Abstract
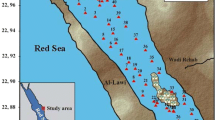
To document the spatial distribution and metal contamination in the coastal sediments of the Al-Khafji area in the northern part of the Saudi Arabian Gulf, 27 samples were collected for Al, V, Cr, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Hg, Sr, As, Fe, Co, and Ni analysis using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). The results revealed the following descending order of the metal concentrations: Sr > Fe > Al > As > Mn > Ni > V > Zn > Cr > Cu > Pb > Co > Hg > Cd. Average levels of enrichment factor of Sr, As, Hg, Cd, Ni, V, Cu, Co, and Pb were higher than 2 (218.10, 128.50, 80.94, 41.50, 12.31, 5.66, 2.95, 2.90, and 2.85, respectively) and that means the anthropogenic sources of these metals, while Al, Zn, Cr and Mn have enrichment factor less than 2, which implies natural sources. Average values of Sr, Hg, Cd, Cr, Ni, and As in the coastal sediments of Al-Khafji area were mostly higher than the values recorded from the background shale and earth crust and from those results along coasts of the Caspian Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. The highest levels of Cu in the northern part of the studied coastline might be due to Al-Khafji desalination plant, while levels of Al, Ni, Cr, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn in the central part may be a result of landfilling and industrial sewage. The highest levels of As, Cd, Co, Cu, Hg, and V in the southern part seem to be due to oil pollutants from Khafji Joint Operations (KJO). The higher values of Sr in the studied sediments in general and particularly in locality 7 could relate to the hypersalinity and aragonitic composition of the scleractinian corals abundant in that area.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin, B. S., & Kırmızıgu, O. (2017). Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Gokcekaya Dam Lake, Eskis¸ehir, Turkey. Environment and Earth Science, 76, 402.
Alharbi, T., Alfaifi, H., & El-Sorogy, A. (2017). Metal pollution in Al-Khobar seawater, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 119, 407–415.
Alharbi, T., & El-Sorogy, A. (2017). Assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments of Al-Khobar area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Journal of the African Earth Sciences, 129, 458–468.
Almasoud, F. I., Usman, A. I., & Al-Farraj, A. S. (2015). Heavy metals in the soils of the Arabian Gulf coast affected by industrial activities: analysis and assessment using enrichment factor and multivariate analysis. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(3), 1691–1703.
Al-Taani, A. A., Batayneh, A., Nazzal, Y., Ghrefat, H., Elawadi, E., & Zaman, H. (2014). Status of trace metals in surface seawater of the Gulf of Aqaba, Saudi Arabia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 86, 582–590.
Carman, C. M., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y. S. (2007). Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environmental Pollution, 147, 311–323.
Cravo, A., Foster, P., & Bebianno, M. J. (2002). Minor and trace elements in the shell of Patella aspera (Roding, 1798). Environment International, 28, 295–302.
de Mora, S., Sheikholeslami, M. R., Wyse, E., Azemard, S., & Cassi, R. (2004a). An assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 61–77.
de Mora, S., Fowler, S. W., Wyse, E., & Azemard, S. (2004b). Distribution of heavy metals in marine bivalves, fish and coastal sediments in the Gulf and Gulf of Oman. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 410–424.
Diaz-de Alba, M., Galindo-Riano, M. D., Casanueva-Marenco, M. J., Garcia-Vargas, M., & Kosore, C. M. (2011). Assessment of the metal pollution, potential toxicity and speciation of sediment from Algeciras Bay (South of Spain) using chemometric tools. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 177–187.
El-Sorogy, A. S., Abdelwahab, M., & Nour, H. (2012). Heavy metals contamination of the Quaternary coral reefs, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Environment and Earth Science, 67, 777–785.
El-Sorogy, A. S., El Kammar, A., Ziko, A., Aly, M., & Nour, H. (2013a). Gastropod shells as pollution indicators, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 87, 93–99.
El-Sorogy, A. S., Nour, H., Essa, E., & Tawfik, M. (2013b). Quaternary coral reefs of the Red Sea coast, Egypt: diagenetic sequence, isotopes and trace metals contamination. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6, 4981–4991.
EL-Sorogy, A. S., Tawfik, M., Almadani, S. A., & Attiah, A. (2016). Assessment of toxic metals in coastal sediments of the Rosetta area, Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 398.
Fang, T. H., Li, J. Y., Feng, H. M., & Chen, H. Y. (2009). Distribution and contamination of trace metals in surface sediments of the East China Sea. Marine Environmental Research, 68, 178–187.
Folk, R. L. (1974). Petrology of sedimentary rocks (p. 184). Austin: Hemphill.
Foster, L. C., Allison, N., Finch, A. A., & Andersson, C. (2009). Strontium distribution in the shell of the aragonite bivalve Arctica islandica. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GC001915.
Hökanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
ISQG. (1995). Interim sediment quality guidelines. Ottawa: Environment Canada 9 pp.
Leopold, E. N., Jung, M. C., Auguste, O., Ngatcha, N., Georges, E., & Lape, M. (2008). Metals pollution in freshly deposited sediments from river Mingoa, main tributary to the municipal lake of Yaounde, Cameroon. Geosciences Journal, 12(4), 337–347.
Lin, C., He, M., Liu, S., & Li, Y. (2012). Contents, enrichment, toxicity and baselines of trace elements in the estuarine and coastal sediments of the Daliao River System, China. Geochemical Journal, 46, 371–380.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environment Management, 19, 18–97.
Muller, G. (1979). Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine-Changes Seity, 1971. Umschau Wissenschaften Technology, 79, 778–783.
Nour, H., & El-Sorogy, A. S. (2017). Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals in Sabratha coastal sediments, Mediterranean Sea, Libya. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 134, 222–229.
Omar, M. B., Mendiguchia, C., Er-Raioui, H., Marhraoui, M., Lafraoui, G., Oulad-bdellah, M. k., Garcia-Vargas, M., & Moreno, C. (2015). Distribution of heavy metals in marine sediments of Tetouan coast (north of Morocco): natural and anthropogenic sources. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74, 4171–4185.
Randolph, R. C., Hardy, J. T., Fowler, S. W., Price, A. R. G., & Pearson, W. H. (1998). Toxicity and persistence of nearshore sediment contamination following the 1991 Gulf War. Environment International, 24, 33–42.
Ruiz, F. (2001). Trace metals in estuarine sediments from the southwestern Spanish coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 482–490.
Rumisha, C., Elskens, M., Leermakers, M., & Kochzius, M. (2012). Trace metal pollution and its influence on the community structure of soft bottom molluscs in intertidal areas of the Dar es Salaam coast, Tanzania. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64, 521–531.
Sadiq, M., & Alam, I. (1989). Metal concentrations in pearl oyster, Pinctada radiata, collected from Saudi Arabian coast of the Arabian Gulf. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 42, 111–118.
Sinex, S. A., & Helz, G. R. (1981). Regional geochemistry of trace elements in Checapeake Bay sediments. Environmental Geology, 3, 315–323.
Taylor, S. R. (1964). Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: a new table. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 28, 1273–1285.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. The Geological Society of America, 72, 175–192.
Vallius, H., Ryabchuk, D., & Kotilainen, A. (2007). Distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in soft surface sediments of the coastal area off Kotka, northeastern Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. In: Vallius, H. (ed.) Holocene sedimentary environment and sediment geochemistry of the eastern gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea, Geological Survey of Finland, Special Paper, 45 33–48.
Uddin, S. (2014). Environmental impacts of desalination activities in the Arabian gulf. International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, 5(2), 114–117.
Youssef, M., & El-Sorogy, A. S. (2016). Environmental assessment of heavy metal contamination in bottom sediments of Al-Kharrar lagoon, Rabigh, Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9, 474.
Youssef, M., El-Sorogy, A. S., Al-Kahtany, K., & Al-Otaibi, N. (2015). Environmental assessment of coastal surface sediments Tarut Island, Arabian Gulf (Saudi Arabia). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 96, 424–433.
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi, R., Jafari, A., & Alibeygi-beni, H. (2017). Potential ecological risk assessment, enrichment, geoaccumulation, and source identification of metals in the surface sediments of Choghakhor wetland, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 398.
Zhao, J., Temimi, M., Al-Azhar, M., & Ghedira, H. (2015). Satellite-based tracking of oil pollution in the Arabian Gulf and the Sea of Oman. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 41(2), 113–125.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through the Research Project No. NFG-15-03-12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alharbi, T., Alfaifi, H., Almadani, S.A. et al. Spatial distribution and metal contamination in the coastal sediments of Al-Khafji area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Environ Monit Assess 189, 634 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6352-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6352-1