Abstract
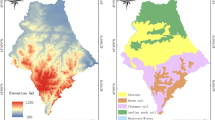
A total of 292 soil samples were taken from surface soil (0–20 cm) of a typical small watershed–Tongshuang in the black soil region of Heilongjiang province, northeast China in June 2005 for examining the concentration of soil organic carbon (SOC). Spatial variability of SOC in relation to topography and land use was evaluated using classical statistics, geostatistics and geographic information system (GIS) analyses. The objective of this study was to provide a scientific basis for land management targeting at improving soil quality in this region. Classical statistical analysis results indicated that the variability of SOC was moderate (C V = 0.30). Slope position and land use types were discriminating factors for its spatial variability. Geostatistics analyses showed that SOC had a strong spatial autocorrelation, which was mainly induced by structural factors. Mean concentration of SOC in surface soil was 2.27% in this watershed, which was a very low level in the northern black soil region of northeast China. In this small watershed, present soil and water conservation measures played an important role in controlling soil loss. But SOC's restoration was unsatisfactory. Nearly three-quarters of the area had worrisome productivity. How to improve SOC concentration targeting at soil fertility is a pressing need in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolstad, P. V., Swank, W. and Vose, J.: 1998, (Predicting southern Appalachianoverstory vegetation with digital terrain data), Landscape Ecol. 13, 271–283.
Cambardella, C. A., Moorman, A. T., Novak, J. M., Parkin, T. B., Karlen, D. L., Turco, R. F. and Konopka, A. E.: 1994, (Field-scale heterogeneity of soilproperties in central Iowa soils), Soil Sci. Soe. Am J. 58:1501–1511.
Eswaran, H., Van den Berg E. and Reich, P.: 1993, (Organic carbon insoils of the world), Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 57, 192–194.
Fan, H. M., Cai, Q. G. and Wang, H. S.: 2004, (Condition of soilerosion in phaeozem region of northeast China), Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 18(2), 66–70.
Gessler, P. E., Chadwick, O. A., Chamran F., Althouse, L. and Holmes, K.: 2000, (Modeling soil–landscape and ecosystem properties using terrain attributes), Soil Sci. Soc. Am J. 64, 2046–2056.
Gessler, P. E., Moore, I. D. McKenzie, N. J. and Ryan, P. J.: 1995, (Soil–landscape modelling and spatial prediction of soil attributes), International Journal of GIS 9(4), 421–432.
Gregorich, E. G. and Aderson, D. W.: 1985, (Effects of cultivation and erosion on soils of four toposeqeences in Canadian prairies), Geoderma 36, 343–354.
Goovaerts, P.: 1999, (Geostatistics in soil science: State-of-the-artand perspectives), Geoderma 89, 1–45.
Guo, X. D., Fu, B. J., Chen, L. D. and Qiu, Y.: 2000, (Time-spacevariation characteristics of soil nutrients in Zunhua plain of Hebeiprovince-Analysis of variation function and Kriging interpolation), Acta Geography Sinica 55(5), 555–566.
Glenna, N. F. and Carr, J. R.: 2003, (The use of Geostatistics inrelating soil moisture to RADARSAT-1 SAR data obtained over the Great Basin, Nevada, USA), Computers {& Geosciences} 29, 577–586.
Karlen, D. L., Mausbach, M. J., Doran, J. W., Cline, R. G., Harris, R.F. and Schuman, G. E.: 1997, (Soil quality: A concept, definition, and frameworkfor evaluation), Soil Sci. Soc. Am J. 61, 4–10.
Knowles, T. A. and Singh, B.: 2003, (Carbon storage in cotton soil of northern New South Wales), Australian Journal of Soil Research 41, 889–903.
Li, H. B. and Reynolds, J. F.: 1995, (On definition and quantificationof heterogeneity), Oikos 73, 280–284.
Li, H. B., Wang, Z. Q. and Wang, Q. C.: 1998, (Theory and method for quantitativestudy of spatial heterogeneity), Journal of Applied Ecology 9(6),162–192.
Liu, X. T., He, Y., Deng, W., Song, Y. X. and Wu Z. J.: ( Researchon Comprehensive Development of Regional Agriculture in Northeast China), SciencePress, Beijing, China. pp. 717.
Luo, P. and Zhang, B. Y.: 2003, (Modes and corresponding technologies of eco-agricultural construction in Baiquan County), Agricultural Environ.{& Develep} 20(1), 21–22.
Meng, K. and Zhang, X. Y.: 1998, (Degradation mechanism of black soil and itsecological restoration in Songnen plain), Chinese Journal of Soil Science 29(3), 100–102.
Meng, K., Zhang, X. Y. and Sui, Y. Y.: 2003, (Impedient factors in black soil inthe Northern-Northeast China). Soil (2), 145–147, 151.
Miller, P. M., Singer, M. J. and Nielsen, D. R.: 1998, (Spatialvariability of wheat yield and soil properties on complex hill), Soil Sci.Soc. Am J. 52, 1133–1141.
Murage, E. W., Karanja, N. K., Smithson, P. C. and Woomer, P. L.: 2000, (Diagnostic indicators of soil quality in productive and non-productive smallholders' fields of Kenya's Central Highlands), Agr. Ecosyst. Environ 79, 1–8.
Park, S. J., McSweeney, K., and Lowery, B.: 2001, (Prediction of soils using a process based terrain characterization) Geoderma 103, 249–272.
Pierson, F. B. and Mulla, D. J.: 1990, (Aggregate stability in the Palous region of Washington: effect of landscape position), Soil Sci. Soc. Am J. 54, 1407–1412.
Post, W. M., Emanuel, W. R. and Zinke, P. J.: 1982, (Soil carbon pools and world life zones), Nature 298, 156–159.
Puget, P. and Lal, R.: 2005, (Soil organic carbon and nitrogen in a Mollisol incentral Ohio as affected by tillage and land use), Soil and TillageResearch 80(1–2), 201–213.
Robertso, G. P.:' Geostatistics for Environmental Sciences': GS+User's Guide, Version 5. Gamma Design Software, MI. 2000, pp. 200.
Ross, D. J., Tate, K. R., Scott, N. A. and Feltham, C. W.: 1999, (Land-use change:Effects on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus pools and fluxes in three adjacentecosystems), Soil Biology and Biochemistry 31(6), 803–813.
Schuur, E. A. G., Chadwick, O. A. and Matson, P. A.: 2001, (Carbon cycling andsoil carbon storage in Mesic to wet Hawaiian Montane forest), Ecology 82(11), 3182–3196.
Slater, McSweeney, B. K. K. and Ventura, S. J.: 1994, (A spatial framework for integrating soil-landscape and pedogenic models), In: Bryant R. B. and Amold R. W. (Eds). Quantitative Modeling of Soil Forming Processes, SSSA specoal publication. 39, pp. 169–185.
Sun, J. M. and Liu, T. S.: 2001, (Desertification in the northeastern China), Quaternary Sciences 21(1), 72–78.
Trangmar, B. B. and Yost, R. S.: 1985, (Application of Geostatistics to spatialstudies of soil properties), Advanced Agronomy 38, 44–94.
Venteris, E. R., McCarty, G. W., Ritchie, J. C. and Gish, T.: 2004, (Influence of management history and landscape variables on soil organic carbon and soil redistribution), Soil Science 169(11), 787–795.
Wang, J., Fu, B. J., Qiu, Y. and Chen, L. D.: 2001, (Soil nutrients in relation toland use and slope position in the semi-arid small watershed on loess plateau inChina), Journal of Arid Environments 48, 537–550.
Wang, J. D., Liu, J. S. Liu, S. X. and Yu, J. B.: 2004, (Evaluation on soil organic carbon pool and affecting factors in phaeozem region in Songnen plain), Journal of Agro-Environment Science 23(4), 687–690.
Wang, J. K., Wang, T. Y., Zhang, X. D., Guan, L. Z., Wang, Q. B., Hu, H. Y. and Zhao, Y. C.: 2002, (An approach to the changes of black soil quality (I) –Changes of the Indices of black soil with the Year(s) of reclamation), Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University 33(1), 43–47.
Wang, S. Q. and Zhou, C. H.: 1999, (Estimating soil carbon reservoir of terrestrial ecosystem in China), Geographical Research 18(4), 349–356.
Wang, S. Q., Liu, J. Y. and Yu, G. R.: 2004, (Effects of land use change on the storage of soil organic carbon: A case study of the Qianyanzhou Forest Experimental Station in China), Climatic Change 67(2), 247–255.
Wang, Z. Q.: 2000, Geostatistics and its Application in Ecology, Beijing, Science Press, pp. 162–192.
Yang, X. M., Zhang, X. P., Fang, H. J. and Liang, A. Z.: 2004, (Changes in {Organic Matter and Total Nitrogen of Black Soils in Jilin Province over the Past Two Decades}), Scientia Geographica Sinica 24(6), 710–714.
Zhang, C. S. and McGrath, D.: 2004, (Geostatistical and GIS analyses on soil organic carbon concentrations in grassland of southeastern Ireland from two different periods), Geoderma 119, 261–275.
Zhang, C. S.: 2004, (Methods and achievements of soil and water conservation in Baiquan County), China Soil and Water Conservation 2, 37–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian-Bing, W., Du-Ning, X., Xing-Yi, Z. et al. Spatial Variability of Soil Organic Carbon in Relation to Environmental Factors of a Typical Small Watershed in the Black Soil Region, Northeast China. Environ Monit Assess 121, 597–613 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9158-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9158-5