Abstract
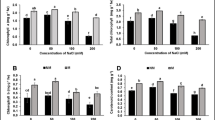
The short-term responses of H2O2-depletion-related parameters in moss Hypnum plumaeforme to the combined stress induced by Pb and Ni were investigated. The results showed that the Pb and Ni stress induced dose-dependent accumulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The increase of peroxidase (POD) activity and decrease of ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity were observed under the combined heavy metal application. The antioxidants, ascorbate (AsA) and proline content, increased significantly when the metals were applied together. The study indicated that the cell damage caused by Pb stress was higher than that caused by Ni stress, Pb and Ni had synergistic effect in inducing the oxidative stress in moss H. plumaeforme, especially under the combination of high concentration of Ni (0.1 and 1.0 mM) and Pb. Content of proline, H2O2 and the activity of POD, all showed a dose-dependent increase under Pb and Ni stress, suggesting their practical value as biomarkers in moss biomonitoring, especially in the case of light pollution caused by heavy metals without the changes in the appearance of mosses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alia, Prasad, K. V., & Saradhi, P. P. (1995). Effect of Zinc on free radicals and proline in Brassica and Cajanus. Phytochemistry, 39, 45–47. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(94)00919-K.
Alia, Mohanty, P., & Matysik, J. (2001). Effect of proline on the production of singlet oxygen. Amino Acids, 21, 195–200. doi:10.1007/s007260170026.
Bartoli, C. G., Simontacchi, M., Tambussi, E., Beltrano, J., Montaldi, E., & Puntarulo, S. (1999). Drought and watering-dependent oxidative stress: Effect on antioxidant content in Triticum aestivum L. leaves. Journal of Experimental Botany, 50, 375–383. doi:10.1093/jexbot/50.332.373.
Bassi, P., Basile, A., Stefenini, A., Vosa, C. B., Maffei, M., Giordano, S., et al. (1995). Effects of lead on nuclear repetitive DNA of the moss Funaria hygrometrica (Bryophyta). Protoplasma, 188, 104–108. doi:10.1007/BF01276800.
Carballeira, A., Vazquez, M. D., & Lopez, J. (2001). Biomonitoring of sporadic acidification of rivers on the basis of release of preloaded cadmium from the aquatic bryophyte Fontinalis antipyretica Hedw. Environmental Pollution, 111, 95–106. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00331-0.
Chakravarty, B., & Srivastava, S. (1997). Effect of cadmium and zinc interaction on metal uptake and regeneration of tolerant plants in linseed. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 61, 45–50. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(96)01078-X.
Choudhury, S., & Panda, S. K. (2004). Induction of oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes in moss Taxithelium nepalense (Schwaegr.) Broth. under lead and arsenic phytotoxicity. Current Science, 87, 342–348.
Choudhury, S., & Panda, S. K. (2005). Toxic effects, oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes in moss Taxithelium nepalense (Schwaegr.) Broth. under chromium and lead phytotoxicity. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 167, 73–90. doi:10.1007/s11270-005-8682-9.
Choudhary, M., Jetley, U. K., Khan, M. A., Zutshi, S., & Fatma, T. (2007). Effect of heavy metal stress on proline, malondialdehyde, and superoxide dismutase activity in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis-S5. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 66, 204–209. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.02.002.
De Azevedo Neto, A. D., Prisco, J. T., Enéas-Filho, J., Braga de Abreu, C. E., & Gomes-Filho, E. (2006). Effect of salt stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive maize genotypes. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 56, 87–94. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.01.008.
Dixit, V., Vivek, P., & Shyam, R. (2001). Differential antioxidative responses to cadmium in root and leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Azad). Journal of Experimental Botany, 52, 1101–1109. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.358.1101.
Greppin, H., Panel, C., & Gaspar, T. (1986). Molecular and physiological aspects of plant peroxidases. Geneva: University of Geneva.
Kadpal, R. P., & Rao, N. A. (1985). Alteration in the biosynthesis of proteins and nucleic acid in finger millet (Eleucine coracana) seedling during water stress and the effect of proline on protein biosynthesis. Plant Science, 40, 73–79. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(85)90044-5.
Knipp, G., & Honermeier, B. (2006). Effect of water stress on proline accumulation of genetically modified potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) generating fructans. Journal of Plant Physiology, 163, 392–397. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2005.03.014.
Koricheva, J., Roy, S., Vranjic, J. A., Haukioja, E., Hughes, P. R., & Hänninen, O. (1997). Antioxidant responses to simulated acid rain and heavy metal deposition in birch seedlings. Environmental Pollution, 95, 249–258. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(96)00071-1.
Liu, Y., Wang, X., Zeng, G., Qu, D., Gu, J., Zhou, M., et al. (2007). Cadmium-induced oxidative stress and response of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Bechmeria nivea (L.) Gaud. Chemosphere, 69, 99–107. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.040.
Lummerzheim, M., Sandroni, M., Castresana, C., De Oliveira, D., Van Montagu, M., Roby, D., et al. (1995). Comparative microscopic and enzymatic characterization of the leaf necrosis induced in Arabidopsis thaliana by lead nitrate and by Xanthomanas campestris pv. Campestris after foliar spray. Plant, Cell & Environment, 18, 499–509. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1995.tb00550.x.
Mishra, S., Srivastava, S., Tripathi, R. D., Kumar, R., Seth, C. S., & Gupta, D. K. (2006). Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere, 65, 1027–1039. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.033.
Mukherjee, S. P., & Choudhuri, M. A. (1983). Implications of water stress-induced changes in the levels of endogenous ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide in vigna seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 58, 166–170. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1983.tb04162.x.
Nikolopoulos, D., & Manetas, Y. (1991). Compatible solutes and in vitro stability of Salsola soda enzyme: Proline incompability. Phytochemistry, 30, 411–413. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(91)83694-G.
Panda, S. K. (2003). Heavy-metal phytotoxicity induces oxidative stress in a moss, Taxithellium sp. Current Science, 84, 631–633.
Piechalak, A., Tomaszewska, B., Baralkiewicz, D., & Malecka, A. (2002). Accumulation and detoxification of lead ions in legumes. Phytochemistry, 60, 153–162. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00067-5.
Prasad, M. N. V. (1997). Trace metals. In M. N. V. Prasad (Ed.), Plant ecophysiology (pp. 207–249). New York: Wiley.
Rao, D. N., Robitaille, G., & Leblance, F. (1977). Influence of heavy metal pollution on lichens and bryophytes. The Journal of the Hattori Botanical Laboratory, 42, 213–239.
Reddy, A. M., Kumar, S. G., Jyothsnakumari, G., Thimmanaik, S., & Sudhakar, C. (2005). Lead induced changes in antioxidant metabolism of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) and bengalgram (Cicer arietinum L.). Chemosphere, 60, 97–104. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.092.
Shakya, K., Chettri, M. K., & Sawidis, T. (2008). Impact of heavy metals (copper, zinc, and lead) on the chlorophyll content of some mosses. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 54, 412–421. doi:10.1007/s00244-007-9060-y.
Singh, S., Eapen, S., & D’Souza, S. F. (2006). Cadmium accumulation and its influence on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative system in an aquatic plant, Bacopa monnieri L. Chemosphere, 62, 233–246. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.017.
Sugiyama, M. (1994). Role of cellular antioxidants in metal-induced damage. Cell Biology & Toxicology, 10, 1–22. doi:10.1007/BF00757183.
Sun, S. Q., Wang, D. Y., He, M., Li, X. Y., & Zhang, C. (2007). Retention capacities of several bryophytes for Hg (II) with special reference to the elevation and morphology of moss growth. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 133, 399–406. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9594-x.
Sun, S. Q., Wang, D. Y., He, M., & Zhang, C. (2009a). Monitoring of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Chongqing, China - based on moss bag technique. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 148, 1–9. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-0133-1.
Sun, S. Q., He, M., Cao, T., Zhang, Y. C., & Han, W. (2009b). Response mechanisms of antioxidants in bryophyte (Hypnum plumaeforme) under the stress of individual or combined Pb and/or Ni. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 149, 291–302. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0203-z.
Tanaka, K., Suda, Y., Konda, N., & Sugahara, K. (1985). O3 tolerance and ascorbate-dependent H2O2 decomposing system in chloroplasts. Plant & Cell Physiology, 26, 1425–1431.
Van Assche, F., Cardinales, C., & Clijsters, H. (1988). Induction of enzyme capacity in plants as a result of heavy metal toxicity: Dose–response relations in Phaseolus vulgaris L. treated with zinc and cadmium. Environmental Pollution, 52, 103–115. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(88)90084-X.
Venekemp, J. H. (1989). Regulation of cytosolic acidity in plants under condition of drought. Physiologia Plantarum, 76, 112–117. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1989.tb05461.x.
Verma, S., & Dubey, R. S. (2003). Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Science, 164, 645–655. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(03)00022-0.
Vincent, C. D., Lawlor, A. J., & Tipping, E. (2001). Accumulation of Al, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb by the bryophyte Scapania undulata in three upland waters of different pH. Environmental Pollution, 114, 93–100. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00201-3.
Weckx, J. E. J., & Clijsters, H. M. M. (1996). Oxidative damage and defense mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris as a result of root assimilation of toxic amounts of copper. Physiologia Plantarum, 96, 506–512. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1996.tb00465.x.
Wu, J. T., Chang, S. J., & Chou, T. L. (1995). Intracellular proline accumulation in some algae exposed to copper and cadmium. Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica, 36, 89–93.
Zacchini, M., Rea, E., Tullio, M., & de Agazio, M. (2003). Increased antioxidative capacity in maize calli during and after oxidative stress induced by a long lead treatment. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 41, 49–54. doi:10.1016/S0981-9428(02)00008-6.
Zhang, J., & Kirkham, M. B. (1996). Antioxidant responses to drought in sunflower and sorghum seedlings. The New Phytologist, 132, 361–373. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1996.tb01856.x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, SQ., He, M., Cao, T. et al. Antioxidative responses related to H2O2 depletion in Hypnum plumaeforme under the combined stress induced by Pb and Ni. Environ Monit Assess 163, 303–312 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0835-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0835-7