Abstract
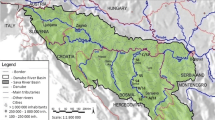
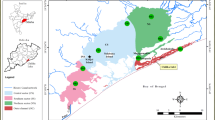
The concentrations of the natural radioactivity in water, soil and sediment samples collected from Bendimahi River which originates near the Tendürek Mountain (Van, Turkey), its tributaries and Van Lake (Turkey) were measured. The gross-alpha and gross-beta radioactivity concentrations were investigated in May and August in 2005. Determination of the gross-alpha and gross-beta radioactivity of river water, soil and sediment samples was obtained by using gas-flow proportional counter, PIC-MPC 9604-α/β counter. In water samples, the obtained results show that in May; gross-alpha and gross-beta activity concentrations varied between 0.063–0.782 and 0.021–0.816 Bq l−1 and in August the values were 0.009–0.037 and 0.081–3.116 Bq l−1, respectively. The gross-alpha and gross-beta activity concentrations in soil samples ranged from 0.800 to 4.277 Bq g−1 and 0.951 to 11.773 Bq g−1 in May and 0.686 to 4.713 Bq g−1 and 0.073 to 9.524 Bq g−1 in August, respectively. Concentrations ranging from 0.782 to 4.596 Bq g−1 and from 0.482 to 10.372 Bq g−1 in May and from 0.580 to 5.824 Bq g−1 and from 0.303 to 9.702 Bq g−1 in August for gross-alpha and gross-beta radioactivity were observed in sediments, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baxter, M. S. (1996). Technologically enhanced radioactivity: an overview. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 32, 3–17.
Bradley, D. A., & Roberts, C. (1998). Foreword. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 49, 147–148.
Cothern, C. R., Lappenbusch, W. L., & Michel, J. (1986). Drinking water contribution to natural background radiation. Health Physics, 50, 33–47.
Dogru, M., & Kulahci, F. (2004). Iso-Radioactivity curves of the water of the Hazar Lake, Elazig, Turkey. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 260, 557–562.
Drndarski, N., Miljevic, N., & Golobocanin, D. (1996). Lognormal distribution of natural radionuclides in freshwater sediments and coal–ash repositories. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 213, 95–102.
Eisenbud, M., & Gessel, T. (1997). Environmental radioactivity. New York: Academic.
Guimond, R. J. (1978). The radiological aspects of fertilizer utilization. In A. A. Moghissi, et al. (Ed.) Radioactivity in consumer products, report NUREG/CP-0001 (pp. 380–393). Washington, DC: Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
ITS (2001). Institution of Turkish Standards, Annual Progress Reports, Ankara.
Lide, D. R. (1994). CRC handbook of chemistry and physics (74th ed.). Boca Raton, USA: CRC.
NCRP (1987). Radiation exposure of the U.S. population from consumer products and miscellaneous sources, NCRP report no. 95, Washington DC.
Oruc, N., Alpman, N., & Karamanderesi, I. H. (1976). Hydrogeology of the spring waters with high F content from the surroundings of Tendürek volcano. Bulletin of Turkey Geology, 19, 1–8.
Osmond, J. K., & Ivanovich, M. (1992). Uranium-series mobilization and surface hydrology. In M. Ivanovich, & R. S. Harmon (Eds.) Uranium-series disequilibrium; application to earth marine and environmental sciences (pp. 259–289). Oxford: Clarendon.
Santschi, P. H., & Honeyman, B. D. (1989). Radionuclides in aquatic environments. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 34, 213–240.
Stephen, G. M. (2004). Background radioactivity in sediments near Los Alamos, New Mexico. Science of the Total Environment, 328, 143–159.
UNSCEAR (1993). Ionizing radiation: sources and effects of ionizing radiation, United Nation Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Report the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes, United Nations Sales Publication, E.94.IX.2, United Nations, New York.
WHO (2006). Guidelines for drinking water quality: incorporating first addendum. Vol. 1, recommendations, (3rd ed.), chapter 9: radiological aspects. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yu, K. N., & Mao, S. Y. (1994). Application of high resolution gamma ray spectrometry measuring radioactivities in drinks in Hong Kong. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 45, 1031–1034.
Yuanxun, Z., Erhkang, L., Deyi, L., Yinsong, W., Yuehchung, Y., Changwan, W., et al. (2003). PIXE and radioactivity measurements for elemental determination in river water and sediment samples. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 258, 415–419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selçuk Zorer, Ö., Ceylan, H. & Doğru, M. Gross alpha and beta radioactivity concentration in water, soil and sediment of the Bendimahi River and Van Lake (Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 148, 39–46 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0137-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0137-x