables, CSP index parameters, IIWQI, and the entropy-based variability of the IIWQI. The spatiotemporal water quality groups were revealed by Q-mode hierarchical dendrograms. Multiple linear regression and two multilayer perceptron neural networks accurately predicted the IIWQI. The findings of this paper could help in better evaluation, interpretation, and management of industrial water quality.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable. All the data used in this paper are provided herein.
References
Abba, S. I., Pham, Q. B., Saini, G., Linh, N. T. T., Ahmed, A. N., Mohajane, M., Khaledian, M., Abdulkadir, R. A., & Bach, Q. (2020). Implementation of data intelligence models coupled with ensemble machine learning for prediction of water quality index. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09689-x
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Water quality indices. Elsevier.
Abbasnia, A., Yousefi, N., Mahvi, A. H., Nabizadeh, R., Radfard, M., Yousefi, M., et al. (2018). Evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and its suitability for assessing water for drinking and irrigation purposes: Case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran). Human and Ecological Risk Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1458596
Abyaneh, H. Z., Varkeshi, M. B., Mohammadi, K., Howard, K., & Marofi, S. (2011). Assessment of groundwater corrosivity in Hamedan Province, Iran using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Geosciences Journal, 15(4), 433–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-011-0032-x
Agatemor, C., & Okolo, P. O. (2008). Studies of corrosion tendency of drinking water in the distribution system at the University of Benin. The Environmentalist, 28, 379–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-007-9152-2
Aghazadeh, N., Chitsazan, M., & Golestan, Y. (2017). Hydrochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in the Ardabil area Iran. Applied Water Science, 7, 3599–3616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0498-9
Al Osman, M., Yang, F., & Massey, I. Y. (2019). Exposure routes and health effects of heavy metals on children. BioMetals, 32(4), 563–573.
Amiri, V., Rezaei, M., & Sohrabi, N. (2014). Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(9), 3479–3490.
Anatole, D. (1996). Physical geology. Lexington.
Anyanwu, B. O., Ezejiofor, A. N., Igweze, Z. N., & Orisakwe, O. E. (2018). Heavy metal mixture exposure and effectsin developing nations: An update. Toxics, 6(4), 65.
Atasoy, A. D., & Yesilnacar, M. I. (2010). Effect of high sulfate concentration on the corrosivity: A case study from groundwater in Harran Plain, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 166, 595–607.
Chen, W., & Liu, W. (2015). Water quality modeling in reservoirs using multivariate linear regression and two neural network models. Advances in Artificial Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/521721
Edwards, M., & Triantafyllidou, S. (2007). Chloride-to-sulfate mass ratio and lead leaching to water. Journal-American Water Works Association, 99(7), 96–109.
Egbueri, J. C., Mgbenu, C. N., & Chukwu, C. N. (2019). Investigating the hydrogeochemical processes and quality of water resources in Ojoto and environs using integrated classical methods. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 5(4), 1443–1461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00613-y
Enyoh, C. E., Andrew, W. V., & Ngozi, J. E. (2018). pH variation and chemometric assessment of borehole water in Orji, Owerri, Imo state Nigeria. Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 5, 2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2380-2391.1000238
Fagbote, E. O., Olanipekun, E. O., & Uyi, H. S. (2014). Water quality index of the groundwater of bitumen deposit impacted farm settlements using entropy weighted method. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11(1), 127–138.
Fetter, C. W. (1990). Applied hydrogeology. Mirril Publishing Company.
Hameed, M., Sharqi, S. S., Yaseen, Z. M., Afan, H. A., Hussain, A., & Elshafie, A. (2017). Application of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques in water quality index prediction: A case study in tropical region Malyasia. Neural Computing & Applications, 28(1), 893–905.
Hsueh, Y. M., Lee, C. Y., Chien, S. N., Chen, W. J., Shiue, H. S., Huang, S. R., Lin, M. I., Mu, S. C., & Hsieh, R. L. (2017). Association of blood heavy metals with developmental delays and health status in children. Science and Reports, 7(1), 43608.
Hwang, J. Y., et al. (2017). Applications of hydrochemical models for the assessment of groundwater. Environment and Natural Resources Research, 20(3), 156–173.
Ighalo, J. O., Adeniyi, A. G., & Marques, G. (2020). Artificial intelligence for surface water quality monitoring and assessment: A systematic literature analysis. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01041-z
Igwe, O., & Omeka, M. E. (2021). Hydrogeochemical and pollution assessment of water resources within a mining area, SE Nigeria, using an integrated approach. International Journal of Energy and Water Resources, 6(2), 161–182.
Isiyaka, H. A., Mustapha, A., Juahir, H., & Phil-Eze, P. (2019). Water quality modelling using artificial neural network and multivariate statistical techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 5(2), 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0551-9
Islam, A. R. M. T., Ahmed, N., Bodrud-Doza, M., & Chu, R. (2017). Characterizing groundwater quality ranks for drinking purposes in Sylhet district, Bangladesh, using entropy method, spatial autocorrelation index, and geostatistics. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(34), 26350–26374.
Ismail, A. I. M., & El-Shamy, A. M. (2009). Engineering behavior of soil materials on the corrosion of mild steel. Applied Clay Science, 42, 356–362.
Juahir, H., Zain, S. M., Toriman, M. E., et al. (2004). Application of artificial neural network models for predicting water quality index. Malaysian Journal of Civil Engineering, 16, 42–55.
Kadam, A. K., Wagh, V. M., Muley, A. A., Umrikar, B. N., & Sankhua, R. N. (2019). Prediction of water quality index using artificial neural network and multiple linear regression modelling approach in Shivganga River basin India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00581-3
Kaur, G., Mandal, A. K., Nihlani, M. C., & Lal, B. (2009). Control of sulfidogenic bacteria in produced water from the Kathloni oilfield in northeast India. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 63, 151–155.
Khalid, G. M., & Usman, A. G. (2021). Application of data-intelligence algorithms for modeling the compaction performance of new pharmaceutical excipients. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00183-w
Krol, A., Mizerna, K., & Bozym, M. (2020). An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384, 121502.
Langelier, W. F. (1936). The analytical control of anti-corrosion water treatment. Journal-American Water Works Association, 28(10), 1500–1521.
Larson, T. E., & Skold, R. V. (1958). Laboratory studies relating mineral quality of water to corrosion of steel and cast iron. Corrosion, 14(6), 43–46.
Li, P., Qian, H., & Wu, J. (2010). Groundwater quality assessment based on improved water quality index in Pengyang County, Ningxia Noethwest China. Journal of Chemistry, 7(S1), S209–S216.
Mahmoud, K., Bebiş, H., Usman, A. G., Salihu, A. N., Gaya, M. S., Dalhat, U. F., Abdulkadir, R. A., Jibril, M. B., Abba, S. I. (2021). Prediction of the effects of environmental factors towards COVID-19 outbreak using AI-based models. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence, 10(1), 35–42. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v10.i1.pp35-42
Mankikar, T. Y. (2021). Comparison of indices for scaling and corrosion tendency of groundwater: Case study of unconfned aquifer from Mahoba District, U.P. State. Applied Water Science, 11, 94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01423-3
Martino, G. D., Fontana, N., Marini, G., & Singh, V. P. (2012). Variability and trend in seasonal precipitation in the continental United States. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 18(6), 630–640.
McFarland, M. L., Provin, T. L., Boellstorf, D. E. (2017). Drinking water problems: Corrosion, U.S.A: Texas AgriLife Extension Service and USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
McGrane, K. (2020). Acidic water: risks, benefits, and more. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/acidicwater. Accessed 30 Jun 2022.
Misaghi, F., Delgosha, F., Razzaghmanesh, M., & Myers, B. (2017). Introducing a water quality index for assessing water for irrigation purposes: A case study of the Ghezel Ozan River. Science of the Total Environment, 589, 107–116.
Mishra, A.K., Özger, M., & Singh, V.P. (2009). An entropy-based investigation into the variability of precipitation. Journal of Hydrology, 370, 139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.03.006
Mukate, S. V., Panaskar, D. B., Wagh, V. M., & Baker, S. J. (2019). Understanding the influence of industrial and agricultural land uses on groundwater quality in semiarid region of Solapur. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00342-3
Najafzadeh, M., Ghaemi, A., & Emamgholizadeh, S. (2018). Prediction of water quality parameters using evolutionary computing-based formulations. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2049-4
Nganje, T. N., Agbor, E. E., Adamu, C. I., Ukpong, A. J., Katte, B. F., Edet, A. E., & Hursthouse, A. S. (2020). Public health challenges as a result of contaminated water sources in Kumba Cameroon. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(4), 1167–1195.
Nguyen, C. K., Clark, B. N., Stone, K. R., & Edwards, M. A. (2011). Role of chloride, sulfate, and alkalinity on galvanic lead corrosion. Corrosion, 10(5006/1), 3600449.
Nhantumbo, C., Carvalho, F., Uvo, C., Larsson, R., & Larson, M. (2018). Applicability of a processes-based model and artificial neural networks to estimate the concentration of major ions in rivers. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 193, 32–40.
NIS. (2007). Nigerian standard for drinking water quality. Nigerian Industrial Standard 554, 13–14.
Omeka, M. E., Egbueri, J. C., & Unigwe, C.O. (2022). Investigating the hydrogeochemistry, corrosivity and scaling tendencies of groundwater in an agrarian area (Nigeria) using graphical, indexical and statistical modelling. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15(13), 1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10514-7
Ouma, Y. O., Okuku, C. O., Njau, E. N. (2020). Use of artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression model for the prediction of dissolved oxygen in rivers: Case study of hydrographic Basin of River Nyando, Kenya. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9570789
Ozel, H. U., Gemici, B. T., Gemici, E., Ozel, H. B., Cetin, M., & Sevik, H. (2020). Application of artificial neural networks to predict the heavy metal contamination in the Bartin River. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10156-w
Ozoko, D. C. (2015). Corrosion potentials of natural waters in Abakaliki, Ebonyi State Nigeria. Journal of Natural Sciences, 5(9), 108–114.
Puckorius, P. R., & Brooke, J. M. (1991). A new practical index for calcium carbonate scale prediction in cooling tower systems. Corrosion, 47(4), 280–284.
Ryznar, J. W. (1944). A new index for determining the amount of calcium carbonate scale formed by a water. Journal American Water Works Association, 36, 472–475.
Sajil Kumar, P. J. (2019). Assessment of corrosion and scaling potential of the groundwater in the Thanjavur district using hydrogeochemical analysis and spatial modeling techniques. SN Applied Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0423-6
Schock, M. R. (1999). Internal corrosion and deposition control. Water quality and treatment: A handbook of community water supplies. McGraw-Hill, USA, pp 1–17.
Shams, M., Mohamadi, A., & Sajadi, S. A. (2012). Evaluation of corrosion and scaling potential of water in rural water supply distribution networks of Tabas. World Applied Sciences Journal, 17(11), 1484–1489.
Shannon, C. E. (1948). A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379–423 (623–656).
Sharma, N., Vaid, U., & Sharma, S. K. (2021). Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purpose using hydrochemical studies in Dera Bassi town and its surrounding agricultural area of Dera Bassi Tehsil of Punjab India. SN Applied Science, 3(245), 1–13.
Sharpe, W. E., & DeWalle, D. R. (1985). Potential health implications for acid precipitation, corrosion, and metals contamination of drinking water. Environmental Health Perspectives, 63, 71–78.
Siddha, S., & Sahu, P. (2020). Assessment of groundwater quality and associated human health risk of Central Gujarat, India. Clean-Soil Air Water, 2000056, 1–17.
Siddha, S., & Sahu, P. (2022). Evaluation of corrosivity and scaling properties of groundwater of Central Gujarat for industrial usage. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15, 891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10197-0
Silva, V. D. P. R., Belo Filho, A. F., Almeida, R. S. R., de Holanda, R. M., & da Cunha Campos, J. H. B. (2016). Shannon information entropy for assessing space–time variability of rainfall and streamflow in semiarid region. Science of the Total Environment, 544, 330–338.
Singh, B., Sihag, P., Singh, V. P., Sepahvand, A., & Singh, K. (2021). Soft computing techniques-based prediction of water quality index. Water Supply. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.157
Singh, K. R., Dutta, R., Kalamdhad, A. S., & Kumar, B. (2019a). Information entropy as a tool in surface water quality assessment. Environment and Earth Science, 78, 15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7998-x
Singh, K. R., Dutta, R., Kalamdhad, A. S., & Kumar, B. (2019b). An investigation on water quality variability and identification of ideal monitoring locations by using entropy based disorder indices. Science of the Total Environment, 647, 1444–1455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.463
Singh, K. R., Goswami, A. P., Kalamdhad, A. S., & Kumar, B. (2019c). Development of irrigation water quality index incorporating information entropy. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00338-z
Singh, V. P. (2011). Hydrologic synthesis using entropy theory. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 16(5), 421–433.
Singh, V. P. (2013). Entropy theory and its application in environmental and water engineering. Wiley.
Singh, V. P. (2014). Entropy theory in hydraulic engineering: An introduction. American Society of Civil Engineers.
Stangierski, J., Weiss, D., & Kaczmarek, A. (2019). Multiple regression models and artificial neural network (ANN) as prediction tools of changes in overall quality during the storage of spreadable processed Gouda cheese. European Food Research and Technology, 245, 2539–2547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03369-y
Stets, E. G., Lee, C. J., Lytle, D. A., Schock, M. R. (2017). Increasing chloride in rivers of the conterminous U.S. and linkages to potential corrosivity and lead action level exceedances in drinking water. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.119
Swamee, P. K., & Tyagi, A. (2000). Describing water quality with aggregate index. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 126(5), 451–455.
Tang, Z., Hong, S., Xiao, W., & Taylor, J. (2006). Characteristics of iron corrosion scales established under blending of ground, surface, and saline waters and their impacts on iron release in the pipe distribution system. Corrosion Science, 48, 322–342.
Tavanpour, N., Noshadi, M., & Tavanpour, N. (2016). Scale formation and corrosion of drinking water pipes: A case study of drinking water distribution system of Shiraz City. Modern Applied Science. https://doi.org/10.5539/mas.v10n3p166
US-EPA. (1984). Corrosion manual for internal corrosion of water distribution systems, United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA), Washington, DC.
Vasconcelos, H. C., et al. (2015). Characterization of the corrosive action of mineral waters from thermal sources: A case study at Azores Archipelago, Portugal. Water, 7, 3515–3530.
Wagh, V. M., Panaskar, D. B., Muley, A. A., Mukate, S. V., Lolage, Y. P., & Aamalawar, M. L. (2016). Prediction of groundwater suitability for irrigation using artificial neural network model: A case study of Nanded tehsil, Maharashtra India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2(4), 1–10.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of American Statistical Association, 58(301), 236–244.
WHO. (2011). Hardness in drinking-water: Background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization.
WHO. (2017). Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva.
Wu, P., & Tan, M. (2012). Challenges for sustainable urbanization: A case study of water shortage and water environment changes in Shandong, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 919–927.
Zhou, Q., Yang, N., Li, Y., Ren, B., Ding, X., Bian, H., & Yao, X. (2020). Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Global Ecology and Conservation, 22, e00925.
Acknowledgements
The author is very grateful to the Editor and the two anonymous Reviewers that contributed great insights for the improvement of the manuscript.
Funding
The present work did not receive any external financial assistance from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Egbueri, J.C. Incorporation of information entropy theory, artificial neural network, and soft computing models in the development of integrated industrial water quality index. Environ Monit Assess 194, 693 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10389-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10389-x