Abstract
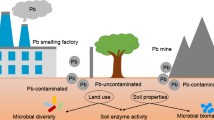
In the process of mining activity, many kinds of heavy metals enter into soils with dust, causing serious contamination to the environment. In this study, six soils were sampled from cropland at different distances from a lead/zinc mine in Heilongjiang Province, China. The total contents of lead and zinc in the vicinal cropland exceeded the third level of environmental quality standard for soil in China, which indicated that soils in this area were moderately contaminated. Bacterial community diversity and population were greatly decreased when the concentrations of lead and zinc were beyond 1,500 and 995 mg kg − 1, respectively, as analyzed by plate counting and polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE). The bands of DGGE patterns varied with the degree of contamination. The activities of soil urease, phosphatase, and dehydrogenase were negatively correlated with the concentrations of lead and zinc. The highest inhibitory effect of heavy metals on soil enzyme activities was observed in urease. It was noted that PCR-DGGE patterns combined with soil enzyme activity analysis can be indices for the soil quality assessment by heavy metal contamination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador, J. A., Glucksman, A. M., Lyons, J. B., & Gorres, J. H. (1997). Spatial distribution of soil phosphatase activity within a riparian forest. Soil Science, 162, 808–825.
Badiane, N. N. Y., Chotte, J. L., Pate, E., et al. (2001). Use of soil enzyme activities to monitor soil quality in natural and improved fallows in semi-arid tropical regions. Applied Soil Ecology, 18, 229–238.
Belyaeva, O. N., Haynes, R. J., & Birukova, O. A. (2005). Barley yield and soil microbial and enzyme activities as affected by contamination of two soils with lead, zinc or copper. Biology and Fertility of Soil, 41, 85–94.
Bi, X. Y., Feng, X. B., Yang, Y. G., et al. (2006). Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou, China. Environment International, 32, 883–890.
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, R. L. (1978). Urease activity in soils. In R. G. Burns (Ed.), Soil enzymes (pp. 149–196). New York: Academic.
Brooks, P. C., McGrath, S. P., Klein, D. A., & Elliot, E. T. (1984). Effects of heavy metals on microbial activity and biomass in field soils treated with sewage sludge (pp. 574–585). Environmental Contamination, CEP, Edinburgh.
Cai, X. D., Qiu, R. L., Chen, G. Z., Zeng, X. W., & Fang, X. H. (2007). Response of microbial communities to phytoremediation of nickel contaminated soils. Frontiers of Agriculture in China, 1(3), 289–295.
Desai, C., Parikh, R. Y., Vaishnav, T., Shouche, Y. S., & Madamwar, D. (2009). Tracking the influence of long-term chromium pollution on soil bacterial community structures by comparative analyses of 16S rRNA gene phylotypes. Research in Microbiology, 160, 1–9.
Dick, R. P., Breakwell, D. P., & Turco, R. F. (1996). Soil enzyme activities and biodiversity measurements and integrative microbial indicators. Methods of Assessing Soil Quality, 49, 247–271.
Doelman, P., Jansen, E., Michels, M., & Van Til, M. (1994). Effects of heavy metals in soil on microbial diversity and activity as shown by the sensitivity-resistance index, an ecologically relevant parameter. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 17, 177–184.
Ellis, J. R., Morgan, P., Weightman, J. A., & Fry, C. J. (2003). Cultivation-dependent and -independent approaches for determining bacterial diversity in heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 3223–3230.
Feris, K. P., Ramsey, P. W., Rillig, M., Moore, J. N., Gannon, J. E., & Holben, W. E. (2004). Determining rates of change and evaluating group-level resiliency differences in hyporheic microbial communities in response to fluvial heavy-metal deposition. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 4756–4765.
Garcia, C., Hernandez, T., & Costa, F. (1997). Potential use of dehydrogenase activity as an index of microbial activity in degraded soils. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 28, 123–134.
Giller, K., Witter, E., & McGrath, S. (1998). Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30, 1398–1414.
Gülser, F., & Erdoǧan, E. (2008). The effects of heavy metal pollution on enzyme activities and basal soil respiration of roadside soils. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 145, 127–133.
Heuer, H., Krsek, M., Baker, P., Smalla, K. W., & Elizabeth, M. H. (1997). Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63(8), 3233–3241.
Hinojosa, M. B., Carreira, J. A., García-Ruíz, R., & Dick, R. P. (2004). Soil moisture pre-treatment effects on enzyme activities as indicators of heavy metal- contaminated and reclaimed soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 1559–1568.
Hu, Q., Qi, H. Y., Zeng, J. H., & Zhang, H. X. (2007). Bacterial diversity in soils around a lead and zinc mine. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 74–79.
Joynt, J., Bischoff, M., Turco, R., Konopka, A., & Nakatsu, CH. (2006). Microbial community analysis of soils contaminated with lead, chromium and petroleum hydrocarbons. Microbiology Ecology, 51(2), 209–219.
Kandeler, E., Kampicher, C., & Horak, O. (1996). Influence of heavy metals on the functional diversity of soil microbial communities. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 23, 299–306.
Kandeler, E., Tscherko, D., Bruce, K. D., Stemmer, M., Hobbs, P. J., Bardgett, R. D., et al. (2000). Structure and function of the soil microbial community in microhabitats of a heavy metal polluted soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 32, 390–400.
Kannan, K., & Oblisami, G. (1990). Influence of paper mill effluent irrigation on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 22, 923–926.
Kelly, J. J., Haggblom, M., & Tate, R. L. (2003). Effects of heavy metal contamination and remediation on soil microbial communities in the vicinity of a zinc smelter as indicated by analysis of microbial community phospholipid fatty acid profiles. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 38, 65–71.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Hesham, A. E. -L., Xia, Y., & He, J. Z. (2007). Soil enzymatic activities and microbial community structure with different application rates of Cd and Pb. Journal of Environment Sciences, 19, 834–840.
Kim, K.-R., Owens, G., & Naidu, R. (2009). Heavy metal distribution, bioaccessibility, and phytoavailability in long-term contaminated soils from Lake Macquarie, Australia. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 47(2), 166–176.
Kizilkaya, R. (2004). Cu and Zn accumulation in earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. in sewage sludge amended soil and fractions of Cu and Zn in casts and surrounding soil. Ecological Engineering, 22, 141–151.
Landmeyer, J. E., Bradley, P. M., & Chapelle, F. H. (1993). Influence of Pb on microbial activity in Pb-contaminated soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25, 1465–1466.
Leita, L., De, N. M., Mühlbachová, G., Mondini, C., Marchiol, L., & Zerbi, G. (1995). Bioavailability and effects of heavy metals on soil microbial biomass survival during laboratory incubation. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 19, 103–108.
Li, Z. J., Xu, J. M., Tang, C. X., Wu, J. J., Muhammad, A., & Wang, H. Z. (2006). Application of 16SrDNA-PCR amplification and DGGE fingerprinting for detection of shift in microbial community diversity in Cu-, Zu-, and Cd-contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere, 62, 1374–1380.
Liao, G. L., Liao, D. X., & Li, Q. M. (2008). Heavy metals contamination characteristics in soil of different mining activity zones. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 18, 207–211.
Liu, H. Y., Probst, A., & Liao, B. H. (2005). Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Science of the Total Environment, 339, 153–166.
Margesin, R., Zimmerbauer, A., & Schinner, F. (2000). Monitoring of bioremediation by soil biological activities. Chemosphere, 40, 339–346.
McLaughlin, M. J., Tiller, K. G., Naidu, R., & Stevens, D. P. (1996). Review: The behaviour and environmental impact of contaminants in fertilisers. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 34, 1–54.
Mette, H. N., & Neils, B. R. (2002). Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) approaches to study the diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Journal of Microbiology Methods, 50, 189–203.
Mijangos, I., P’erez, R., Albizu, I., & Garbisu, C. (2006). Effects of fertilization and tillage on soil biological parameters. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 100–106.
Moffett, B. F., Nicholson, F. A., Uwakwe, N. C., Chambers, B. J., Harris, J. A., & Hill, T. C. J. (2003). Zinc contamination decreases the bacterial diversity of agricultural soil. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 43, 13–19.
Nannipieri, P., Ascher, J., Ceccherini, M. T., Landi, L., Pietramellara, G., & Renella, G. (2003). Microbial diversity and soil functions. European Journal of Soil Science, 54, 655–670.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1982). Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In A. L. Page, et al. (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis (part 2, pp. 539–579) Agron. Monogr.
Ovreas, L., Forney, L., Daae, F. L., & Torsvik, V. (1997). Distribution of bacterioplankton in meromictic Lake Saelenvannet, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 3367–3373.
Quilchano, C., & Maranon, T. (2002). Dehydrogenase activity in Mediterranean forest soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 35, 102–107.
Reddy, G. B., Faza, A., & Bennett, R. (1987). Activity of enzymes in rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere soil amend with sludge. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 19, 203–205.
Renella, G., Mench, M., Landi, L., & Nannipieri, P. (2005). Microbial diversity and hydrolase synthesis in long-term Cd-contaminated soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37, 133–139.
Rodriguez, B. B., Bolbot, J. A., & Tothill, I. E. (2004). Development of urease and glutamic dehydrogenase amperometric assay for heavy metals screening in polluted samples. Biosens Bioelectron, 19(10), 1157–1167.
Sandaa, R., Torsvik, V., & Enger, O. (2001). Influence of long term heavy-metal contamination on microbial communities in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 287–295.
Schinner, F., & Brunner, I. (1984). Effect of lead and cadmium on the microbial activity of a soil. Bodenkultur, 35, 1–12.
SEPAC (1997a). GB/T 17138–1997, Soil quality: Determination of copper, zinc. Beijing: CCAP (in Chinese).
SEPAC (1997b). GB/T 17141–1997, Soil quality: Determination of lead, cadmium. Beijing: CCAP (in Chinese).
Stach, J. E. M., Bathe, S., Clapp, P. J., & Burns, R. G. (2006). PCR-SSCP comparison of 16S rDNA sequence diversity in soil DNA obtained using different isolation and purification methods. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 36, 139–151.
Tabatabai, M. A. (1982). Methods of soil analysis. In A. L. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Part 2: Chemical and microbiological properties (2nd Edn.). Agronomy, No. 9, ASA, SSSA, Madison. WI, USA.
Taylor, J. P., Wilson, B., Mills, M. S., & Burns, R. G. (2002). Comparison of microbial numbers and enzymatic activities in surface soils and subsoils using various techniques. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 387–401.
Thomas, G. W. (1996). Soil pH and soil acidity. In D. L. Sparks, A. L. Page, P. A. Helmke, R. H. Loeppert, P. N. Soltanpour, M. A. Tabatabai, C. T. Johnson, & M. E. Sumner (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 3: Chemical methods. soil sci. soc (pp. 475–490). Madison, WI: SSSA. Am. Book Ser. 5.
Trasar-Cepeda, C., Leirós, M. C., Seoane, S., & Gil-Sotres, F. (2000). Limitations of soil enzymes as indicators of soil pollution. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32, 1867–1875.
Tomoyoshi, M., Masami, K. K., & Takejiro, T. (2005). Effects of Pb, Cu, Sb, In and Ag contamination on the proliferation of soil bacterial colonies, Soil dehydrogenase activity, and phospholipid fatty acid profiles of soil microbial communities. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 164, 103–118.
Wang, X. L., Xu, J. M., Yao, H. Y., & Xie, Z. M. (2003). Effects of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb compound contamination on soil microbial community. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (in Chinese), 23(1), 22–27.
Wang, Y. P., Shi, J. Y., Wang, H., et al. (2007). The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 67, 75–81.
Wyszkowska, J., Kucharski, M., Kucharski, J., & Borowik, A. (2009). Activity of dehydrogenases, catalase and urease in copper polluted soil. Journal of Elementology, 14(3), 605–617.
Yang, Z. X., Liu, S. Q., Zheng, D. W., & Feng, S. D. (2006). Effects of cadmium, zinc and lead on soil enzyme activities. Journal of Environment Science (China), 18(6), 1135–1141.
Yeates, G. W., Orchard, V. A., Speir, T. W., Hunt, J. L., & Hermans, M. C. C. (1994). Impact of pasture contamination by copper, chromium, arsenic timber preservative on soil biological activity. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 18, 200–208.
Zhou, J. Z., Bruns, A. M., & Tiedje, J. M. (1996). DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 316–322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Ren, G., Chen, B. et al. Effects of lead and zinc mining contamination on bacterial community diversity and enzyme activities of vicinal cropland. Environ Monit Assess 182, 597–606 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1900-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1900-6