Abstract
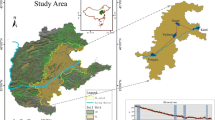
The dynamics of soil organic carbon (SOC) in cropland is one of the central issues related to both soil fertility and environmental safety. However, little information is available at county level regarding the spatiotemporal variability of SOC in the southwestern mountainous region of China. Thus, this study aimed to explore spatiotemporal changes of SOC in the cultivated soil layer of dry land in Mojiang County, Yunnan Province, China. Data were obtained from the second national soil survey (SNSS) of 1985 and soil tests for fertilizer application carried out by the Mojiang Agricultural Bureau in 2006. The ANOVA test was applied to determine any significant differences between the datasets, while semivariogram analysis was performed on geostatistics via an ordinary Kriging method in order to map spatial patterns of soil organic carbon density (SOCD). The results revealed that SOCD in the cultivated soil layer significantly decreased from 3.93 kg m-2 in 1985 to 2.89 kg m-2 in 2006, with a total soil organic carbon stock (SOCS) decrease of 41.54×104 t over the same period. SOCS levels fell most markedly in yellow-brown soil at a rate of 51.52%, while an increase of 8.70% was found in the analysed latosol. Geostatistical analysis also showed that the recorded changes in SOCD between 1985 and 2006 were spatially structured. The decreasing trend might be attributed to the combined action of intense cultivation, major crop residue removal without any protective tillage measures, unreasonable fertilization and natural climatic diversity inducing a large decrease in SOC in the studied cultivated dry land region of Mojiang County. Therefore, management measures such as protective tillage should be undertaken in order to enhance soil C sequestration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar RE, Kelly F, Hei RD (1988) Effects of cultivation on soils in northern great plains range land. Soil Science Society of America Journal 52(4): 1081–1085. http://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1988.03615995005200040034x
Alvarez R, Lavado RS (1998) Climate, organic matter and clay content relationship in the Pampa and Chaco soils. Argentina. Geoderma 83(97): 127–141. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(97)00141-9
Anderson JM (1992) Responses of soils to climate change. Advances in Ecological Research 22: 163–210. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60136-1
Bellamy PH, Loveland PJ, Lan BR, et al. (2005) Carbon losses from all soils across England and Wales 1978-2003. Nature 437(7056): 245–248. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature04038
Berndtsson R, Bahri A, Jinno K (1993) Spatial dependence of geochemical elements in a semiarid agricultural field: II. Geostatistical Properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal 57(5): 1323–1329. http://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1993. 03615995005700050027x
Bordovsky DG, Choudhary M, Gerard GC (1993) Effect of tillage, cropping, and residue management on soil properties in the Texas rolling plains. Soil Science 164: 331–340. http://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-199905000-00005
Burgess TM, Webster R (1980) Optimal interpolation and isarithmic mapping of soil properties: I. The semi-variogram and punctual kriging. European Journal of Soil Science 31(2): 315–331. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1980.tb02084.x
Buringh P (1984) Organic carbon in soils of the world. In: Woodwell GM(Ed.), The Role of terrestrial Vegetation in the Global Carbon Cycle: Measurement by Remote Sensing, New York: Wiley. pp 91–109.
Callesen I, Liski J, Raulund-Rasmussen K, et al. (2003) Soil carbon stores in Nordic well-drained forest soils relationships with climate and texture class. Global Change Biology 9(3): 358–370. http://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00587.x
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Novak JM, et al. (1994) Fieldscale variability of soil properties in central low a soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 58(5): 1501–1511. http://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
Chen H, Zhao Y, Feng H, et al. (2015) Assessment of climate change impacts on soil organic carbon and crop yield based on long-term fertilization applications in Loess Plateau, China. Plant and Soil 390:401–417. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2332-1
Chien YJ, Lee DY, Guo HY, et al. (1997) Geostatistical analysis of soil properties of mid-west Taiwan soils. Soil Science 162(4):291–298.http://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-199704000 -00007
Dai FQ, Zhou QG, Lv ZQ, et al. (2014) Spatial prediction of soil organic matter content integrating artificial neural network and ordinary kriging in Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Indicators 45: 184–194. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.04.003
Ding XL, Han XZ, Liang Y, et al. (2012) Changes in soil organic carbon pools after 10 years of continuous manuring combined with chemical fertilizer in a Mollisol in China. Soil and Tillage Research 122(6): 36–41. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2012.02.002.
Follett RF (2001) Soil management concepts and carbon sequestration zin cropland soils. Soil and Tillage Research 61(1/2):77–92. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(01)00180-5
Galbraith JM, Kleinamn PJA, Bryant RB (2003) Sources of uncertainty affecting soil organic carbon estimates in northern New York. Soil Science Society of America Journal 67(4): 1206–1212. http://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2003.1206
Gervois S, Ciais P, de Noblet-Ducoudre N, et al. (2008) Carbon and water balance of European croplands throughout the 20th century. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 22: GB2022.
Goovaerts P (1997) Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Guo LP, Lin E (2001) Carbon sink in cropland soils and emission of greenhouse gases from paddy soils: A review of work in China. Chemosphere Global Change Science 3(4): 413–418. http://doi.org/10.1016/S1465-9972(01)00019-8
Han D, Sun Z, Li F, et al. (2016) Changes and controlling factors of cropland soil organic carbon in North China Plain over a 30-year period. Plant and Soil 403: 437–453. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2803-7
Han P, Zhang W, Wang G, et al. (2016) Changes in soil organic carbon in croplands subjected to fertilizer management: a global meta-analysis. Scientific Reports 6.
Hao XH, Liu SL, Wu JS, et al. (2008) Effect of long-term application of inorganic fertilizer and organic amendments on soil organic matter and microbial biomass in three subtropical paddy soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 81(1): 17–24. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9145-z
Heikkinen J, Ketoja E, Nuutinen V, et al. (2013) Declining trend of carbon in Finnish cropland soils in 1974-2009. Global Change Biology 19: 1456–1469. http://doi.org/10.1111/gcb. 12137
Holling SE, Bernacchi CJ, Meyers P (2005) Carbon budget of mature no-till ecosystem in North Central Region of the United States. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 130(1): 59–69. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.01.005
Homann PS, Sollins P, Chappell HN, et al. (1995) Soil organic carbon in a mountainous, forested region: relation to site characteristics. Soil Science Society of America Journal 59(5): 1468–1475. http://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1995.03615995005900050037x
Huang S, Rui WY, Peng XX, et al. (2010) Organic carbon fractions affected by long-term fertilization in a subtropical paddy soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 86(1): 153–160. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9279-2
Huang Y, Sun WJ (2006) Changes in topsoil organic carbon of croplands in mainland China over the last two decades. Chinese Science Bulletin 51(15): 1785–1803. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2056-6
Huang Y, Sun W J, Zhang W, et al. (2010) Change in soil organic carbon of terrestrial ecosystems in China: a minireview. Science China. Life Sciences 53(7): 766–775. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-010-4022-4
Huang ZZ, Dou X L (2011) Soil testing and fertilizer recommendation in Yunnan Province from 2005 to 2009. Yunnan Science Technology Press. (In Chinese)
Hutchinson JJ, Campbell CA, Desjardins RL (2007) Some perspectives on carbon sequestration in agriculture. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 142: 288–302. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.030
Isaaks EH, Shrivastava RM (1989) An introduction to applied geostatistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Jaiyeoba IA (2003) Changes in soil properties due to continuous cultivation in Nigerian semiarid Savannah. Soil and Tillage Research 70(1):91–98.http://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(02)00138-1
Jenkinson DS, Adams DE, Wild A (1991) Model estimates of CO2 emission from soil in response to global warming. Nature 351(6324): 304–306. http://doi.org/10.1038/351304a0
Jia SW (2009) Soil organic carbon loss under different slope gradients in Loess hilly region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 16(2):30–33. (In Chinese)
Jiang Y, Zhang YG, Liang WJ, et al. (2003) Spatial variability of soil nutrients in cultivated surface soil of Sujiatun District, Shenyang City. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 14(10): 1673–1676. (In Chinese)
Jiang Y, Zhuang QL, Liang WJ (2007) Soil organic carbon pool and its affecting factors in farm land ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Ecology 26(2): 278–285. (In Chinese)
Knorr W, Prentice IC, House JI, et al. (2005) Long-term sensitivity of soil carbon turnover to warming. Nature 433(7023): 298–301. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature03226
Koch HJ, Stockfisch N (2006) Loss of soil organic matter upon ploughing under a loess soil after several years of conservation tillage. Soil and Tillagel Research 86(1):73–83. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2005.02.029
Krige DG (1951) A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. Journal of the Chemical Metallurgical and Mining Society of South Africa 94(3): 95–111. http://doi.org/10.2307/3006914
Lal R (2004) Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 304(5677): 1623–1627. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097396
Li Z, Sun B, Lin XX (2001) Density of soil organic carbon and factors controlling its turnover in east China. Scientia Geographic Sinica 21(4): 301–307. (In Chinese)
Li C, Wang X (2003) Modeling soil organic carbon change in croplands of China. Ecological Applications 13(2): 115–128. http://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(2003)013[0327:MSOCCI]2.0.CO
Li LJ, Han XZ (2016) Changes of soil properties and carbon fractions after long-term application of organic amendments in Mollisols. Catena 143:140–144. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.04.007
Liski J, Ilvesniemi H, Makela A (1999) CO2 emissions from soil in responses to climatic warming are overestimated: the decomposition on old soil organic matter is tolerant of temperature. Ambio 28(2): 171–174.
Liu GS, Jiang NF, Zhang LD (1996) Soil physical and chemical analysis. Beijing: Standard Press in China. (In Chinese)
Liu Y, Zhao EX, Huang W, et al. (2010) Characteristic analysis of precipitation and temperature trend in Yunnan province in recent 46 years. Journal of Catastrophology 25(1):39–44. (In Chinese)
Lu F, Wang XK, Han B, et al. (2009) Soil carbon sequestrations by nitrogen fertilizer application, straw return and no-tillage in China’s cropland. Global Change Biology 15(2): 281–305. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01743.x
Luo YQ, Wan SQ, Hui DF, et al. (2001) Acclimatization of soil respiration to warming in a tall grass prairie. Nature 413(6856): 622–625. http://doi.org/10.1038/35098065
Malo DD, Schumacher TE, Doolittle JJ (2005) Long-term cultivation impacts on selected soil properties in the northern Great Plains. Soil and Tillage Research 81(2):277–291. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.09.015
Mao DH, Wang ZM, Wu CS, et al. (2014) Topsoil carbon stock dynamics in the Songnen plain of Northeast China from 1980 to 2010. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 23(2): 531–539.
Matheron G (1963) Principles of geostatistics. Economic Geology 58(8):1246–1266. http://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo. 58.8.1246
Meersmans J, Van Wesemael B, Goidts E, et al. (2011) Spatial analysis of soil organic carbon evolution in Belgian croplands and grasslands, 1960-2006. Global Change Biology 17(1): 466–479. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02183.x
Mi YH, Pan YH, Sha LJ, et al. (2006). Comprehensively harnessing measures to control soil, water and nutrients loss in slope cultivated land of red soil in Yunnan. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 20(2):17–21. (In Chinese)
Mational Soil Survey Office (1998) Soils of China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (In Chinese)
Mational Soil Survey Station of Mojiang County in Yunnan Province (1985) Soils in Mojiang County, Yunnan Province. Yunnan Science Technology Press. (In Chinese)
Oechel WC (1993) Recent change of arctic tundra ecosystems from a carbon sink to a source. Nature 361(6412): 520–523. http://doi.org/10.1038/361520a0
Pan GX, Zhao QG (2005) Study on evolution of organic carbon stock in agricultural soils of China: Facing the challenge of global change and food security. Advances in Earth Science 20(4): 384–393. (In Chinese)
Pan GX, Xu XW, Smith P, et al. (2010) An increase in topsoil SOC stock of China’s croplands between 1985 and 2006 revealed by soil monitoring. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 136(s1-2): 133–138. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.12.011
Post WM, Emanuel WR, Zinke PJ, et al. (1982) Soil carbon pools and world life zones. Nature 298(5870): 156–159. http://doi.org/10.1038/298156a0
Puget P, Lal R (2005) Soil organic carbon and nitrogen in a Mollisol in central Ohio as affected by tillage and land use Soil Tillage Research 80(1-2): 201–213. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.03.018
Reijneveld A, Van Wensem J, Oenema O (2009) Soil organic carbon contents of agricultural land in the Netherlands between 1984 and 2004. Geoderma 152(s3-4):231–238. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.06.007
Saby NPA, Arrouays D, Antoni V, et al. (2008) Changes in soil organic carbon in a mountainous French region, 1990-2004. Soil Use and Management 24(3): 254–262. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-2743.2008.00159.x
Shi YG, Zhao XN, Zhang SL, et al. (2016) The effects of longterm fertilizer applications on soil organic carbon and hydraulic properties of a Loess soil in China. Land Degradation and Development 27(1): 60–67. http://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2391
Sleutel S, De Neve S, Singier B, et al. (2006) Organic C levels in intensively managed arable soils -long-term regional trends and characterization of fractions. Soil Use and Management 22(2):188–196.
Smith P (2004) Carbon sequestration in croplands: The potential in Europe and the global context. European Journal of Agronomy 20(3): 229–236. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja. 2003.08.002
Song GH, Li LQ, Pan GX, et al. (2005) Topsoil organic carbon storage of China and its loss by cultivation. Biogeochemistry 74(1): 47–62. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-2222-3
Song L (2013) Evolution of soil organic carbon and evaluation of carbon sequestration potential in cultivated land of lower reaches of Liaohe river plain. Liaoning. PhD thesis, Shengyang Agricultural University. p 47. (In Chinese)
Soil and Fertility Station of Yunnan, Soil Census Office of Yunnan (1996) Soil of Yunnan Province. Yunnan Science Technology Press. (In Chinese)
Szillasi P, Jordan G, van Rompaey A, et al. (2006) Impacts of historical land use changes on erosion and agricultural soil properties in the Kali Basin at Lake Balat, Hungary. Catena 68(2-3):96–108.http://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2006.03.010
Tang HJ, Qiu JJ, Ranst EV, et al. (2006) Estimations of soil organic carbon storage in cropland of China based on DNDC model. Geoderma 134(1-2):200–206. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.10.005
Tian K, Zhao YC, Xu XH, et al. (2014) A meta-analysis of field experiment data for characterizing the cultivated soil layer organic carbon changes under different fertilization treatments in uplands of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 34(13): 3735–3743. (In Chinese)
Tian K, Zhao Y, Xu X, et al. (2015) Effects of long-term fertilization and residue management on soil organic carbon changes in paddy soils of China: A meta-analysis. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 204: 40–50. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2015.02.008
Vincent C, Bouahom B, Valentine C (2010) Soil organic carbon stocks in Laos: spatial variations and controlling factors. Global Change Biology 16(4): 1380–1393. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02013.x
Wang SL, Huang M, Shao XM, et al. (2004) Vertical distribution of soil organic carbon in China. Environmental Management 33(1): 200–209. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-003-9130-5
Wang YZ, Xiao HA, Zhou P, et al. (2015) Distribution and dynamics of cropland soil organic carbon in Jianghan plain: A case study of Qianjiang city. Environment Science 38(9): 3422–3428. (In Chinese)
Webster R. (1985) Quantitative spatial analysis of soil in the field. Advances in Soil Science 3(596): 1–70. http://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-5090-6_1
Webster R. Oliver M A (2001) Geostatistics for environment scientists. Chichester, Wiley. p 271.
Wu J (2011) Carbon accumulation in paddy ecosystems in subtropical china: Evidence from landscape studies. European Journal Soil Science 62(1):29–34. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01325.x
Wynn JG, Bird MI, Vallen L, et al. (2006) Continental-scale measurement of the soil organic carbon pool with climatic, edaphic, and biotic controls. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 20(1): 630–637. http://doi.org/10.1029/2005GB002576
Xu L, He NP, Yu GR, et al. (2015) Differences in pedotransfer functions of bulk density lead to high uncertainty in soil organic carbon estimation at regional scales: Evidence from Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. Journal of Geophysical Research and Biogeosciences 120(8): 1567–1575. http://doi.org/10.1002/2015JG002929
Yu DS, Shi XZ, Wang HJ, et al. (2007) National scale analysis of soil organic carbon storage in China based on Chinese soil taxonomy. Pedosphere 17(1):11–18. http://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60002-2
Yu YQ, Yao H, Zhang W (2012) Modeling soil organic carbon change in croplands of china, 1980-2009. Global and Planetary Change 82(82-83): 115–128. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.12.005
Zhang Y, Zhao YC, Shi XZ, et al. (2008) Variation of soil organic carbon estimate in mountain regions: A case study from southwest China. Geoderma 146: 44–456. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.06.015
Zhang D, Zhou ZH, Zhang B, et al. (2012) The effects of agricultural management on selected soil properties of the arable soils in Tibet, China. Catena 93(6): 1–8. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.01.004
Zhang L, Wang J, Huang Y, et al. (2015) Characteristics of drought based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index from 1961 to 2010 in Yunnan province. Journal of Natural Resources 31(5): 141–146. (In Chinese)
Zhang L, Zhuang Q, He Y, et al. (2016) Toward optimal soil organic carbon sequestration with effects of agricultural management practices and climate change in Tai-Lake paddy soils of China. Geoderma 275: 28–39. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.04.001
Zhao YC, Shi XZ, Weindorf DC, et al. (2006) Map scale effects on soil organic carbon stock estimation in North China. Soil Science Society of America Journal 70(4):1377–1386.
Zhao JX, He SJ, Zhang Q, et al. (2016) Changes of total nitrogen and ph in plough layer of dryland in past 20 years-a case study of Mojiang County, Yunnan Province. Chinese Journal of Soil Science 47(4): 868–875. (In Chinese)
Zheng JM, Ren JZ, Zhang WC (2010) Analysis on variation characteristics of temperature and rainfall in Yunnan in the last 100 years. Journal of Catastrophology 25(3):24–31. (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported as a special project by the Agriculture Ministry of China (Grant No. 201503119) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41471232).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Jx., Dai, Fq., He, Sj. et al. Spatiotemporal variation of soil organic carbon in the cultivated soil layer of dry land in the South-Western Yunnan Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 14, 2484–2497 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4314-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4314-7