Abstract
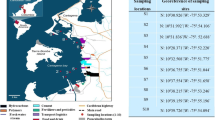
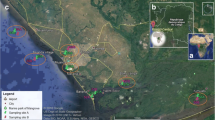
Mercury and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) accumulate in organisms through food webs and exert potentially toxic effects on aquatic organisms and humans. This study examined the levels of mercury and PCDD/Fs in organisms and sediment samples collected from a saltwater pond at the An-Shun site, a chloralkali factory that shut down in Tainan City, Taiwan. It was also a pentachlorophenol production plant. After the factories were shut down in the 1980s, mercury and PCDD/Fs contamination remained, posing severe health hazards. The correlation between PCDD/Fs congener accumulation patterns in distinct fish organs and the sediment was evaluated. Mercury and PCDD/Fs levels in all the fish samples exceeded food safety limits, and the concentrations of mercury and PCDD/Fs in each species were closely correlated (n = 12, Spearman’s rank correlation [R] = 0.811, p < 0.01). The mercury concentrations were positively but non-significantly correlated with the weight (n = 11, R = 0.741, p < 0.01) and length (n = 11, R = 0.618, p < 0.05) of the species. The fish likely accumulated the contaminants through ingestion of other organisms or the sediment. However, after the pollutants entered a fish, they exhibited distinct accumulation patterns because of their differing chemical properties. Specifically, the mercury concentration was correlated with organism weight and length, whereas the PCDD/Fs concentration was associated with organ lipid content. The study results are valuable for assessing the health risks associated with ingesting mercury- and PCFF/F-contaminated seafood from the study site.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alibabić, V., Vahčić, N., & Bajramović, M. (2007). Bioaccumulation of metals in fish of Salmonidae family and the impact on fish meat quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 131(1–3), 349–364.
Alonso, D., Pineda, P., Olivero, J., González, H., & Campos, N. (2000). Mercury levels in muscle of two fish species and sediments from the Cartagena Bay and the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta, Columbia. Environmental Pollution, 109(1), 157–163.
Arnot, J. A., & Gobas, F. A. (2006). A review of bioconcentration factor (BCF) and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) assessments for organic chemicals in aquatic organisms. Environmental Reviews, 14(4), 257–297.
Barron, M. G. (1990). Bioconcentration. Will water-borne organic chemicals accumulate in aquatic animals? Environmental Science & Technology, 24(11), 1612–1618.
Chang, H. J., Wang, S., Li, H. W., Lin, K. H., Chao, C. C., & Lai, Y. C. (2010). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofuran contents in fish and sediment near a pentachlorophenol contaminated site. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 45(8), 923–931.
Chang, H. J., Wang, S., Wang, Y. F., Li, H. W., & Wang, L. C. (2011a). Contributions of dry and wet depositions of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans to a contaminated site resulting from a penetachlorophenol manufacturing process. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175(1–4), 475–485.
Chang, J. W., Chen, H. L., Su, H. J., Liao, P. C., Guo, H. R., & Lee, C. C. (2011b). Simultaneous exposure of non-diabetics to high levels of dioxins and mercury increases their risk of insulin resistance. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185(2), 749–755.
Chang, J. W., Liao, P. C., & Lee, C. C. (2012). Dietary intake of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs from fresh foods around Taiwan. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 20(4), 805–813.
Chen, H. H. (2006). Distribution of mercury in fishes and environmental media of a contaminated site and the influence of biological behavior (Master’s thesis). Taipei, Taiwan: National Taiwan University.
Clarkson, T. W. (1992). Mercury: major issues in environmental health. Environmental Health Perspectives, 100, 31–38.
Connell, D. W. (1990). Bioaccumulation of xenobiotic compounds. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Cook, P. M., Kuehl, D. W., Walker, M. K., & Peterson, R. E. (1991). Bioaccumulation and toxicity of TCDD and related compounds in aquatic ecosystems. In M. J. Gallo, R. J. Scheuplein, & K. A. Van der Heijden (Eds.), Biological basis for risk assessment of dioxins and related compounds, Banbury Report, Volume 35 (pp. 143–165). New York, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Coleman, P. J., Lee, R. G. M., Alcock, R. E., & Jones, K. C. (1997). Observations on PAH, PCB, and PCDD/F trends in UK urban air 1991–1995. Environmental Science and Technology, 31(7), 2120–2124.
Debdas, M. (2011). Health impact of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin: a critical review. Air & Waste Management Association, 48(2), 157–165.
Diliberto, J. J., Burgin, D. E., & Birnbaum, L. S. (1999). Effects of CYP1A2 on disposition of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, 2,3,4,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran, and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl in CYP1A2 knockout and parental (C57BL/6N and 129/Sv) strains of mice. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 159(1), 52–64.
Fiedler, H., Hutzinger, O., & Timms, C. W. (1990). Dioxins: sources of environmental load and human exposure. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 29(3), 157–234.
Franke, C., Studinger, G., Berger, G., Böhling, S., Bruckmann, U., Cohors-Fresenborg, D., & Jöhncke, U. (1994). The assessment of bioaccumulation. Chemosphere, 29(7), 1510–1514.
Fries, G. F., Paustenbach, D. J., Mather, D. B., & Luksemburg, W. J. (1999). A congener specific evaluation of transfer of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans to milk of cows following ingestion of pentachlorophenol-treated wood. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(8), 1165–1170.
Gobas, F. A. P. C., & Morrison, H. A. (2000). Bioconcentration and bio-magnification in the aquatic environment. In R. S. Boethling & M. Mackay (Eds.), Handbook of property estimation methods for chemicals (pp. 189–231). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Guidotti, M., Protano, C., Dominici, C., Chiavarini, S., Cimino, N., & Vitali, M. (2013). Determination of selected polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans in marine sediments by the application of gas-chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 90(5), 525–530.
Goldman, L. R., Harnly, M., Flattery, J., Patterson, D. G., & Needham, L. L. (2000). Serum polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans among people eating contaminated home-produced eggs and beef. Environmental Health Perspectives, 108(1), 13–19.
Hamelink, J. L., Landrum, P. F., Bergman, H. L., & Benson, W. H. (Eds.). (1994). Bioavailability: physical, chemical, and biological interactions. SETAC special publication. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Hornung, H., Krumgalz, B. S., & Cohen, Y. (1984). Mercury pollution in sediments, benthic organisms and inshore fishes of Haifa Bay, Israel. Marine Environmental Research, 12(3), 191–208.
Huang, S. W. (2006). Mercury and selenium concentrations in fishes from the water reservoir of a chlor-alkali plant in Tainan (Master’s thesis). Kaohsiung, Taiwan: National Sun Yat-Sen University.
Huang, S., Chen, C., & Chen, M. (2008). Total and organic Hg in fish from the reservoir of a chlor-alkali plant in Tainan, Taiwan. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 16(2), 75–80.
Johansen, H. R., Alexander, J., Rossland, O. J., Planting, S., Lovik, M., Gaarder, P. I., et al. (1996). PCDDs, PCDFs, and PCBs in human blood in relation to consumption of crabs from a contaminated Fjord area in Norway. Environmental Health Perspectives, 104(7), 756–764.
Kang, Y. S., Yamamuro, M., Masunaga, S., & Nakanishi, J. (2002). Specific biomagnification of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in tufted ducks, common cormorants and their prey from Lake Shinji, Japan. Chemosphere, 46(9–10), 1373–1382.
Kannan, K., Nakata, H., Stafford, R., Masson, G. R., Tanabe, S., & Giesy, J. P. (1998). Bioaccumulation and toxic potential of extremely hydrophobic polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in biota collected at a superfund site contaminated with Aroclor 1268. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(9), 1214–1221.
Kannan, K. (1999). Clam-sediment accumulation factors for polychlorinated biphenyl congeners at a contaminated estuarine marsh. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 68(1–2), 159–167.
Kucuksezgin, F., Uluturhan, E., Kontas, A., & Altay, O. (2002). Trace metal concentrations in edible fishes from Izmir Bay, Eastern Aegean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(8), 827–832.
Kudo, A., Fujikawa, Y., Miyahara, S., Zheng, J., Takigami, H., Sugahara, M., et al. (1998). Lessons from Minamata mercury pollution, Japan—after a continuous 22 years of observation. Water Science and Technology, 38(7), 187–193.
Lee, C. C., Guo, Y. L., Kuei, C. H., Chang, H. Y., Hsu, J. F., Wang, S. T., et al. (2006). Human PCDD/F levels near a pentachlorophenol contamination site in Tainan, Taiwan. Chemosphere, 65(3), 436–448.
Lee, R. G. M., Green, N. J. L., Lohmann, R., & Jones, K. C. (1999). Seasonal, anthropogenic, air mass, and meteorological influences on the atmospheric concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs): evidence for the importance of diffuse combustion sources. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(17), 2864–2871.
Mackay, D., & Fraser, A. (2000). Bioaccumulation of persistent organic chemicals: mechanisms and models Canadian Environmental Modelling Centre, Trent University, Peterborough. Environmental Pollution, 110(3), 375–391.
Malisch, R., & Kotz, A. (2014). Dioxins and PCBs in feed and food—review from European perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 491, 2–10.
Milbrath, M. O., Wenger, Y., Chang, C. W., Emond, C., Garabrant, D., Gillespie, B. W., et al. (2009). Apparent half-lives of dioxins, furans, and polychlorinated biphenyls as a function of age, body fat, smoking status, and breast-feeding. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117(3), 417–425.
Manh, H. D., Kido, T., Tai, P. T., Okamoto, R., Honma, S., Liang, S. X., et al. (2015). Levels of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in breast milk samples from three dioxin-contaminated hotspots of Vietnam. Science of the Total Environment, 511(2015), 416–422.
Myers, A. L., Watson-Leung, T., Jobst, K. J., Shen, L., Besevic, S., Organtini, K., et al. (2014). Complementary nontargeted and targeted mass spectrometry techniques to determine bioaccumulation of halogenated contaminants in freshwater species. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(23), 13844–13854.
Naito, W., Jin, J., Kang, Y. S., Yamamuro, M., Masunaga, S., & Nakanishi, J. (2003). Dynamics of PCDDs/DFs and coplanar-PCBs in an aquatic food chain of Tokyo Bay. Chemosphere, 53(4), 347–362.
Olson, J. R. (1994). Pharmacokinetics of dioxin and related chemicals. In A. Schecter (Ed.), Dioxins and health (pp. 163–197). New York, NY: Plenum Press.
Otter, R. R., Bailey, F. C., Fortner, A. M., & Adams, S. M. (2012). Trophic status and metal bioaccumulation differences in multiple fish species exposed to coal ash-associated metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 85, 30–36.
Pickard, S. W., & Clarke, J. U. (2008). Benthic bioaccumulation and bioavailability of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans from surficial Lake Ontario sediments. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 34(3), 418–433.
Sakurai, T., Kim, J. G., Suzuki, N., Matsuo, T., Li, D. Q., Yao, Y., et al. (2000). Ploychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in sediment, soil, fish, shellfish and crab samples from Tokyo Bay area, Japan. Chemosphere, 40(6), 627–640.
Scoville, S. A., & Lane, O. P. (2013). Cerebellar abnormalities typical of methylmercury poisoning in a fledged saltmarsh sparrow, Ammodramus caudacutus. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 90(5), 616–620.
Sin, D. W. M., Choi, J. Y. Y., & Louie, K. K. (2002). A study of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the atmosphere of Hong Kong. Chemosphere, 47(6), 647–653.
Spacie, A., McCarty, L. S., & Rand, G. M. (1995). Bioaccumulation and bioavailability in multiphase systems. In G. M. Rand (Ed.), Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology: effects, environmental fate, and risk assessment (2nd ed., pp. 493–521). Washington, DC: Taylor and Francis.
Stahl, L. L., Snyder, B. D., Olsen, A. R., & Pitt, J. L. (2009). Contaminants in fish tissue from US lakes and reservoirs: a national probabilistic study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150(1-4), 3–19.
Tillitt, D. E., Ankley, G. T., Giesy, J. P., Ludwig, J. P., Kurita-Matsuba, H., Weseloh, D. V., et al. (1992). Polychlorinated biphenyl residues and egg mortality in double-crested cormorants from Great Lakes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 11(9), 1281–1288.
Turoczy, N. J., Mitchell, B. D., Levings, A. H., & Rajendram, V. S. (2001). Cadmium, copper, mercury, and zinc concentrations in tissues of the King Crab (Pseudocarcinus gigas) from southeast Australian waters. Environment International, 27(4), 327–334.
Tyler, A. O., Millward, G. E., Jones, P. H., & Turner, A. (1994). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in sediments from UK estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 39(1), 1–13.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1994). Tetra-through octa-chlorinated dioxins and furans by isotope dilution HRGC/HRMS, Revision B, Method-1613B.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2000). Exposure and human health reassessment of 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and related compounds National Academy Sciences Review Draft, EPA/600/P-00/001Bb.
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2010). Persistent organic pollutants: a global issue, a global response. Washington DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Van der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13(2), 57–149.
van Ede, K. I., Andersson, P. L., Gaisch, K. P., van den Berg, M., & van Duursen, M. B. (2014). Comparison of intake and systemic relative effect potencies of dioxin-like compounds in female rats after a single oral dose. Archives of Toxicology, 88(3), 637–646.
Wang, I. C., & Lee, W. J. (2010). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, polychlorinated dibenzofurans and polychlorinated biphenyls in farmed fish, water, sediment, and feed. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 45(2), 201–210.
Wang, M. S., Wang, C. L., Chang-Chien, G. P., & Lin, L. F. (2005). Characterization of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the stack flue gas of a municipal solid waste incinerator, in the ambient air, and in the banyan leaf. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 5(2), 171–184.
Xu, W., Yunhe, H., Hung, Y. S., & Yuexian, Z. (2013). A comparative analysis of Spearman’s rho and Kendall’s tau in normal and contaminated normal models. Signal Processing, 93, 261–276.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by China Petrochemical Development Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, PY., Liu, CW. & Liu, WY. Bioaccumulation of mercury and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in salty water organisms. Environ Monit Assess 188, 12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5019-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5019-z