Abstract
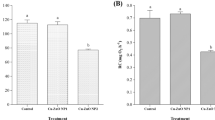
The aim was to investigate the toxicity of selected metal oxide nanoparticles (MO-NPs) on the brine shrimp Artemia salina, by evaluating mortality and behavioural and biochemical responses. Larvae were exposed to tin(IV) oxide (stannic oxide (SnO2)), cerium(IV) oxide (CeO2) and iron(II, III) oxide (Fe3O4) NPs for 48 h in seawater, with MO-NP suspensions from 0.01 to 1.0 mg/mL. Mortality and behavioural responses (swimming speed alteration) and enzymatic activities of cholinesterase, glutathione-S-transferase and catalase were evaluated. Although the MO-NPs did not induce any mortality of the larvae, they caused changes in behavioural and biochemical responses. Swimming speed significantly decreased in larvae exposed to CeO2 NPs. Cholinesterase and glutathione-S-transferase activities were significantly inhibited in larvae exposed to SnO2 NPs, whereas cholinesterase activity significantly increased after CeO2 NP and Fe3O4 NP exposure. Catalase activity significantly increased in larvae exposed to Fe3O4 NPs. In conclusion, swimming alteration and cholinesterase activity represent valid endpoints for MO-NP exposure, while glutathione-S-transferase and catalase activities appear to be NP-specific.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi, H. (1984). Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology, 105, 121–126.
Alyuruk, H., Demir, G. K., & Cavas, L. (2013). A video tracking based improvement of acute toxicity test on Artemia salina. Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology. doi:10.1080/10236244.2013.814224.
Amiard-Triquet, C. (2009). Behavioral disturbances: the missing link between sub-organismal and supra-organismal responses to stress? Prospects based on aquatic research. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 15, 87–110.
Ates, M., Daniels, J., Arslan, Z., & Farah, O. I. (2013a). Effects of aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on Artemia salina: assessment of nanoparticle aggregation, accumulation, and toxicity. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 3339–3348.
Ates, M., Daniels, J., Arslan, Z., Farah, O. I., & Rivera, H. F. (2013b). Comparative evaluation of impact of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles on brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae: effects of particle size and solubility on toxicity. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 15, 225.
Barahona, M. V., & Sanchez-Fortun, S. (1999). Toxicity of carbamates to the brine shrimp Artemia salina and the effect of atropine, BW284c51, iso-OMPA and 2-PAM on carbaryl toxicity. Environmental Pollution, 104, 469–476.
Barsan, N., Schweizer-Berberich, M., & Gopel, W. (1999). Fundamental and practical aspects in the design of nanoscaled SnO2 gas sensors: a status report, Fresenius. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 365, 287–304.
Baun, A., Hartmann, N. B., Grieger, K., & Kusk, K. O. (2008). Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: a brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology, 17, 387–395.
Buffet, P. E., Tankoua, O. F., Pan, J.-F., Berhanu, D., Herrenknecht, C., Poirier, L., et al. (2011). Behavioural and biochemical responses of two marine invertebrates Scrobicularia plana and Hediste diversicolor to copper oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere, 84, 166–174.
Buzea, C., Blandino, P., & Robb, K. (2007). Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: sources and toxicity. Biointerphases, 2, MR17–MR172.
Canesi, L., Fabbri, R., Gallo, G., Vallotto, D., Marcomini, A., & Pojana, G. (2010a). Biomarkers in Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to suspension of selected nanoparticles (nanocarbon black, C60 fullerene, nano-TiO2, nano-SiO2). Aquatic Toxicology, 100, 168–177.
Canesi, L., Ciacci, C., Vallotto, D., Gallo, G., Marcomini, A., & Pojana, G. (2010b). In-vitro effects of suspensions of selected nanoparticles (C60 fullerene, TiO2, SiO2) on Mytilus hemocytes. Aquatic Toxicology, 96, 151–158.
Cornejo-Garrido, H., Kibanova, D., Nieto-Camacho, A., Guzmàn, J., Ramirez-Apan, T., Fernandez-Lomelin, P., et al. (2011). Oxidative stress, cytotoxicity, and cell mortality induced by nano-sized lead in aqueous suspensions. Chemosphere, 84, 1329–1335.
Cornelis, G., Ryan, B., McLaughlin, M. J., Kirbi, J. K., Beak, D., & Chittleborough, D. (2011). Solubility and batch retention of CeO2 nanoparticles in soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 2777–2782.
D’Agata, A., Fasulo, S., Dallas, L. J., Fisher, A. S., Maisano, M., Readman, J. W., et al. (2013). Enhanced toxicity of “bulk” titanium dioxide compared to “fresh” and “aged” nano-TiO2 in marine mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Nanotoxicology, 8, 549–558.
de Oliveira, P., Gomes, A. Q., Pacheco, T. R., de Almeida, V. V., Saldanha, C., & Calado, A. (2012). Cell-specific regulation of cholinesterase expression under inflammatory conditions. Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation, 51, 129–137.
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andres, V., & Featherstone, R. M. (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of cholinesterase activity. Biochemical Pharmacology, 7, 88–95.
EPA (2002). Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. 5th ed. http://water.epa.gov/scitech/methods/cwa/wet/disk2_index.cfm. Accessed October 2002.
Falugi, C., Rakonczay, Z., Thielecke, H., Guida, C., Aluigi, M.G. (2011). Cholinergic pesticides. In: Pesticides—the impacts of pesticides exposure, Agricultural and Biological Sciences. Ed. Stoytcheva M, ISBN: 978-953-307-531-0, Chapter 11: 221-242.
Falugi, C., Aluigi, M. G., Chiantore, M. C., Privitera, D., Ramoino, P., Gatti, M. A., et al. (2012). Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in immune cells of the sea urchin. Marine Environmental Research, 76, 114–121.
Falugi, C., & Aluigi, M. G. (2012). Early appearance and possible functions of non-neuromuscular cholinesterase activities. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 5, 54.
Gaiser, B. K., Biswas, A., Rosenkaranz, P., Jepson, M. A., Lead, J., Stone, V., et al. (2011). Effects of silver and cerium dioxide micro- and nano-sized particles on Daphnia magna. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 13, 1227.
Galloway, T., Lewis, C., Dolciotti, I., Johnston, B. D., Moger, J., & Regoli, F. (2010). Sublethal toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide and carbon nanotubes in a sediment dwelling marine polychaete. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1748–1755.
Gambardella, C., Aluigi, M. G., Ferrando, S., Gallus, L., Ramoino, P., Gatti, A. M., et al. (2013). Developmental abnormalities and changes in cholinesterase activity in sea urchin embryos and larvae from sperm exposed to engineered nanoparticles. Aquatic Toxicology, 130(131), 77–85.
Gambardella, C., Gallus, L., Gatti, M., Faimali, M., Carbone, S., Antisari Vittori, L., Falugi, C., Ferrando, S. (2014). Toxicity and transfer of metal oxide nanoparticles from microalgae to sea urchin larvae. Chemistry and Ecology. doi:10.1080/02757540.2013.873031.
Garaventa, F., Gambardella, C., Di Fino, A., Pittore, M., & Faimali, M. (2010). Swimming speed alteration of Artemia sp. and Brachionus plicatilis as a sub-lethal behavioural end-point for ecotoxicological surveys. Ecotoxicology, 19, 512–519.
Habig, W. H., Pabst, M. J., & Jakoby, W. B. (1974). Glutathione S-transferase, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 249, 7130–7139.
Halliwell, B., & Gutteridge, J. M. C. (1999). Free radicals in biology and medicine. New York: Oxford University Press.
Hui, C., Shen, C., Yang, T., Bao, L., Tian, J., Ding, H., et al. (2008). Large-scale Fe3O4 nanoparticles soluble in water synthesized by a facile method. Journal of Physiology and Chemistry Part C, 12, 11336–11339.
Hund-Rinke, K., & Simon, M. (2006). Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 13, 225–232.
Idota, Y., Kubota, T., Matsufuji, A., Maekawa, Y., & Miyasaka, T. (1997). Tin-based amorphous oxide: a high-capacity lithium-ion-storage material. Science, 276, 1395–1397.
Jamnik, P., & Raspor, P. (2003). Stress response of yeast Candida intermedia to Cr(VI). Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 17, 316–323.
Jemec, A., Tišler, T., Drobne, D., Sepčić, K., Fournier, D., & Trebše, P. (2007). Comparative toxicity of imidacloprid, of its commercial liquid formulation and of diazinon to a non-target arthropod, the microcrustacean Daphnia magna. Chemosphere, 68, 1408–1418.
Jemec, A., Drobne, D., Remškar, M., Sepčić, K., & Tišler, T. (2008a). Effects of ingested nano-sized titanium dioxide on terrestrial isopods (Porcellio scaber). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 9, 1904–1914.
Jemec, A., Tišler, T., Drobne, D., Sepčić, K., Jamnik, P., & Roš, M. (2008b). Biochemical biomarkers in chronically metal-stressed daphnids. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C, 147, 61–68.
Klaine, S. J., Alvarez, P. J. J., Batley, G. E., Fernandes, T. F., Handy, R. D., Lyon, D. Y., et al. (2008). Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 1825–1851.
Koehler, A., Marx, U., Broeg, K., Bahns, S., & Bressling, J. (2008). Effects of nanoparticles in Mytilus edulis gills and hepatopancreas—a new threat to marine life? Marine Environmental Research, 66, 12–14.
Kokkali, V., Katramados, I., & Newman, J. D. (2011). Monitoring the effect of metal ions on the mobility of Artemia salina nauplii. Biosensors, 1, 45.
Koutsaftis, A., & Aoyama, I. (2007). Toxicity of four antifouling biocides and their mixtures on the brine shrimp Artemia salina. Science of the Total Environment, 387, 166–174.
Little, E. E., & Finger, S. E. (1990). Swimming behaviour as an indicator of sublethal toxicity in fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 9, 13–19.
Little, E. E., Archeski, R. D., Flerov, B. A., & Kozlovskaya, V. I. (1990). Behavioral indicators of sublethal toxicity in rainbow trout. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 19, 380–385.
Mancini, I., Sicurelli, A., Guella, G., Turk, T., Maček, M., & Sepčić, K. (2004). Synthesis and bioactivity of linear oligomers related to polymeric alkylpyridinium metabolites from the Mediterranean sponge Reniera sarai. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 2, 1368–1375.
Montes, M. O., Hanna, S. K., Lenihan, H. S., & Keller, A. A. (2012). Uptake, accumulation and biotransformation of metal oxide nanoparticles by a marine suspension-feeder. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 225–226, 139–145.
Nunes, B. S., Carvalho, F. D., Guilhermino, L. M., & Van Stappenn, G. (2006). Use of the genus Artemia in ecotoxicity testing. Environmental Pollution, 144, 453–462.
Peng, X., Palma, S., Fisher, N. S., & Wong, S. S. (2011). Effect of morphology of ZnO nanostructures on their toxicity to marine algae. Aquatic Toxicology, 102, 186–198.
Persoone, G., & Wells, P. G. (1987). Artemia in aquatic toxicology: a review. In P. Sorgeloos, D. A. Bengtson, W. Decleir, & F. Jasper (Eds.), Artemia research and its application (Morphology, genetics, strain characterization, Vol. 1, pp. 259–275). Wetteren: Toxicology. Universa Press.
Radhika Rajasree, S. R., Ganesh Vumar, V., Stanley Abraham, L., & Indabakandan, D. (2010). Studies on the toxicological effects of engineered nanoparticles in environment—a review. International Journal of Applied Bioengineering, 4, 2.
Scott, G. R., & Sloman, K. A. (2004). The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquatic Toxicology, 68, 369–392.
Sorgeloos, P., Van Der Wielen, R., & Persoone, G. (1978). The use of Artemia nauplii for toxicity tests—a critical analysis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2, 249–255.
Taylor, P., & Brown, J. H. (1999). Acetylcholine. In G. J. Siegel, B. W. Agranoff, R. W. Albers, S. K. Fisher, & M. D. Uhler (Eds.), Basic neurochemistry: molecular, cellular, and medical aspects (pp. 213–242). Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven.
Tso, C., Zhung, C., Shih, Y., Tseng, Y. M., Wu, S., & Doong, R. (2010). Stability of metal oxide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Water Science and Technology, 61, 127–133.
Varò, I., Navarro, J. C., Amat, F., & Guilhermino, L. (2002). Characterisation of cholinesterases and evaluation of the inhibitory potential of chlorpyrifos and dichlorvos to Artemia salina and Artemia parthenogenetica. Chemosphere, 48, 563–569.
Venkateswara Rao, J., Kavitha, P., Jakka, N. M., Sridhar, V., & Usman, P. K. (2007). Toxicity of organoposphates on morphology and locomotor behavior in brine shrimp, Artemia salina. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 53, 227–232.
Wang, Z., Zhao, J., Li, F., Gao, D., & Xing, B. (2009). Absorption and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by different nanoparticles. Chemosphere, 77, 67–73.
Xia, J., Fu, S., Cao, Z., Peng, J., Peng, J., Dai, T., et al. (2013). Ecotoxicological effects of waterborne PFOS exposure on swimming performance and energy expenditure in juvenile goldfish (Carassius auratus). Journal of Environmental Science, 25, 1672–1679.
Yin, Z., Ivanov, V. N., Habelhah, H., Tew, K., & Ronai, Z. (2000). Glutathione S-transferase elicits protection against H2O2-induced cell death via coordinated regulation of stress kinases. Cancer Research, 60, 4053–4057.
Zhang, X. J., Yang, L., Zhao, Q., Caen, J. P., He, H. Y., Jin, Q. H., et al. (2002). Induction of acetyl-cholinesterase expression during apoptosis in various cell types. Cell Death and Differentiation, 9, 790–800.
Zhu, B. K., Wang, P., Zhang, X. D., Jiang, C. C., Li, H., Avery-Kiejda, K. A., et al. (2008). Activation of Jun N-terminal kinase is a mediator of vincristine-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 19, 189–200.
Acknowledgments
Chiara Gambardella would like to thank Prof Carla Falugi for her kind suggestions, and POSDRU/89/1.5/S/63663-Sectorial Operational Programme for Human Resources Development through the project “Transnational network for integrated management of postdoctoral research in Science Communication. Institutional framing (postdoctoral school) and scholarship programme (CommScie).” The Slovenian authors gratefully acknowledge the Slovenian Research Agency, and Tina Mesarič acknowledges the Slovene Human Resources Development and Scholarship Fund for financial support. The experiments comply with the current European laws of bioethics. Dr. Christopher Berrie is acknowledged for editing and appraisal of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 501 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gambardella, C., Mesarič, T., Milivojević, T. et al. Effects of selected metal oxide nanoparticles on Artemia salina larvae: evaluation of mortality and behavioural and biochemical responses. Environ Monit Assess 186, 4249–4259 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3695-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3695-8