Abstract
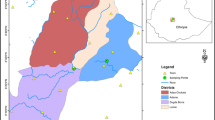
Vegetable gardening in floodplains in western Nigeria has assumed economic significance but with attendant pressure on urban field in the dry season. This study assessed soil properties and bioconcentration of cadmium (Cd), iron (Fe) and lead (Pb), in edible parts of Celosia argentea and Corchorus olitorius grown in floodplains. Soil and vegetable samples were collected at 20 m intervals from rural (Atoyo and Ewuga) and urban (GRA Rd. and Lafarge) floodplain gardens in Sagamu. Six samples were collected per location making a total of 24 samples each of soil and vegetable. Samples were analyzed for soil properties and heavy metal concentration in the vegetables. Transfer factor (TF), contamination factor (CF), daily intake of metals (DIM), health risk index (HRI) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) were also determined. Soil properties varied significantly, with the highest soil concentration of Cd (0.91 mg kg−1) and Fe (208.20 mg kg−1) recorded at Lafarge. The highest soil Pb (223.77 mg kg−1) was at Atoyo. Bioaccumulation of Fe was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher in C. argentea than C. olitorius. Heavy metal bioaccumulation beyond allowable limits was recorded for Cd (0.46 mg kg−1) and Pb (49.30 mg kg−1) by C. argentea and C. olitorius, respectively. Soil contamination was dominated by Cd at Lafarge and by Pb at Atoyo. The DIM and HRI indices indicated no risk of Cd, Fe and Pb consumption in the vegetables. Geoaccumulation index revealed that Lafarge and Atoyo soils were extremely contaminated with Cd and Pb, respectively. Leafy vegetables grown in urban and rural floodplain soils adjacent to waste dumpsite are accumulators of Cd and Pb with food poisoning as the consequence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmone-Marsan, F., & Biasioli, M. (2010). Trace elements in soils of urban areas. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 213, 121–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0372-6.
Anderson, J. M., & Ingram, J. S. L. (1993). Tropical soil biology and fertility: A handbook of Method of Analysis (pp. 38–39). UK: International Wallingford.
Arora, M., Kiran, B., Rani, S., Rani, A., Kaur, B., & Mittal, N. (2008). Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chemistry, 111, 811–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.04.049.
Asmaa, R. M., Magda, M. H., Shafeek, M. R., & Aisha, H. A. (2014). Growth, yield and leaf content of Jews mallow plant (Corchorus olitorius) by soil fertilizer with different level of compost manure and chemical fertilizer. Middle East Journal of Agriculture Research, 3(3), 543–548.
Ayantobo, O. O., Awomeso, J. A., Oluwasanya, G. O., Bada, B. S., & Taiwo, A. M. (2014). Non-cancer human health risk assessment from exposure to heavy metals in surface and groundwater in Igun Ijesha, Southwest Nigeria. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 10(3), 301–310. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2014.301.311.
Azeez, J. O., Mesele, S. A., Sarumi, B. O., Ogundele, J. A., Uponi, A. O., & Hassan, A. O. (2014). Soil metal pollution as a function of traffic density and distance from road in emerging cities: A case study of Abeokuta, southwestern Nigeria. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 60(2), 275–295. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2013.792406.
Bambara, L. T., Kabore, K., Cisse, O., Derra, M., Zougmoré, F., & Bentil, N. (2015). Assessment of pollution in agricultural soil and interrelationship between the heavy metals at Paspanga, Burkina Faso. Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology., 9(8), 2319–2399. https://doi.org/10.9790/2402-09818490.
Bandow, N., & Simon, F. G. (2016). Significance of cadmium from artists’ paints to agricultural soil and the food chain. Environmental Sciences Europe, 28, 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-016-0077-6.
Bartkowiak, A., Lemanowicz, J., & Hulisz, P. (2017). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in salt-affected soils in the Natura 2000 area (Ciechocinek, north-Central Poland). Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 24, 27175–27187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0323-5.
Beesley, L., Inneh, O. S., Norton, G. J., Moreno-Jimenez, E., Pardo, T., Clemente, R., & Dawson, J. J. C. (2014). Assessing the influence of compost and biochar amendments on the mobility and toxicity of metals and arsenic in a naturally contaminated mine soil. Environmental Pollution, 186, 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.026.
Bortey-Sam, N., Nakayama, S. M. M., Akoto, O., Ikenaka, Y., Baidoo, E., Mizukawa, H., & Ishizuka, M. (2015). Ecological risk of heavy metals and a metalloid in agricultural soils in Tarkwa, Ghana. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health, 12(9), 11448–11465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120911448.
Bouyoucos, G. H. (1962). Hydrometer method for making particle size analysis of soils. Agronomy Journal, 54, 464–465. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1962.00021962005400050028x.
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, C. S. (1982). Nitrogen-Total. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties (pp. 595–624). Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America.
Buccolieri, A., Buccolieri, G., Cardellicchio, N., Dell'Atti, A., Di Leo, A., & Maci, A. (2006). Heavy metals in marine sediments of Taranto gulf, Ionian Sea, southern Italy. Marine Chemistry, 99, 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2005.09.009.
Cui, Y. J., Zhu, Y. G., Zhai, R. H., Chen, D. Y., Huang, Y. Z., Qui, Y., & Liang, J. Z. (2004). Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables in an area near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environment International, 30(6), 785–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.01.003.
Degraeve, N. (1981). Carcinogenic, teratogenic and mutagenic effects of cadmium. Mutation Research, 86(1), 115–135.
Dixit, R., Wasiullah, Malaviya, D., Pandiyan, K., Singh, U. B., Sahu, A., Shukla, R., Singh, B. P., Rai, J. P., Sharma, P. K., Lade, H., & Paul, D. (2015). Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: An overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability, 7(2), 2189–2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7022189.
Ediene, V. F., & Iren, O. B. (2017). Impact of abattoir effluents on the pH, organic matter, heavy metal levels and microbial composition of surrounding soils in Calabar municipality. Asian Journal of Environment and Ecology, 2(3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.9734/AJEE/2017/33341.
Ettler, V., Vanek, A., Mihaljevič, M., & Bezdička, P. (2005). Contrasting lead speciation in forest and tilled soils heavily polluted with lead metallurgy. Chemosphere, 58, 1449–1459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.084.
European Union (EU). (2015). Commission regulation (EC) No. 1005/2015 of 25 June 2015 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of lead in certain foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European UnionL 161/9.
European Union (EU). (2006). Commission regulation (EC) no. 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L, 364, 5–24.
FAO/WHO (1983). Summary of evaluations performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on food additives TRS 696-JECFA 27/29.
Fiori, C. S., Rodrigues, A. P., Santelli, R. E., Cordeiro, R. C., Carvalheira, R. G., Araujo, P. C., Castilhos, Z. C., & Bidone, E. D. (2013). Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A case study of coastal water bodies from the Rio de Janeiro state, southeastern Brazil. Geochimica Brasiliensis, 27(1), 24–36. https://doi.org/10.21715/gb.v27i1.386.
Foulkes, E.C. 1986. Absorption of cadmium. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, E.C. Foulkes, Ed. Springer Verlag, Berlin. 80, 75-100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-70856-5_3
Goher, M. E., Farhat, H. I., Abdo, M. H., & Salem, S. G. (2014). Metal pollution assessment in the surface sediment of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 40, 213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2014.09.004.
Gong, Q., Deng, J., Xiang, Y., Wang, Q., & Yang, L. (2008). Calculating pollution indices by heavy metals in ecological geochemistry assessment and a case study in parks of Beijing. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(3), 230–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60042-4.
Grant, C. A., Buckley, W. T., Bailey, L. D., & Selles, F. (1998). Cadmium accumulation in crops. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 78(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.4141/P96-100.
Håkanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Hani, A., & Pazira, E. (2011). Heavy metals assessment and identification of their sources in agricultural soils of southern Teheran. Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 176, 677–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1671-5.
Hindy, K. T., & Farag, S. A. (1983). Composition of suspended and settled particulate matter from the deposition: A comparative study. Environment Pollution, Series B, 11, 205–210.
Ilhan, S., Savaroğlu, F., & Çolak, F. (2007). Antibacterial and antifungal activity of Corchorus olitorius L. (Molokhia) extracts. International Journal of Natural and Engineering Sciences, 1(3), 59–61.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Al-Mamun, M. H., & Masunaga, S. (2015). Potential ecological risk of hazardous elements in different land-use urban soils of Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 512–513, 94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.100.
Jalili, M., & Azizkhan, R. (2009). Lead toxicity resulting from chronic ingestion of opium. West Journal of Emerging Medicine, 10(4), 244–246.
Jan, F. A., Ishaq, M., Khan, S., Ihsanullah, I., Ahmad, I., & Shakirullah, M. (2010). A comparative study of human health risks via consumption of food crops grown on wastewater irrigated soil (Peshawar) and relatively clean water irrigated soil (lower Dir). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179, 612–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.047.
Jolly, Y. N., Islam, A., & Akbar, S. (2013). Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables and possible health risk assessment. Springer Plus, 2(1), 385. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-385.
Kachenko, A. G., & Singh, B. (2006). Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in urban and metal smelter contaminated sites in Australia. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 169, 101–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-2027-1.
Knoema (2007). Nigeria-Vegetable consumption. Retrieved from https://knoema.com/atlas/Nigeria/topics/Food-Security/Food-Consumption/Vegetables-consumption.
Kucha, H., Martens, A., Ottenburgs, R., de Vos, W., & Viaene, W. (1996). Primary minerals of Pb-Zn mining and metallurgical dumps and their environmental behaviour at Plombières, Belgium. Environmental Geology, 27, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00770598.
Lado, L. R., Hengl, T., & Reuter, H. I. (2008). Heavy metals in European soils: A geostatistical analysis of the FOREGS geochemical database. Geoderma, 148(2), 189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.09.020.
Lato, A., Radulov, I., Berbecea, A., Lato, K., & Crista, F. (2012). The transfer factor of metals in soil-plants system. Research Journal of Agricultural Science, 44(3), 67–72.
Li, J. & Heap, A. D. 2008. A Review of Spatial Interpolation Methods for Environmental Scientists. Geoscience Australia, Record 2008/23, 137 pp.
Liu, G., Xue, W., Tao, L., Liu, X., Hou, J., Wilton, M., Gao, D., Wang, A., & Li, R. (2013). Vertical distribution and mobility of heavy metals in agricultural soils along Jishui River affected by mining in Jiangxi province, China. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 42(10), 1450–1456. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300668.
Mahmood, A., & Malik, R. N. (2014). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore, Pakistan. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7, 91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.002.
Martínez, L. L. G., & Poleto, C. (2014). Assessment of diffuse pollution associated with metals in urban sediments using the geoaccumulation index (Igeo). Journal of Soils and Sediments, 14, 1251–1257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-0871-y.
McLean, E. O., Dumford, S. W. F., & Coronel, S. W. (1982). A comparison of several methods of determining lime requirements of soil. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 30, 26–30.
Mirecki, N., Agič, R., Šunić, L., Milenković, L., & Ilić, Z. S. (2015). Transfer factor as indicator of heavy metals content in plants. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 24(11), 4212–4219.
Monfared, S. H., Matinizadeh, M., Shirvany, A., Amiri, G. Z., Fard, R. M., & Rostami, F. (2013). Accumulation of heavy metal in Platanus orientalis, Robinia pseudoacacia and Fraxinus rotundifolia. Journal of Forestry Research, 24(2), 391–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-012-0313-x.
Müller, G. (1979). Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine-changesseity. Umschau in Wissenschaft und Technik, 79, 778–783.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1996). Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In D. L. Sparke (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods SSSA book series no. 5 (pp. 961–1010). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Oguntade, O. A., Adetunji, M. T., & Azeez, J. O. (2015). Uptake of manganese, iron, copper, zinc and chromium by Amaranthus cruentus L. irrigated with untreated dye industrial effluent in low land field. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 2875–2881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.10.022.
Oguntade, O. A., Odusanya, O. A., Olagunju, S. O., Oduntan, O. B., Adewusi, K. M., & Adegoke, A. T. (2017). Residual effect of composted poultry manure on yield and bioaccumulation of Iron, zinc, Lead and cadmium in tissues of common cockscomb (Celosia argentea L.) grown on soils from waste dumpsite and farmland. African Journal of Agriculture Technology and Environment, 6(1), 79–88.
Oguntade, O. A., Odusanya, O. A., Olagunju, S. O., Adewusi, K. M., & Adegoke, A. T. (2018). Residual effect of composted kitchen waste and poultry manure soil amendments on yield and concentrations of copper, iron, manganese and zinc in leaf tissue of jute mallow (Corchorus olitorius Linn). Ife Journal of Agriculture, 30(2), 65–76.
Oyedele, D. J., Asonugho, C., & Awotoye, O. O. (2006). Heavy metals in soil and accumulated by edible vegetable after phosphate fertilizer application. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 5(4), 1446–1453.
Padmavathiamma, P. K., & Li, L. Y. (2007). Phytoremediation technology: Hyper accumulation metals in plants. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 184(1–4), 105–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9401-5.
Pająk, M., Halecki, W., & Gąsiorek, M. (2017). Accumulative response of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) to heavy metals enhanced by Pb-Zn ore mining and processing plants: Explicitly spatial considerations of ordinary kriging based on a GIS approach. Chemosphere, 168, 851–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.125.
Payne, R. W., Harding, S. A., Murray, D. A., Soutar, D. M., Baird, D. B., Glaser, A. I., Channing, I. C., Welham, S. J., Gilmour, A. R., Thompson, R., & Webster, R. (2009). GenStat for windows (12 edition) introduction. Hemel: VSN International.
Paz-Ferreiro, J., Lu, H., Fu, S., Méndez, A., & Gascó, G. (2014). Use of phytoremediation and biochar to remediate heavy metal polluted soils: A review. Solid Earth, 5, 65–75. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-5-65-2014.
Pietrzykowski, M., Socha, J., & van Doorn, N. S. (2014). Linking heavy metal bioavailability (cd, cu, Zn and Pb) in scots pine needles to soil properties in reclaimed mine areas. Science of the Total Environment, 470-471, 501–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.008.
Proshad, R., Islam Md, S., Haque, M. A., Hoque, M. F., & Ahmed, S. (2018). Apportionment of hazardous elements in agricultural soils around the industrial vicinity of Bangladesh. SF Journal of Environmental and Earth Science, 1(1), 1001.
Radwan, M. A., & Salama, A. K. (2006). Market basket survey for some heavy metals in Egyptian fruits and vegetables. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 44(8), 1273–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.02.004.
Rahman, M. A., & Ishiga, H. (2012). Trace metal concentrations in tidal flat coastal sediments, Yamaguchi prefecture, Southwest Japan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(9), 5755–5771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2379-x.
Roy, M., & McDonald, L. M. (2015). Metal uptake in plants and health risk assessments in metal-contaminated smelter soils. Land Degradation & Development, 26(8), 785–792. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2237.
Salem, H. M., Eweida, E. A., & Farag, A. (2000). Heavy metals in drinking water and their environmental impact on human health. ICEHM, 542–556.
Salt, D. E., Blaylock, M., Kumar, N. P., Dushenkov, V., Ensley, B. D., Chet, I., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoremediation: A novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology, 13(5), 468–474.
Santos Bermejo, J. C., Beltrán, R., & Gómez Ariza, J. L. (2003). Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel River (Southwest Spain). Environment International, 29(1), 69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00147-2.
Schippers, R. R. (2002). African indigenous vegetables. An overview of the cultivated species. Natural resources international limited and 94 horticultural development services. Chatham: Natural Resources Institute/ACP-EU Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation.
Shakeri, A., Moore, F., & Modabberi, S. (2009). Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the shiraz industrial complex zone soil, south shiraz, Iran. World Applied Sciences Journal, 6(3), 413–425.
Sharma, R. K., Agrawal, M., & Marshall, F. M. (2008). Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals (cu, Zn, cd and Pb) in Varanasi City, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 142, 269–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9924-7.
Sipos, P., Németh, T., Kis, V. K., & Mohai, I. (2008). Sorption of copper, zinc and lead on soil mineral phases. Chemosphere, 73(4), 461–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.06.046.
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Xie, X., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1–3), 455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.074.
Tani, F. H., & Barrington, S. (2005). Zinc and copper uptake by plants under two transpiration rates. Part I. wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environmental Pollution, 138(3), 538–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.06.005.
Tasrina, R. C., Rowshon, A., Mustafizur, A. M. R., Rafiqul, I., & Ali, M. P. (2015). Heavy metals contamination in vegetables and its growing soil. Journal Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2(3), 142. https://doi.org/10.4172/2380-2391.1000142.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth's crust. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 72(2), 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]2.0.CO;2.
Udo, E. J., Ibia, T. O., Ogunwale, J. A., Ano, A. O., & Esu, I. E. (2009). Manual of soil, plant and water analyses. Lagos: Sibon Books Ltd 183 pp.
Usman, A. R. A., Kuzyakov, Y., & Stahr, K. (2005). Effect of immobilizing substances and salinity on heavy metals availability to wheat grown on sewage sludge-contaminated soil. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 14(4), 329–344. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320380590954051.
Vacca, A., Bianco, M. R., Murolo, M., & Violante, P. (2012). Heavy metals in contaminated soils of the Rio Sitzerri floodplain (Sardinia, Italy): Characterization and impact on pedodiversity. Land Degradation & Development, 23(4), 250–364. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2153.
Varol, M. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1939). An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37, 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003.
Weldesilassie, A., Frör, O., Boelee, E., & Dabbert, S. (2009). The economic value of improved wastewater irrigation: A contingent valuation study in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics, 34(3), 428–449 https://hdl.handle.net/10568/40679. Accessed December, 2009
WHO. (1996). Permissible limits of heavy metals in soil and plants (Geneva: World Health Organization), Switzerland.
WHO. (2000). Safety evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. International Programme on Chemical Safety. WHO Food Additive Series 52.
WHO. (2003). Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO expert consultation, World Health Organization, Technical Report Series, 916 Geneva, Switzerland.
WHO. (2011). Joint FAO/WHO food standards programme codex committee on contaminants in foods. The Hague: Fifth Session.
Wierzbowska, J., Kovačik, P., Sienkiewicz, S., Krzebietke, S., & Bowszys, T. (2018). Determination of heavy metals and their availability to plants in soil fertilized with different waste substances. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6941-7.
Wilson, B., & Pyatt, F. B. (2007). Heavy metal dispersion, persistence and bioaccumulation around an ancient copper mine situated Anglesey, UK. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety, 66, 224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.02.015.
Woszczyk, M., Spychalski, W., & Boluspaeva, L. (2018). Trace metal (cd, cu, Pb, Zn) fractionation in urban-industrial soils of Ust-Kamenogorsk (Oskemen), Kazakhstan-implications for the assessment of environmental quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 62–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6733-0.
Xia, X., Chen, X., Liu, R., & Liu, H. (2011). Heavy metals in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. Journal of Hazardous Material, 186(2–3), 2043–2050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.104.
Yu, G. B., Liu, Y., Yu, S., Wu, S. C., Leung, A. O. W., Luo, X. S., & Wong, M. H. (2011). Inconsistency and comprehensiveness of risk assessments for heavy metals in urban surface sediments. Chemosphere, 85(6), 1080–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.039.
Zhuang, W., & Gao, X. (2014). Integrated assessment of heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay and the coastal waters of the Zhangzi Island, China: Comparison among typical marine sediment quality indices. PLoSOne, 9, e94145. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094145.
Zhuang, P., McBride, M. B., Xia, H., Li, N., & Li, Z. (2009). Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Science Total Environment, 407, 1551–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.061.
Acknowledgements
The authors are sincerely grateful to farmers (male and female) in the study area for their understanding and allowing us to carry out this study in their farms. We are equally thankful to Professor O. A. Enikuomehin for his suggestions while proof reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguntade, O.A., Adegbuyi, A.A., Nassir, A.L. et al. Geoassessment of heavy metals in rural and urban floodplain soils: health implications for consumers of Celosia argentea and Corchorus olitorius vegetables in Sagamu, Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 192, 164 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8077-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8077-9