Abstract
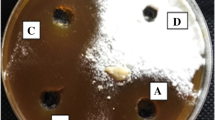
Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus are aflatoxin-producing fungi that can infect peanut seeds in field crops. An association between A. parasiticus proteolytic enzyme activities and peanut fungal infection was examined. For this study, a model of inductive and non-inductive culture media to produce A. parasiticus extracellular protease before infection was used. These A. parasiticus cultures were used to infect peanut seeds of cultivars resistant and susceptible to aflatoxin contamination. Peanut seeds of both cultivars exposed to fungi grown on casein medium (inductive medium) showed higher internal and external infection and a higher fungal protease content than those observed on potato dextrose agar (PDA) and sucrose medium (non-inductive media). A further study showed higher fungal colonisation and aflatoxin contamination in seeds of the resistant cultivar pre-incubated with Aspergillus extracellular proteases than in those incubated without proteases. Moreover, protease activities affected the viability of non-infected resistant cultivar seeds, inhibiting germination and radicle elongation and enhancing seed tissue injury. The results strongly suggest that protease production by A. parasiticus is involved in peanut seed infection and aflatoxin contamination resulting in seed tissue damage, affecting seed viability and facilitating the access of fungi through the testa. The analysis of fungal extracellular proteases formed on peanut seed during infection showed that A. flavus and A. parasiticus produced metallo and serine proteases; however, there were differences in the molecular masses of the enzymes between both species. The greatest activity in both species was by serine protease, that could be classified as subtilase.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abnet, C. C. (2007). Carcinogenic food contaminants. Cancer Investigation, 25, 189–196. doi:10.1080/07357900701208733.
Asis, R., Barrionuevo, D. L., Giorda, L. M., Nores, M. L., & Aldao, M. A. (2005). Aflatoxin Production in six peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes infected with Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus, isolated from peanut production areas of Cordoba, Argentina. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53, 9274−9280. doi:10.1021/jf051259+.
Bindschedler, L. V., Sanchez, P., Dunn, S., Mikan, J., Thangavelu, M., Clarkson, J. M., et al. (2003). Deletion of the SNP1 trypsin protease from Stagonospora nodorum reveals another major protease expressed during infection. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 38, 43−53. doi:10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00517-0.
Brown, R. L., Chen, Z. Y., Cleveland, T. E., Cotty, P. J., & Cary, J. W. (2001). Variation in vitro α-amylase and protease activity is related to the virulence of Aspergillus flavus isolates. Journal of Food Protection, 64, 401–404.
Brown, R. L., Cleveland, T. E., Cotty, P. J., & Mellon, J. E. (1992). Spread of Aspergillus flavus in cotton bolls, decay of intercarpellary membranes, and production of fungal pectinases. Phytopathology, 82, 462–467. doi:10.1094/Phyto-82-462.
Carlile, A. J., Bindschedler, L. V., Bailey, A. M., Bowyer, P., Clarkson, J. M., & Cooper, R. M. (2000). Characterization of SNP1, a cell wall-degrading trypsin, produced during infection by Stagonospora nodorum. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 13, 538–550. doi:10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.5.538.
Chen, Z.-Y., Brown, R. L., Damann, K. E., & Cleveland, T. E. (2007). Identification of maize kernel endosperm proteins associated with resistance to aflatoxin contamination by Aspergillus flavus. Phytopathology, 97, 1094–1103. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-97-9-1094.
Di Pietro, A., Huertas Gonzales, M. D., Gutierrez-Corona, J. F., Martinez-Cadena, G., Meglecz, E., & Roncero, M. I. G. (2001). Molecular characterization of a subtilase from the vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 14, 653–662. doi:10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.5.653.
Dowell, F. E., Dorner, J. W., Cole, R. J., & Davidson Jr., J. I. (1990). Aflatoxin reduction by screening farmers stock peanuts. Peanut Science, 17, 6–8.
Guo, B. Z., Russin, J. S., Cleveland, T. E., Brown, R. L., & Damman, K. E. (1996). Evidence for cutinase production by Aspergillus flavus and its possible role in infection of corn kernels. Phytopathology, 86, 824–829. doi:10.1094/Phyto-86-824.
Holbrook, C. K., Rucker, D. M., Wilson, J. E., Hook, J. E., & Matheron, M. E. (2000). Preharvest aflatoxin contamination in drought-tolerant and drought-intolerant peanut genotypes. Peanut Science, 27, 45–48.
Horn, B. W. (2006). Relationship between soil densities of Aspergillus species and colonization of wounded peanut seeds. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 52, 951–960. doi:10.1139/W06-050.
Kolattukudy, P. E., Lee, J. D., Rogers, L. M., Zimmerman, P., Ceselski, S., Fox, B., Stein, B., & Copelan, E. A. (1993). Evidence for possible involvement of an elastolytic serine protease in Aspergillosis. Infection and Immunity, 61, 2357–2368.
Liang, X. Q., Luo, M., & Guo, B. Z. (2006). Resistance mechanisms to Aspergillus flavus infection and aflatoxin contamination in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea). The Plant Pathology Journal, 5, 115–124.
Luo, M., Liang, X. Q., Dang, P., Holbrook, C. C., Bausher, M. G., Lee, R. D., & Guo, B. Z. (2005). Microarray-based screening of differentially expressed genes in peanut in response to Aspergillus parasiticus infection and drought stress. Plant Science, 169, 695–703. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.05.020.
Mellon, J. E., Cotty, P. J., & Dowd, M. K. (2007). Aspergillus flavus hydrolases: their roles in pathogenesis and substrate utilization. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77, 497–504. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-1201-8.
Middleton, K. J., Pande, S., Sharma, S. B., & Smith, D. H. (1994). Groundnut Crop: A scientific basis for improvement. In (Ed.), Diseases (pp. 336–78). London: Chapman & Hall.
Monod, M., Capoccia, S., Léchenne, B., Zaugg, C., Holdom, M., & Jousson, O. (2002). Secreted proteases from pathogenic fungi. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 292(5–6), 405–419. doi:10.1078/1438-4221-00223.
Movahedi, S., & Heale, J. B. (1990). The roles of aspartic proteinase and endo-pectin lyase enzymes in the primary stages of infection and pathogenesis of the various host tissues by different isolates of Botrytis cinerea. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 36, 303–324. doi:10.1016/0885-5765(90)90061-2.
Olivieri, F., Zanetti, M. E., Oliva, C. R., Covarrubias, A. A., & Casalongue, C. A. (2002). Characterization of an extracellular serine protease of Fusarium eumartii and its action on pathogenesis related proteins. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 108, 63–72. doi:10.1023/A:1013920929965.
Pekkarinen, A. I., & Jones, B. (2002). Trypsin-like proteinase produced by Fusarium culmorum grown on grain proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50, 3849–3855. doi:10.1021/jf020027x.
Plummer, K. M., Clark, S. J., Ellis, L. M., Loganathan, A., Al-Samarrai, T. H., Rikkerink, E. H. A., et al. (2004). Analysis of a secreted aspartic peptidase disruption mutant of Glomerella cingulata. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 110, 265–274. doi:10.1023/B:EJPP.0000019796.78598.8c.
Ramesh, M. V., Sirakova, T., & Kolattukudy, P. E. (1994). Isolation, characterization, and cloning of the cDNA and the gene for an elastinolytic serine proteinase from Aspergillus flavus. Infection and Immunity, 62, 79–85.
Ramesh, M. V., Sirakova, T., & Kolattukudy, P. E. (1995). Cloning and characterization of the cDNAs and genes (mep20) encoding homologous metalloproteinases from Aspergillus flavus and A. fumigatus. Gene, 165, 121–125. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00434-8.
Reed, C. E., & Kita, H. (2004). The role of protease activation of inflammation in allergic respiratory diseases. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 114, 997–1008. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.07.060.
Reichard, U., Buttner, S., Eiffert, H., Staib, F., & Ruchel, R. (1990). Purification and characterisation of an extracellular serine proteinase from Aspergillus fumigatus and its detection in tissue. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 33, 243–251.
Rhodes, J. C., Amlung, T. W., & Muller, M. S. (1990). Isolation and characterization of an elastinolytic proteinase from Aspergillus flavus. Infection and Immunity, 58, 2529–2534.
Roncero, M. I. G., Hera, C., Ruiz-Rubio, M., García Maceira, F. I., Madrid, M. P., Caracuel, Z., et al. (2003). Fusarium as a model for studying virulence in soilborne plant pathogens. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 62, 87–98. doi:10.1016/S0885-5765(03)00043-2.
Sarath, G., De La Motte, R. S., & Wagner, F. W. (1989). Proteolytic Enzymes: A Practical Approach. In (Ed.), Protease Assay Methods (pp. 25–55). Oxford: IRL Press.
Sieber, P., Schorderet, M., Ryser, U., Buchala, A., Kolattukudy, P., Metraux, J. P., et al. (2000). Transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing a fungal cutinase show alterations in the structure and properties of the cuticle and postgenital organ fusions. The Plant Cell, 12, 721–738.
Sreedhar, L., Kobayashi, D. Y., Bunting, T. E., Hillman, B. I., & Belanger, F. C. (1999). Fungal proteinase expression in the interaction of the plant pathogen Magnaporthe poae with its host. Gene, 235, 121–129. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00201-2.
St Leger, R. J., Joshi, L., & Roberts, D. W. (1997). Adaptation of proteases and carbohydrates of saprophytic, phytopathogenic and entomopathogenic fungi to the requirements of their ecological niches. Microbiology, 143, 1983–1992.
Tubajika, K. M., & Damann, K. E. (2001). Sources of resistance to aflatoxin production in maize. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49, 2652–2656. doi:10.1021/jf001333i.
Williams, J. H., Phillips, T. D., Jolly, P. E., Stiles, J. K., Jolly, C. M., & Aggarwal, D. (2004). Human aflatoxicosis in developing countries: a review of toxicology, exposure, potential health consequences, and interventions. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 80, 1106–1122.
Xu, H., Annis, S., Linz, J., & Trail, F. (2000). Infection and colonization of peanut pods by Aspergillus parasiticus and the expression of the aflatoxin biosynthetic gene, nor-1, in infection hyphae. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 56, 185–196. doi:10.1006/pmpp.2000.0265.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the critical review and constructive comments of Dr. L.M. Giorda in the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from Agencia Cordoba Ciencia and Agencia Nacional de Promocion Cientifica y Tecnologica, Argentina. Ramon Asis and Virginia Muller are members and fellow, respectively, of CONICET (Argentina). The authors thank Dr. Olga Ortiz Carranza and Silvia Caceres for her technical assistance in a review of the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asis, R., Muller, V., Barrionuevo, D.L. et al. Analysis of protease activity in Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus on peanut seed infection and aflatoxin contamination. Eur J Plant Pathol 124, 391–403 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9426-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9426-7