Abstract
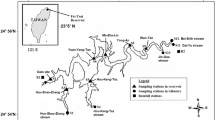
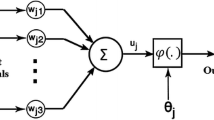
The water quality of reservoirs is one of the key factors in the operation and water quality management of reservoirs. Dissolved oxygen (DO) in water column is essential for microorganisms and a significant indicator of the state of aquatic ecosystems. In this study, two artificial neural network (ANN) models including back propagation neural network (BPNN) and adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approaches and multilinear regression (MLR) model were developed to estimate the DO concentration in the Feitsui Reservoir of northern Taiwan. The input variables of the neural network are determined as water temperature, pH, conductivity, turbidity, suspended solids, total hardness, total alkalinity, and ammonium nitrogen. The performance of the ANN models and MLR model was assessed through the mean absolute error, root mean square error, and correlation coefficient computed from the measured and model-simulated DO values. The results reveal that ANN estimation performances were superior to those of MLR. Comparing to the BPNN and ANFIS models through the performance criteria, the ANFIS model is better than the BPNN model for predicting the DO values. Study results show that the neural network particularly using ANFIS model is able to predict the DO concentrations with reasonable accuracy, suggesting that the neural network is a valuable tool for reservoir management in Taiwan.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkoyunlu, A., Altun, H., & Cigizoglu, H. K. (2011). Depth-integrated estimation of dissolved oxygen in a lake. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 137(10), 961–967.
Boano, F., Revelli, R., & Ridolfi, L. (2006). Stochastic modelling of DO and BOD components in a stream with random inputs. Advances in Water Resources, 29(9), 1341–1350.
Bonnet, M. P., & Poulin, M. (2004). DyLEM-1D: a 1D physical and biochemical for plankton succession, nutrients and dissolved oxygen cycling application to hyper-eutrophic reservoir. Ecological Modelling, 180(2–3), 317–344.
Chaves, P., & Kojiri, T. (2007). Conceptual fuzzy neural network model for water quality simulation. Hydrological Processes, 21(5), 634–646.
Chen, Y. J., & Wu, S. C. (2006). Behavior of storm-induced suspension interflow in subtropical Feitsui Reservoir, Taiwan. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(2), 1125–1133.
Cho, K. H., Park, Y., Kang, J. H., Ki, S. J., Cha, S., Lee, S. W., & Kim, J. H. (2009). Interpretation of seasonal water quality variation in the Yeongsan Reservoir, Korea using multivariate statistical analysis. Water Science and Technology, 59(11), 2219–2226.
Chou, W. S., Lee, T. C., Lin, J. Y., & Yu, S. L. (2007). Phosphorus load reduction goals for Feitsui Reservoir watershed, Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 131(1–3), 385–408.
Curi, W. F., Unny, T. E., & Kay, J. J. (1995). A stochastic physical system approach to modeling river water quality. Stochastic Hydrology and Hydraulics, 9(2), 117–132.
Fletcher, R., & Powell, M. J. D. (1963). A rapid convergent descent method for minimization. The Computer Journal, 6(2), 163–168.
Gardner, M. W., & Dorling, S. R. (1998). Artificial neural network (the multilayer perceptron)—a review of application in atmospheric sciences. Atmospheric Environment, 32(14–15), 2626–2636.
Jang, J. S. R. (1992). Self-learning fuzzy controllers based on temporal back propagation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 3(5), 714–723.
Jang, J. S. R. (1993). ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, Cybernetics, 23(3), 665–685.
Karakaya, N., Evrendilek, F., & Gungor, K. (2011). Modeling and validating long-term dynamics of diel dissolved oxygen with particular reference to pH in a temperate shallow lake (Turkey). Clean-Soil, Air, Water, 39(11), 966–971.
Keskin, M. E., Taylan, D., & Terzi, O. (2006). Adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach for modelling hydrological time series. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 51(4), 588–598.
Kuo, J. T., Liu, W. C., Lin, R. T., Lung, W. S., Yang, M. D., Yang, C. P., & Chu, S. C. (2003). Water quality modeling for the Feitsui Reservoir in northern Taiwan. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 39(4), 671–687.
Kuo, J. T., Hsieh, M. H., Lung, W. S., & She, N. (2007). Using artificial network for reservoir eutrophication prediction. Ecological Modelling, 200(1–2), 171–177.
Lindim, C., Pinho, J. L., & Vieira, J. M. P. (2011). Analysis of spatial and temporal patterns in a large reservoir using water quality and hydrodynamic modeling. Ecological Modelling, 222(14), 2485–2494.
Liu, W. C., Chen, W. B., & Nobuaki, K. (2009). Impact of phosphorus load reduction on water quality in a stratified reservoir-eutrophication modeling study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 159(1–4), 393–406.
Najah, A., El-Shafie, A., Karim, O. A., Jaafar, O., & El-Shafie, A. H. (2011). An application of different artificial intelligences techniques for water quality prediction. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 6(22), 5298–5308.
Najah, A., El-Shafie, A., Karim, O. A., & Jaafar, O. (2012). Water quality prediction model utilizing integrated wavelet-ANFIS model with cross-validation. Neural Computing and Applications, 21(5), 833–841.
Nayak, P. C., Sudheer, K. P., Ragan, D. M., & Ramasastri, K. S. (2004). A neuro fuzzy computing technique for modeling hydrological time series. Journal of Hydrology, 291(1–20), 52–66.
Nourani, V., & Komasi, M. (2013). A geomorphology-based ANFIS model for multi-station modeling of rainfall-runoff process. Journal of Hydrology, 490, 41–55.
Palani, S., Liong, S. Y., & Tkalich, P. (2008). An ANN application for water quality forecasting. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(9), 1586–1597.
Rankovic, V., Radulovic, J., Radojevic, I., Ostojic, A., & Comic, L. (2012). Prediction of dissolved oxygen in reservoirs using adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 14(1), 167–179.
Rezaeianzadeh, M., Tabari, H., & Yazdi, A. A. (2013). Flood flow forecasting using ANN, ANFIS and regression models. Neural Computing and Applications. doi:10.1007/s00521-013-1443-6.
Rucinski, D. K., Beletsky, D., DePinto, J. V., Schwab, D. J., & Scavia, D. (2010). A simple 1-dimensional, climate based dissolved model to central basin of Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 36(3), 465–476.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., & Williams, R. J. (1986). Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 323, 533–536.
Sengorur, B., Dogan, E., Koklu, R., & Samamdar, A. (2006). Dissolved oxygen estimation using artificial neural network for water quality control. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 15(9), 1064–1067.
Singh, K. P., Basant, A., Malik, A., & Jain, G. (2009). Artificial neural network modeling of the river water quality—a case study. Ecological Modelling, 220(6), 888–895.
Soltani, F., Kerachian, R., & Shirangi, E. (2010). Developing operating rules for reservoirs considering the water quality issues: application of ANFIS-based surrogate models. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(9), 6639–6645.
Soyupak, S., Karaer, F., Gurbuz, H., Kivrak, E., Senturk, E., & Yazici, A. (2003). A neural network-based approach for calculating dissolved oxygen profiles in reservoirs. Neural Computing & Applications, 12(3–4), 166–172.
Stansbury, J., Kozimor, L., Admiraal, D., & Dove, E. (2008). Water quality modeling of the effects of macrophytes on dissolved oxygen in a shallow tailwater reservoir. Lake and Reservoir Management, 24(4), 339–348.
Takagi, T., & Sugeno, M. (1985). Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, Cybernetics, 15(1), 116–132.
Talei, A., Chua, L. H. C., & Wong, T. S. W. (2010). Evaluation of rainfall and discharge inputs used by adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) in rainfall-runoff modeling. Journal of Hydrology, 319(3–4), 248–262.
TWMC (Taipei Water Management Committee). (2003). A report of implementation efficiency on protecting water quality/quantity for Taipei Water Source Domain. Taipei: MOEA (in Chinese).
Wen, X., Fang, J., Diao, M., & Zhang, C. (2013). Artificial neural network modeling of dissolved oxygen in the Heihe River, Northwestern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(5), 4361–4371.
White, J. D., Prochnow, S. J., Filstrup, C. T., Scott, J. T., Byars, B. W., & Zygo-Flynn, L. (2010). A combined watershed-water quality modeling analysis of the Lake Waco reservoir: I. Calibration and confirmation of predicted water quality. Lake and Reservoir Management, 26(2), 147–158.
Yao, J. Y., Xiao, P., Zhang, Y. H., Zhan, M., & Cheng, J. W. (2011). A mathematical model of algal blooms based on the characteristics of complex networks theory. Ecological Modelling, 222(20–22), 3727–3733.
Ying, Z., Jun, N., Fuvi, C., & Liang, G. (2007). Water quality forecast through application of BP neural network at Yuqiao reservoir. Journal Zhejiang University-Science A, 8(9), 1482–1487.
Acknowledgments
The project under which this study was conducted is supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan, under grant no. NSC 100-2625-M-239-001. The authors would like to express their appreciation to the Feitsui Reservoir Administration Bureau for providing the observational data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WB., Liu, WC. Artificial neural network modeling of dissolved oxygen in reservoir. Environ Monit Assess 186, 1203–1217 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3450-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3450-6