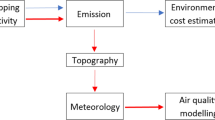
Abstract
Ships are significant air pollution sources as their high powered main engines often use heavy fuels. The major atmospheric components emitted are nitrogen oxides, particulate matter (PM), sulfur oxide gases, carbon oxides, and toxic air pollutants. Shipping emissions cause severe impacts on health and environment. These effects of emissions are emerged especially in territorial waters, inland seas, canals, straits, bays, and port regions. Candarli Gulf is one of the major industrial regions on the Aegean side of Turkey. The marine environment of the region is affected by emissions from ships calling to ten different ports. In this study, NO x , SO2, CO2, hydrocarbons (HC), and PM emissions from 7,520 ships are estimated during the year of 2007. These emissions are classified regarding operation modes and types of ships. Annual shipping emissions are estimated as 631.2 t year − 1 for NO x , 573.6 t year − 1 for SO2, 33,848.9 t year − 1 for CO2, 32.3 t year − 1 for HC, and 57.4 t year − 1 for PM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACCAP (Action on Climate Change and Air Pollution) (2007). Cat. no.: En84-52/2007, presented by Canadian Minister of Environment.
AHM (Aliaga Harbour Master) (2007). www.aliagadenizcilik.gov.tr.
ARB (Air Resources Board) (2004). Health effects of particulate matter and ozone air pollution. American Lung Association of California. aah.ucdavis.edu/docs/AAH_IC_Readings_2006.pdf.
Avol, E. L. (2001). Respiratory effects of relocating to areas of differing air pollution levels. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 164, 2067–2072.
Cerrahogulları (2009). Ports of Turkey. http://www.cerrahogullari.com.tr/ports.htm#aegean.
Corbett, J., & Koehler, H. (2003). Updated emissions from ocean shipping. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D20), 4650.
Corbett, J., Fischbeck, P., & Pandis, S. (1999). Global nitrogen and sulphur inventories for oceangoing ships. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104, 3457–3470.
Deniz, C., & Durmuşoğlu, Y. (2008). Estimating shipping emissions in the region of the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Science of the Total Environment, 390(Issue 1), 255–261.
EC (2005). Official Journal of the European Union: Directive 2005/33/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 July2005 Amending Directive 1999/32/EC. Brussels: European Commission.
Elbir, T., & Muezzinoglu, A. (2004). Estimation of emission strengths of primary air pollutants in the City of Izmir, Turkey. Atmospheric Environment, 38(2004), 1851–1857.
Endresen, Ø., Sørgard, E., Sundet, J. K., Dalsøren, S. B., Isaksen, I. S. A., Berglen, T. F., et al. (2003). Emissions from international sea transportation and environmental impact. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D17), 4560 (ACH 14—p. 1–22).
ENTEC (2005). Preliminary assignment of ship emissions to European Countries, final report. UK: ENTEC.
Eyring, V., Köhler, H. W., van Aardenne, J., & Lauer, A. (2005). Emissions from International Shipping: 1. The last 50 years. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110, 17305.
FEI (Finnish Environment Institute) (2006). Ship emissions and technical emission reduction potential in the Northern Baltic Sea. Helsinki: FEI.
Fournier, A. (2006). Controlling air emissions from marine vessels. Santa Barbara: Donald Bren School of Environmental Science and Management University of California Santa Barbara.
Gauderman, W. J., et al. (2002). Association between air pollution and lung function growth in Southern California children: Results from a second cohort. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 166(1), 74–84.
ICCT (The International Council on Clean Transportation) (2007). Air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from ocean-going ships: Impacts, mitigation options and opportunities for managing growth. Washington, DC: The International Council on Clean Transportation. www.theicct.org.
IMO (International Maritime Organization) (2000). Study of greenhouse gas emissions from ships. Issue no. 2–31. Trondheim: IMO.
Lavender, K., Reynolds, G., & Webster, A. (2006). Emission inventory guidebook (p. 9). UK: Lloyds Register of Shipping.
Lowles, I. (1998). Emissions of sulphur dioxide from Ships. In Coasts and benefits of controlling sulphur dioxide emissions from ships in the North Sea and Seas to the West of Britain, a report to the Department of the Environmental, Transport and the Regions.
Marr, I. L., Rosser, D. P., & Meneses, C. A. (2007). An air quality survey and emissions inventory at Aberdeen harbor. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 6379–6395. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.04.049.
McConnell, R. (2002). Asthma in exercising children exposed to ozone: A cohort study. Lancet, 359, 386–391.
Saxe, H., & Larsen, T. (2004). Air pollution in three Danish Ports. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 4057–4067.
UNCTAD (2008). Review of maritime transport, 2008. Geneva: UNCTAD.
Wichmann, H.-E. (2007). Diesel exhaust particles. Inhalation Toxicology, 19(No. s1), 241–244.
Yang, D., & Kwan, S. H. (2007). An emission inventory of marine vessels in Shanghai in 2003. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(15), 5183–5190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deniz, C., Kilic, A. & Cıvkaroglu, G. Estimation of shipping emissions in Candarli Gulf, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 171, 219–228 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1273-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1273-2