Abstract
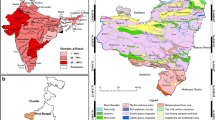
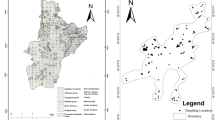
A total of 72 groundwater samples were collected from open wells and boreholes during pre- and post-monsoon periods in Tuticorin. Samples were analyzed for physicochemical properties, major cations, and anions in the laboratory using the standard methods given by the American Public Health Association. The fluoride concentration was analyzed in the laboratory using Metrohm 861 advanced compact ion chromatography. The geographic information system-based spatial distribution map of different major elements has been prepared using ArcGIS 9.3. The fluoride concentration ranges between 0.16 mg/l and 4.8 mg/l during pre-monsoon and 0.2–3.2 mg/l during post-monsoon. Alkaline pH, low calcium concentrations, high groundwater temperatures, and semiarid climatic conditions of the study area may cause elevated fluoride concentrations in groundwater, by increasing the solubility of fluoride-bearing formations (fluoride). Linear trend analysis on seasonal and annual basis clearly depicted that fluoride pollution in the study area is increasing significantly. Fluoride concentrations showed positive correlations with those of Na+ and HCO3 − and negative correlations with Ca2+ and Mg2+. The alkaline waters were saturated with calcite in spite of the low Ca2+ concentrations. Northwestern parts of the study area are inherently enriched with fluorides threatening several ecosystems. The saturation index indicates that dissolution and precipitation contribute fluoride dissolution along with mixing apart from anthropogenic activities.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, V., Vaish, A. K., & Vaish, P. (1997). Groundwater quality: focus on fluoride and fluorosis in Rajasthan. Current Science, 73, 743–746.
Antony Ravindran, A., & Selvam, S. (2014). Coastal disaster damage and neotectonic subsidence study using 2DERI technique in Dhanushkodi, Rameshwaram Island, Tamilnadu, India. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 19(8), 1117–1122.
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). New York: American Public Health Association.
Athavale, R. N., & Das, R. K. (1999). Beware! Fluorosis is zeroing in on you. Down to Earth, 8, 24–25.
Ayazi, M. H., Pirasteh, S., Arvin, A. K. P., Pradhan, B., Nikouravan, B., & Mansor, S. (2010). Disasters and risk reduction in groundwater: Zagros Mountain Southwest Iran using geoinformatics techniques. Disaster Advances, 3(1), 51–57.
Balasubramanaian, A., Thirugnana, R., Chellaswamy, S., & Radhakrishnan, V. R. (1993). Numerical modeling for prediction and control of saltwater enchroment in the coastal aquifers of Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu (21), Tech. Report.
Brindha, K., Rajesh, R., Murugan, R., & Elango, L. (2011). Fluoride contamination in groundwater in parts of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1348-0.
Chadha, D. K., & Tamta, S. R. (1999). Occurrence and origin of groundwater fluoride in phreatic zone of Unnao district, Uttar Pradesh. Journal of Applied Geochemistry, 1, 21–26.
Chae, G. T., Yun, S. T., Mayer, B., Kim, K. H., Kim, S. Y., Kwon, J. S., Kim, K., & Koh, Y. K. (2007). Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. The Science of the Total Environment, 385, 272–283.
Chidambaram, S., Prasanna, M. V., Vasu, K., Shahul Hameed, A., Unnikrishna Warrier, C., & Srinivasamoorthy, K. (2007). Study on the stable isotope signatures in groundwater of Gadilam river basin, Tamilnadu, India. Indian Journal of Geochemistry, 22(2), 209–221.
CPCB. (2008). Guideline for water quality management. Delhi: Central Pollution Control Board.
Dar, M. A., Sankar, K., & Dar, I. A. (2010). Fluorine contamination in ground water: a major challenge. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1–4), 955–968.
Datta, P. S., Tyagi, S. K., Mookerjee, P., Bhattacharya, S. K., Gupta, N., & Bhatnagar, P. D. (1999). Groundwater NO3 and F contamination process in Pushkar valley, Rajasthan as reflected from 18O isotopic signature and 3H recharge studies. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 56, 209–219.
de Souza, C. F., Lima, J. F., Jr., Pereira Franco Adriano, M. S., De Carvalho, F. G., Soares Forte, F. D., Farias Oliveira, R. D., Pessoa Silva, A., & Correia Sampaio, F. (2012). Assessment of groundwater quality in a region of endemic fluorosis in the northeast of Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2900-x.
Deshmukh, A. N., Wadaskar, P. M., & Malpe, D. B. (1995). Fluorine in environment: a review. In A. N. Deshmukh, D. B. Yedekar, & K. K. K. Nair (Eds.), Fluorine in environment. Gondwana Geological Magazine, 9 (pp. 1–20).
Deutsch, W. J. (1997). Groundwater geochemistry: fundamentals and application to contamination. Boca Raton: CRC.
El Afly, M. (2012). Integrated geostatistics and GIS techniques for assessing groundwater contamination in Al Arish area, Sinai, Egypt. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 5(2), 197–215. doi:10.1007/s12517-010- 0153-y.
Farooqi, A., Masuda, H., & Firdous, N. (2007). Toxic fluoride and arsenic contaminated groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur districts, Punjab, Pakistan and possible contaminant sources. Journal of Environment and Pollution, 145, 839–849.
Fejerskov, O., & Kidd, E. (2007). Cárie dentária: A doença e seu tratamento clínico: Santos (p. 352).
Galagan, D. J., & Vermillion, J. R. (1957). Determining optimum fluoride concentrations. Public Health Reports, 72(6), 491–493.
Gilpin, L., & Johnson, A. H. (1980). Fluorine in agricultural soils of Southern Pennsylvania. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44, 255–258.
Handa, B. K. (1975). Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride containing groundwater in India. Groundwater, 13(3), 275–281.
Kim, K., & Jeong, G. Y. (2005). Factors influencing natural occurrence of fluoride-rich groundwaters: a case study in the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula. Chemosphere, 58, 1399–1408. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004. 10.002.
Larsen, S., & Widdowson, A. E. (1971). Soil fluorine. Journal of Soil Science, 22(2), 10–221.
Li, D., Huang, D., Guo, C., & Guo, X. (2014). Multivariate statistical analysis of temporal–spatial variations in water quality of a constructed wetland purification system in a typical park in Beijing, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 4219. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4219-2.
Liu, A., Ming, J., & Ankumah, R. O. (2005). Nitrate contamination in private wells in rural Alabama, United States. The Science of the Total Environment, 346(1–3), 112–120.
Magesh, N. S., & Chandrasekar, N. (2011). Evaluation of spatial variations in groundwater quality by WQI and GIS technique: a case study of Virudunagar District, Tamil Nadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0496-z.
Manap, M. A., Nampak, H., Pradhan, B., Lee, S., Sulaiman, W. N. A., & Ramli, M. F. (2012). Application of probabilistic-based frequency ratio model in groundwater potential mapping using remote sensing data and GIS. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0795-z.
Manap, M. A., Sulaiman, W. N. A., Ramli, M. F., Pradhan, B., & Surip, N. (2013). A knowledge driven GIS modelling technique for prediction of groundwater potential zones at the Upper Langat Basin, Malaysia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(5), 1621–1637. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0469-2.
Mohamed, I., Othman, F., Ibrahim, A. I. N., Alaa-Eldin, M. E., & Yunus, R. M. (2014). Assessment of water quality parameters using multivariate analysis for Klang River basin, Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 4182. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4182-y.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, V. S., & Saxena, V. K. (2010). Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 388(1–2), 100–111.
Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N., & Gibbs, B. F. (2001). Remediation technologies for metal contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Engineering Geology, 60(1–4), 193–200.
Narany, T. S., Ramli, M. F., Aris, A. Z., Sulaiman, W. N. A., & Fakharian, K. (2014). Spatiotemporal variation of groundwater quality using integrated multivariate statistical and geostatistical approaches in Amol–Babol Plain, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(9), 5797–5815.
Neshat, A., Pradhan, B., Pirasteh, S., & Shafri, H. Z. M. (2013). Estimating groundwater vulnerability to pollution using modified DRASTIC model in the Kerman agricultural area, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2690-7.
Omonona, O. V., Onwuka, O. S., & Okogbue, C. O. (2013). Characterization of groundwater quality in three settlement areas of Enugu metropolis, southeastern Nigeria, using multivariate analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(2), 651–664.
Pati, S., Dash, M. K., Mukherjee, C. K., Dash, B., & Pokhrel, S. (2014). Assessment of water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in the coastal region of Visakhapatnam, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(10), 6385–6402.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A geographic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Transactions of the American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Pradhan, B. (2009). Ground water potential zonation for basaltic watersheds using satellite remote sensing data and GIS techniques. Central European Journal of Geosciences, 1(1), 120–129. doi:10.2478/v10085-009-0008-5.
Ramkumar, T., Venkatramanan, S., Anitha Mary, I., Mi, T., & Ramesh, G. (2010). Hydrogeochemical quality of groundwater in Vedaraniyam Town, Tamil Nadu, India. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2(1), 44–48.
Rammohana Rao, N.V. (1982). Geochemical factors influencing the distribution of fluoride in rocks, soils and water resources of Nalgonda District, AP Unpublished Ph.D thesis, Osmania University, Hyderabad.
Rammohana Rao, N. V., Suryaprakasa Rao, K., & Schuiling, R. D. (1993). Fluorine distribution in waters of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 21, 84–89.
Rangarajan, R., Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., & Singh, S. V. (2009). Estimation of natural recharge and its relation with aquifer parameters in and around Tuticorin town, Tamil Nadu India. Current Science, 97(2), 217–226.
Selvam, S. (2012). Use of remote sensing and GIS techniques for land use and land cover mapping of Tuticorin coast, Tamilnadu. Universal Journal of Environmental Research and Technology, 2(4), 233–241.
Selvam, S. (2014). Irrigational feasibility of groundwater and evaluation of hydrochemistry facies in the SIPCOT industrial area, South Tamilnadu, India: a GIS approach. Water Quality, Exposure and Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-014-0146-2.
Selvam, S., & Sivasubramanian, P. (2012). Groundwater potential zone identification using geoelectrical survey: a case study from Medak district, Andhra Pradesh, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 3(1), 55–62.
Selvam, S., Seshunarayana, T., Manimaran, G., Sivasubramanian, P., & Manimaran, D. (2010). Groundwater investigation using geoelectrical survey: a case study from Kanukunta Village, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Outreach, 4, 59–62.
Selvam, S., Iruthaya Jeba Dhana Mala, R., & Muthukakshmi, V. (2013a). A hydrochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality index in Thoothukudi district, Tamilnadu, South India. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Applications, 2(3), 25–37.
Selvam, S., Manimaran, G., & Sivasubramanian, P. (2013b). Hydrochemical characteristics and GIS-based assessment of groundwater quality in the coastal aquifers of Tuticorin Corporation, Tamilnadu, India. Applied Water Science, 3, 145–159.
Selvam, S., Manimaran, G., & Sivasubramanian, P. (2013c). Cumulative effects of septic system disposal and evolution of nitrate contamination impact on coastal groundwater in Tuticorin, South Tamilnadu, India. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Science, 4(4), 1207–1218.
Selvam, S., Manimaran, G., Sivasubramanian, P., Balasubramanian, N., & Seshunarayana, T. (2014a). GIS-based evaluation of water quality Index of groundwater resources around Tuticorin coastal city, South India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71, 2847–2867.
Selvam, S., Antony Ravindaran, A., Rajamanickam, M., & Sridharan, M. (2014b). Microbial contamination in the sediments and groundwater of Tuticorin Corporation, South India using GIS. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(4), 337–340.
Selvam, S., Manimaran, G., Sivasubramanian, P., & Seshunarayana, T. (2014c). Geoenvironmental resource assessment using remote sensing and GIS: a case study from southern coastal region. Research Journal of Recent Sciences, 3(1), 108–115.
Selvam, S., Magesh, N. S., Chidambaram, S., Rajamanickam, M., & Sashikkuma, R. M. C. (2014d). A GIS based identification of groundwater recharge potential zones using RS and IF technique: a case study in Ottapidaram Taluk, Tuticorin District, Tamil Nadu. Environmental Earth Sciences. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3664-0.
Selvam, S., Magesh, N. S., Sivasubramanian, P., Soundranayagam, J. P., Manimaran, G., & Seshunarayana, T. (2014e). Deciphering of groundwater potential zones in Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 84, 597–608.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Nanthakumar, C., & Vasanthavigar, M. (2011). Groundwater quality assessment from a hard rock terrain, Salem district of Tamilnadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 4(1), 91–102.
Subba Rao, N., & Devadas, D. J. (2003). Fluoride incidence in groundwater in an area of Peninsula India. Environmental Geology, 45, 243–251. doi:10.1007/s00254-003-0873-3.
Subyani, A. M. (2010). Identifying the hydrochemical processes of groundwater in Wadi Na’man, western Saudi Arabia using factor analysis. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 5(3), 501–511. doi:10.1007/s12517-010-0207-1.
Susheela, A. K., Bhatnagar, M., Gnanasundaram, N., & Saraswathy, T. R. (1999). Structural aberrations in fluorosed human teeth: biochemical and scanning electron microscopic studies. Current Science, 77, 1677–1681.
WHO. (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol. 1. Recommendations (3rd ed., p. 515). Geneva: WHO.
Wodeyar, B. K., & Sreenivasan, G. (1996). Occurrence of fluoride in the ground waters and its impact in Peddavankahalla basin, Bellary District, Karnataka—a preliminary study. Current Science, 70, 71–73.
Acknowledgments
The author is thankful to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, for awarding INSPIRE Fellowship to carry out this study (Ref. No. DST/INSPIRE FELLOWSHIP/2010/(308), date: 3 August 2010). I am also grateful to Shri A.P.C.V. Chockalingam, Secretary, and Dr. C. Veerabahu, Principal, V.O.C College, Tuticorin, for their support to carry out the study. I am thankful to the anonymous reviewers who have provided their valuable suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvam, S. A preliminary investigation of lithogenic and anthropogenic influence over fluoride ion chemistry in the groundwater of the southern coastal city, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 187, 106 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4326-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4326-8