Abstract
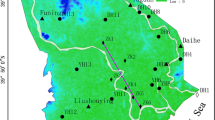
This paper presents the results of an assessment about interaction between Urmia Lake (UL) and coastal groundwater in the Urmia aquifer (UA). This aquifer is the most significant contributor to the freshwater supply of the coastal areas. The use of hydrochemical facies can be very useful to identify the saltwater encroachment or freshening phases in the coastal aquifers. In this study, the analysis of salinization/freshening processes was carried out through the saturation index (SI), ionic deltas (Δ), binary diagrams, and hydrochemical facies evolution (HFE) diagram. Based on the Gibbs plot, the behavior of the major ions showed that the changes in the chemical composition of the groundwater are mainly controlled by the water-soil/rock interaction zone and few samples are relatively controlled by evaporation. A possible explanation for this phenomenon is that the deposited chloride and sulfate particles can form the minor salinity source in some coastal areas when washed down by precipitation. The SI calculations showed that all groundwater samples, collected in these periods, show negative saturation indices, which indicate undersaturation with respect to anhydrite, gypsum, and halite. In addition, except in a few cases, all other samples showed the undersaturation with respect to the carbonate minerals such as aragonite, calcite, and dolomite. Therefore, these minerals are susceptible to dissolution. In the dry season, the SI calculations showed more positive values with respect to dolomite, especially in the northern part of UA, which indicated a higher potential for precipitation and deposition of dolomite. The percentage of saltwater in the groundwater samples of Urmia plain was very low, ranging between 0.001 and 0.79 % in the wet season and 0.0004 and 0.81 % in the dry season. The results of HFE diagram, which was taken to find whether the aquifer was in the saltwater encroachment phase or in the freshening phase, indicated that except for a few wells near the coast, there is very little hydraulic interaction between UA and UL. In this coastal area, most of the samples that were collected repeatedly in both wet and dry seasons showed the same hydrochemical facies, which suggested that the seasonal groundwater fluctuations cannot significantly change the chemical composition of groundwater.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri, V., Rezaei, M., & Sohrabi, N. (2014). Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72, 3479–3490.
Amiri, V., Sohrabi, N., & Altafi Dadgar, M. (2015). Evaluation of groundwater chemistry and its suitability for drinking and agricultural uses in the Lenjanat plain, central Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74, 6163–6176.
Andersen, M. S., Jakobsen, V. N. R., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemical processes and solute transport at the seawater/freshwater interface of a sandy aquifer. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 3979–3994.
APHA (American Public Health Association), (1985). Standard methods of the examination of water/wastewater (16th ed.). New York: APHA, AWWA, and WPCF.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. 2nd edition, CRC Press.
Asfahani, J., & Abou Zakhem, B. (2013). Geoelectrical and hydrochemical investigations for characterizing the salt water intrusion in the Khanasser valley, Northern Syria. Acta Geophysica, 61(2), 422–444.
Barker, A. P., Newton, R. J., & Bottrell, S. H. (1998). Processes affecting groundwater chemistry in a zone of saline intrusion into an urban aquifer. Applied Geochemistry, 13, 735–749.
Barlow, P. M., & Reichard, E. G. (2010). Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrogeology Journal, 18, 247–260.
Bear, J., Cheng, A. H. D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D., & Herrera, I. (Eds.) (2013). Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: concepts, methods and practices. Springer Science & Business Media.
Boluda-Botella, N., Valdes-Abellan, J., & Pedraza, R. (2014). Applying reactive models to column experiments to assess the hydrogeochemistry of seawater intrusion: optimising ACUAINTRUSION and selecting cation exchange coefficients with PHREEQC. Journal of Hydrology, 510, 59–69.
Bouzourra, H., Bouhlila, R., Elango, L., Slama, F., & Ouslati, N. (2015). Characterization of mechanisms and processes of groundwater salinization in irrigated coastal area using statistics, GIS, and hydrogeochemical investigations. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(4), 2643–2660.
Buschmann, J., & Berg, M. (2009). Impact of sulfate reduction on the scale of arsenic contamination in groundwater of the Mekong, Bengal and Red River deltas. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 1278–86.
Carreira, P. M., Marques, J. M., & Nunes, D. (2014). Source of groundwater salinity in coastline aquifers based on environmental isotopes (Portugal): natural vs. human interference. A review and reinterpretation. Applied Geochemistry, 41, 163–175.
Cary, L., Petelet-Giraud, E., Bertrand, G., Kloppmann, W., Aquilina, L., Martins, V., Hirata, R., Montenegro, S., Pauwels, H., Chatton, E., Franzen, M., Aurouet, A., Lasseur, E., Picot, G., Guerrot, C., Fléhoc, C., Labasque, T., Santos, J. G., Paiva, A., Braibant, G., & Pierre, D. (2015). Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): a multi-isotope approach. Science of the Total Environment, 530–531, 411–429.
Chen, K., & Jiao, J. J. (2014). Modeling freshening time and hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in coastal aquifers of Shenzhen, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71, 2409–2418.
Chen, K., Jiao, J., Huang, J., & Huang, R. (2007). Multivariate statistical evaluation of trace elements in groundwater in a coastal area in Shenzhen, China. Environmental Pollution, 147, 771–780.
Choudhury, K., Saha, D. K., & Chakraborty, P. (2001). Geophysical study for saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 46, 189–200.
Cimino, A., Cosentino, C., Oieni, A., & Tranchina, L. (2008). A geophysical and geochemical approach for seawater intrusion assessment in the Acquedolci coastal aquifer (Northern Sicily). Environmental Geology, 55, 1473–1482.
El Yaouti, F., El Mandour, A., Khattach, D., Benavente, J., & Kaufmann, O. (2009). Salinization processes in the unconfined aquifer of Bou-Areg (NE Morocco): a geostatistical, geochemical, and tomographic study. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 16–31.
Esmaeili-Vardanjani, M., Rasa, I., Amiri, V., Yazdi, M., & Pazand, K. (2015). Evaluation of groundwater quality and assessment of scaling potential and corrosiveness of water samples in Kadkan aquifer, Khorasan-e-Razavi Province, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 53. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4261-0.
Fidelibus, M. D. (2003). Environmental tracing in coastal aquifers: old problems and new solutions. In Coastal aquifers intrusion technology: Mediterranean countries (Vol. II, pp. 79–111). Madrid: Publ. IGME.
Ged, E. C. (2013). Saltwater intrusion impacts on bromide concentration and disinfection byproduct formation: model evaluation and laboratory scale analysis. Master thesis, University of Florida.
Gerritse, R. G., & George, R. J. (1988). The role of soil organic matter in the geochemical cycling of chloride and bromide. Journal of Hydrology, 101(1-4), 83–95.
Ghiglieri, G., Carletti, A., & Pittalis, D. (2012). Analysis of salinization processes in the coastal carbonate aquifer of Porto Torres (NW Sardinia, Italy). Journal of Hydrology, 432–433, 43–51.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 17, 1088–1090.
Giménez-Forcada, E. (2010). Dynamic of sea water interface using hydro chemical facies evolution diagram. Ground Water, 48(2), 212–216.
Goldberg, S., & Kabengi, N. J. (2010). Bromide adsorption by reference minerals and soils. Vadose Zone Journal, 9, 780–786.
Gurunadha Rao, V. V. S., Tamma Rao, G., Surinaidu, L., Mahesh, J., Mallikharjuna Rao, S. T., & Mangaraja Rao, B. (2013). Assessment of geochemical processes occurring in groundwaters in the coastal alluvial aquifer. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 8259–8272.
Han, D. M., Song, X. F., Currell, M. J., Yang, L., & Xiao, G. Q. (2014). Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. Journal of Hydrology, 508, 12–27.
Harman, H. H. (1960). Modern factor analysis. University of Chicago Press.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34, 807–816.
ISO (International Standards Organisation) (1993). Water quality—sampling—part 11: guidance on sampling of ground waters. ISO 5667-11.
Jones, B. F., Vengosh, A., Rosenthal, E., & Yechieli, Y. (1999). Geochemical investigations. In J. Bear, A. H. D. Cheng, S. Soreq, D. Ouazar, & I. Herrera (Eds.), Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers—concepts, methods and practices, ch. 3 (pp. 51–72). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Jorgensen, N. O., Andersen, M. S., & Engesgaard, P. (2008). Investigation of a dynamic seawater intrusion event using strontium isotopes (87Sr/86Sr). Journal of Hydrology, 348, 257–269.
Kaiser, H. F. (1958). The varimax criteria for analytical rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 23, 187–200.
Kamei, T., Ikeda, J., Ishida, H., Ismda, S., Onishi, I., Partoazar, H., Sasajima, S., & Nishimur, S. (1973). A general report on the geological and paleontological survey in Maragheh Area, North-West Iran. Internal Report, Geological Survey of Iran.
Katz, B. G., Eberts, S. M., & Kauffman, L. J. (2011). Using Cl/Br ratios and other indicators to assess potential impacts on groundwater quality from septic systems: a review and examples from principal aquifers in the United States. Journal of Hydrology, 397, 151–166.
Kim, K. Y., Park, Y. S., Kim, G. P., & Park, K. H. (2009). Dynamic fresh water-saline water interaction in the coastal zone of Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrogeology Journal, 17, 617–629.
Kouzana, L., Ben Mammou, A., & Sfar Felfoul, M. (2009). Seawater intrusion and associated processes: case of the Korba aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 341, 21–35.
Krouse, H. R., & Mayer, B. (2000). Sulphur and oxygen isotopes in sulphate. In P. Cook & A. L. Herczeg (Eds.), Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology (pp. 195–231). Boston: Kluwer Academic.
Langman, J. B., & Ellis, A. S. (2010). A multi-isotope (δD, δ18O, 87Sr/86Sr and δ11B) approach for identifying saltwater intrusion and resolving groundwater evolution along the Western Caprock Escarpment of the Southern High plains, New Mexico. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 159–174.
Lee, J. Y., & Song, S. H. (2007). Evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal areas: implications for sustainable agriculture. Environmental Geology, 52(7), 1231–1242.
Li, J., He, M., Han, W., & Gu, Y. (2009). Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 976–981.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313, 77–89.
Lowers, H. A., Breit, G. N., Foster, A. L., Whitney, J., Yount, J., Uddin, M. N., & Muneem, A. A. (2007). Arsenic incorporation into authigenic pyrite, Bengal Basin sediment, Bangladesh. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71, 2699–717.
Lucas, Y., Schmitt, A. D., Chabaux, F., Clément, A., Fritz, B., Elsass, P., & Durand, S. (2010). Geochemical tracing and hydrogeochemical modelling of water-rock interactions during salinization of alluvial groundwater (Upper Rhine Valley, France). Applied Geochemistry, 25, 1644–1663.
Mandilaras, D., Lambrakis, N., & Stamatis, G. (2008). The role of bromide and iodide ions in the salinization mapping of the aquifer of Glafkos River basin (northwest Achaia, Greece). Hydrological Processes, 22, 611–622.
Manno, E., Vassallo, M., Varrica, D., Dongarrà, G., & Hauser, S. (2006). Hydrogeochemistry and water balance in the coastal wetland area of “Biviere di Gela”, Sicily, Italy. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 178(1-4), 179–193.
Martinez, R., Sánchez-Mata, D., & Costa, M. (1999). Boreal and western temperate forest vegetation (syntaxonomical synopsis of the potential natural plant communities of North America II). Itinera Geobotanica, 12, 3–311.
Matiatos, I., Alexopoulos, A., & Godelitsas, A. (2014). Multivariate statistical analysis of the hydrogeochemical and isotopic composition of the groundwater resources in northeastern Peloponnesus (Greece). Science of the Total Environment, 476–477, 577–590.
McArthur, J. M., Sikdar, P. K., Hoque, M. A., & Ghosal, U. (2012). Waste-water impacts on groundwater: Cl/Br ratios and implications for arsenic pollution of groundwater in the Bengal Basin and Red River Basin, Vietnam. Science of the Total Environment, 437, 390–402.
Melloul, A., & Collin, M. (2006). Hydrogeological changes in coastal aquifers due to sea level rise. Ocean and Coastal Management, 49, 281–297.
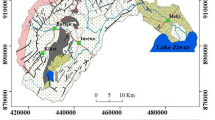
Ministry of Energy (2010). Integrated management plan for Lake Urmia Basin. Internal report, 91pp.
Mollema, P. N., Antonellini, M., Dinelli, E., Gabbianelli, G., Greggio, N., & Stuyfzand, P. J. (2013). Hydrochemical and physical processes influencing salinization and freshening in Mediterranean low-lying coastal environments. Applied Geochemistry, 34, 207–221.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., Puranik, S. C., & Singh, V. P. (2010). Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163(1-4), 215–227.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, S., & Singh, V. S. (2011). Hydrochemical characteristic of coastal aquifer from Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175, 531–550.
Mongelli, G., Monni, S., Oggiano, G., Paternoster, M., & Sinisi, R. (2013). Tracing groundwater salinization processes in coastal aquifers: a hydrogeochemical and isotopic approach in the Na-Cl brackish waters of northwestern Sardinia, Italy. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 17, 2917–2928.
Morell, I., Medina, J., Pulido-Bosch, A., & Fernández-Rubio, R. (1986). The use of bromide and strontium as indicators of marine intrusion in the aquifer of Oropesa-Torreblanca. Castellón. Spain. Proc. 9th. Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Delft, Denmark 61-72.
Morell, I., Pulido-Bosch, A., Sanchez-Martos, F., Vallejos, A., Daniele, L., Calaforra, J. M., Roig, A. F., & Renau, A. (2008). Characterization of the salinisation processes in aquifers using boron isotopes; application to South-Eastern Spain. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 187, 65–80.
Morrow, F. J., Ingham, M. R., & McConchie, J. A. (2010). Monitoring of tidal influences on the saline interface using resistivity traversing and cross-borehole resistivity tomography. Journal of Hydrology, 389, 69–77.
Nakhaei, M., Amiri, V., Rezaei, K., & Moosaei, F. (2015). An investigation of the potential environmental contamination from the leachate of the Rasht waste disposal site in Iran. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 74, 233–246.
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). (2012). Oroomieh climate normals 1961-1990. Retrieved December 27.
Ozler, H. M. (2003). Hydrochemistry and salt-water intrusion in the Van aquifer, East Turkey. Environmental Geology, 43, 759–775.
Panno, S. V., Hackley, K. C., Hwang, H. H., Greenberg, S. E., Krapac, I. G., Landsberger, S., & O’Kelly, D. J. (2006). Characterization and identification of Na-Cl sources in groundwater. Ground Water, 44, 176–187.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2), a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey, Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259.
Petelet-Giraud, E., Négrel, P., Guerrot, C., Aunay, B., & Dörfliger, N. (2013). Origins and processes of salinization of a Plio-Quaternary coastal Mediterranean multilayer aquifer: the Roussillon Basin case study. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 7, 681–684.
Rodellas, V., Garcia-Orellana, J., Garcia-Solsona, E., Masqué, P., Antonio Domínguez, J., Ballesteros, B. J., Mejías, M., & Zarroca, M. (2012). Quantifying groundwater discharge from different sources into a Mediterranean wetland by using 222Rn and Ra isotopes. Journal of Hydrology, 466–467, 11–22.
Russak, A., & Sivan, O. (2010). Hydrogeochemical tool to identify salinization or freshening of coastal aquifers determined from combined field work, experiments, and modeling. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(11), 4096–4102.
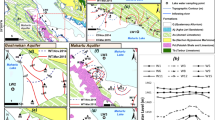
Sartipi, A. H., Haghfarshi, E., Karimi, H., Shiva, E., Seidi Sahbari, P., Vakil Baghmisheh, F., & Zamani mehr, S. (2014). Geological report of the Urmia map (1:25000); 5065 III SW. (In Persian).
Saxena, V. K., Mondal, N. C., & Singh, V. S. (2004). Identification of seawater ingress using Sr and B in Krishna delta. Current Science, 86(4), 586–590.
Sayles, F. L., & Mangelsdorf, P. C., Jr. (1977). The equilibration of clay minerals with sea water: exchange reactions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 951–960.
Schiavo, M. A., Hauser, S., & Povinec, P. P. (2009). Stable isotopes of water as a tool to study groundwater-seawater interactions in coastal south-eastern Sicily. Journal of Hydrology, 364, 40–49.
Schroeder, R. A., & Rivera, M. (1993). Physical, chemical and biological data for detailed study of irrigation drainage in the Salton Sea area, California. US Geological Survey Open-File report 93-83. Menlo Park, CA: US Geological Survey.
Schryer, D. R. (1982). Heterogeneous atmospheric chemistry. American Geophysical Union, 28
Seaman, J. C., Bertsch, P. M., Korom, S. F., & Miller, W. P. (1996). Physicochemical controls on nonconservative anion migration in coarse-textured alluvial sediments. Ground Water, 34(5), 778–783.
Singh, V. S., Sarwade, D. V., Mondal, N. C., Nanadakumar, M. V., & Singh, B. (2009). Evaluation of groundwater resources in a tiny Andrott Island, Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 158(1-4), 145–154.
Skrzypek, G., Dogramaci, S., & Grierson, F. P. (2013). Geochemical and hydrological processes controlling groundwater salinity of a large inland wetland of northwest Australia. Chemical Geology, 357, 164–177.
Terzic’, J., Markovic, T., & Pekas, Z. (2008). Influence of seawater intrusion and agricultural production on the Blato Aquifer, Island of Korčula, Croatia. Environmental Geology, 54, 719–729.
Tomaszkiewicz, M., Abou Najm, M., & El-Fadel, M. (2014). Development of a groundwater quality index for seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Environmental Modelling & Software, 57, 13–26.
Vandenbohede, A., & Lebbe, L. (2012). Groundwater chemistry patterns in the phreatic aquifer of the central Belgian coastal plain. Applied Geochemistry, 27, 22–36.
Vengosh, A. (2014). Salinization and saline environments. Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 11, 325–378.
Ward, J. H., Jr. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58(301), 236–244.
Warner, N. R., Lgourna, Z., Bouchaou, L., Boutalebb, S., Tagmab, T., Hsaissouneb, M., & Vengosha, A. (2013). Integration of geochemical and isotopic tracers for elucidating water sources and salinization of shallow aquifers in the sub-Saharan Drâa Basin, Morocco. Applied Geochemistry, 34, 140–151.
Whittemore, D. O., & Davis, S. N. (1995). Patterns of Cl/Br with Cl concentration in the hydrosphere. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 27(6), 465–466.
Wilson, S. R., Ingham, M., & McConchie, J. A. (2006). The applicability of earth resistivity methods for saline interface definition. Journal of Hydrology, 316, 301–312.
WMO (World Meteorological Organisation). (2014). http://worldweather.wmo.int/en/city.html?cityId=1454
World Health Organization (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. 4th ed. Available:http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/2011/dwq_chapters/en/.
Yechieli, Y., Kafri, U., & Sivan, O. (2009). The inter-relationship between coastal sub-aquifers and the Mediterranean Sea, deduced from radioactive isotopes analysis. Hydrogeology Journal, 17, 265–274.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008). A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Journal of Environmental Management, 86(1), 80–87.
Zghibi, A., Zouhri, L., Tarhouni, J., & Kouzana, L. (2013). Groundwater mineralisation processes in Mediterranean semiarid systems (Cap-Bon, North east of Tunisia): hydrogeological and geochemical approaches. Hydrological Processes, 27(22), 3227–323.
Zhang, X., Qian, H., Chen, J., & Qiao, L. (2014). Assessment of groundwater chemistry and status in a heavily used semi-arid region with multivariate statistical analysis. Water, 6(8), 2212–2232.
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by Geological Survey of Iran (GSI). We thank all members of GSI for their kind cooperation that made this research possible. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. We also like to thank the Prof. Yu-Pin Lin, associate editor of EMAS journal, for his helpful comments and support during the review process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was funded by the Geological Survey of Iran (GSI).
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, V., Nakhaei, M., Lak, R. et al. Investigating the salinization and freshening processes of coastal groundwater resources in Urmia aquifer, NW Iran. Environ Monit Assess 188, 233 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5231-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5231-5