Abstract
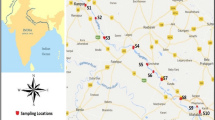
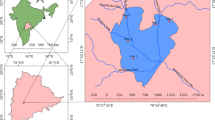
Hussainsagar Lake in the heart of Hyderabad City (India) receives toxic substances through five streams draining from a catchment area of 245 km2. Of particular interest are heavy metals received from urban runoff as well as municipal sewage and industrial effluents. Heavy metals entering the lake get adsorbed onto the suspended sediments, which eventually settle down in the bottom of the lake. In this study, fractionation of metal ions has been studied on the bed sediments of Hussainsagar Lake in order to determine the ecotoxic potential of metal ions. Comparison of sediments with average shale values indicated anthropogenic enrichment with copper, nickel, lead, cadmium, and zinc. The risk assessment code as applied to the present study reveals that 10–17% of manganese, 10–18% of nickel, 14–24% of chromium, 10–19% of lead, 21–30% of cadmium, and 18–28% of zinc exist in exchangeable fraction and, therefore, comes under medium risk category and may enter into food chain. The association of these metals with the exchangeable fraction may cause deleterious effects to aquatic life. The present database will help in formulating guidelines for carrying out dredging operations under restoration programs in the Hussainsagar Lake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra Sekhar, K., Chary, N. S., Kamala, C. T., Suman Raj, D. S., & Sreenivasa Rao, A. (2003). Fractionation studies and bioaccumulation of sediment bound heavy metals in Kolleru lake by edible fish. Environment International, 29, 1001–1008. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00094-1.
Davidson, C. M., Thomas, R. P., McVey, S. E., Perala, R., Littlejohn, D., & Ure, A. M. (1994). Evaluation of sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of heavy metals in sediments. Analytica Chimica Acta, 291, 277–186. doi:10.1016/0003-2670(94)80023-5.
Forstner, W., & Muller, G. (1975). Factors controlling the distribution of minor and trace elements (heavy metals V, Li, Sr) in recent lacustrine sediments. Resumes des Publications IX Congress Intl. De Sedimentologie, Nice, Theme II (p. 6).
Forstner, W., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1979). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. New York: Springer.
Fytianos, K., & Lourantou, A. (2004). Speciation of elements in sediment samples collected at lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Environment International, 30, 11–17. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00143-0.
Gibbs, R. J. (1977). Transport phases of transition metals in the Amazon and Yukon rivers. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 88, 829–843. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1977)88<829:TPOTMI>2.0.CO;2.
Gurunadha Rao, V. V. S., Prakash, B. A., Mahesh Kumar, K., & Chandrasekhar, S. V. N. (2004). Surface water and groundwater quality data base in the Hussainsagar catchment area (p. 39). CSIR Network Project on Groundwater Studies Activity (iv)—Anthropogenic Pollution.
Gurunadha Rao, V. V. S., & Yoshida, M. (2004). Investigation of potentially toxic elements of sediments in Hussainsagar Lake (p. 10). JICA Collaborative Research Report.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
HUDA (2003a). Brochure on lakes around Hyderabad (p. 36). International Workshop on Urban Lakes Conservation and Management, 16–18 June, Hyderabad, organized by Hyderabad Urban Development Authority, Hyderabad, India.
HUDA (2003b). Hyderabad Urban Development Authority, report of the proceedings of the international workshop on urban lakes conservation and management, Hyderabad (p. 15).
Jain, C. K. (2001). Adsorption of zinc onto bed sediments of the river Ganga: Adsorption models and kinetics. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 46(3), 419–433.
Jain, C. K. (2004). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Research, 38(3), 569–578. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.042.
Jain, C. K., & Ali, I. (2000a). Adsorption of cadmium on riverine sediments: Quantitative treatment of the large particles. Hydrological Processes, 14, 261–270. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(20000215)14:2<261::AID-HYP924>3.0.CO;2-N.
Jain, C. K., & Ali, I. (2000b). Arsenic: Occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Research, 34(17), 4304–4312. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00182-2.
Jain, C. K., Malik, D. S., & Yadav, R. (2007). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of lake Nainital, Uttaranchal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 130, 129–139. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9383-6.
Jain, C. K., & Sharma, M. K. (2002). Adsorption of cadmium on bed sediments of river Hindon: Adsorption models and kinetics. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 137, 1–19. doi:10.1023/A:1015530702297.
Jain, C. K., Singhal, D. C., & Sharma, M. K. (2004). Adsorption of zinc on bed sediment of River Hindon: Absorption models and kinetics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B114, 231–239. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.09.001.
Jain, C. K., Singhal, D. C., & Sharma, M. K. (2005). Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the river Hindon, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 105(1–3), 193–207. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-3498-z.
Kodarkar, M. S. (1995). Conservation of lakes (with special reference to water bodies in and around Hyderabad) (p. 82). Indian Association of Aquatic Biologists Publication no. 3.
Li, R. Y., Yang, H., Zhou, Z. G., Lu, J. J., Shao, X. H., & Jin, F. (2007). Fractionation of heavy metals in sediments from Dianchi Lake, China. Pedosphere, 17, 265–272. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60033-2.
Lima, M. C., Giacomelli, M. B. O., Stupp, V., Roberge, F. D., & Barrera, P. B. (2001). Speciation analysis of copper and lead in Tubaco River sediments using the Tessier sequential extraction procedure. Quimica Nova, 24, 734–742.
Luoma, A., & Campbell, P. C. G. (1987). Partitioning of trace metals in sediment: Relationship with bioavailability. Hydrobiology, 149, 43–52. doi:10.1007/BF00048645.
Marin, B., Valladon, M., Polve, M., & Monaco, A. (1997). A reproducibility testing of a sequential extraction scheme for the determination of trace metal speciationin a marine reference sediment by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 342, 91–112. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(96)00580-6.
Moore, J. W., & Ramamoorthy, S. (1984). Heavy metals in natural waters. Applied monitoring and impact assessment. New York: Springer.
Nembrini, G. P. (1982). Speciation of Fe and Mn in a sediment core of the Baie de Villefrance (Mediterranean Sea, France). Environmental Technology Letters, 3, 545–552. doi:10.1080/09593338209384161.
Pardo, R., Barrado, E., Castrillejo, Y., Velasco, M. A., & Vega, M. (1993). Study of the contents and speciation of heavy metals in river sediments by factor analysis. Analytical Letters, 26, 1719–1739.
Patra, A. K., Pendkar, N., & Chakrapani, G. J. (2006). Heavy metal fractionation and mineralogy in sediments of Nainital lake, Kumaun Himalaya. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 68, 181–185.
Pempkowiase, J., Sikora, A., & Biemacka, E. (1999). Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments vs. their bioaccumulation by mussels. Chemosphere, 39(2), 313–321. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00112-5.
Perin, G., Craboledda, L., Lucchese, M., Cirillo, R., Dotta, L., Zanette, M. L., et al. (1985). Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of Northern Adriatic sea—a new approach for environmental toxicity determination. In T. D. Lekkas (Ed.), Heavy metal in the environment (Vol. 2, pp. 454–456). Edinburgh: CEP Consultants.
Quevauviller, P., Rauret, G., Muntau, H., Ure, A. M., Rubio, R., & Lopaz-Sanchez, J. F. (1994). Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the determination of extractable trace metal contents in sediments. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 349, 808–814. doi:10.1007/BF00323110.
Salomons, W., & Forstner, U. (1980). Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments. Part II: Evaluation of environmental impact. Environmental Technology Letters, 506–517. doi:10.1080/09593338009384007.
Samanidou, V., & Fytianos, K. (1987). Partitioning of heavy metals into selective chemical fractions in sediments from rivers in northern Greece. The Science of the Total Environment, 67, 279–285. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(87)90219-1.
Shen, J., Liu, E., Zhu, Y., Hu, S., & Qu, W. (2007). Distribution and chemical fractionation of heavy metals in recent sediments fro Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia, 581, 141–150. doi:10.1007/s10750-006-0523-3.
Singh, S. P., Tack, F. M., & Verloo, M. G. (1998). Heavy metal fractionation and extractability in dredged sediment derived surface soils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 102, 313–328. doi:10.1023/A:1004916632457.
Smith, J. D., & Milne, P. J. (1979). Determination of Fe in suspended matter and sediments of the Yana River Estuary and the distribution of Cu, Pb, Zn and Mn in the sediments. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 30, 731–739. doi:10.1071/MF9790731.
Soylak, M., Uzek, U., Narin, I., Tuzen, M., Turkoglu, O., & Elci, L. (2004). Application of the sequential extraction procedure for dust samples from Kayseri-Turkey. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 13(5), 454–457.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedures for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851. doi:10.1021/ac50043a017.
Tuzen, M. (2003). Determination of trace metals in River Yesilimak sediments in Tokat, Turkey using sequential extraction procedure. Microchemical Journal, 74, 105–110. doi:10.1016/S0026-265X(02)00174-1.
Wang, W. X., & Fisher, N. S. (1999). Assimilation efficiencies of chemical contaminants in aquatic invertebrates: A synthesis. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 2034–2045. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<42034:AEOCCI>2.3.CO;2.
Wang, H., Wang, C. X., Wang, Z. J., & Cao, Z. H. (2004). Fractionation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Taihu Lake, East China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26, 303–309. doi:10.1023/B:EGAH.0000039594.19432.80.
Yao, Z. G. (2008). Comparison between BCR sequential extraction and geo-accumulation method to evaluate metal mobility in sediments of Dongting Lake, Central China. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 26, 14–22. doi:10.1007/s00343-008-0014-7.
Yao, Z. G., Bao, Z. Y., & Gao, P. (2006). Environmental assessment of trace metals in sediments from Dongting Lake, Central china. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 17, 310–319. doi:10.1016/S1002-0705(07)60004-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, C.K., Gurunadha Rao, V.V.S., Prakash, B.A. et al. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of Hussainsagar Lake, Hyderabad, India. Environ Monit Assess 166, 57–67 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0984-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0984-8