Abstract
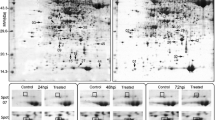
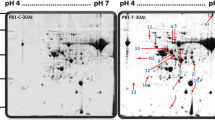
A proteomic approach was used to identify host proteins altering in abundance during Peronospora viciae infection of a susceptible cultivar of pea (Pisum sativum cv. Livioletta). Proteins were extracted from fully developed pea leaflets at 4 days post-inoculation, before visible symptoms were apparent. Cytoplasmic proteins and membrane- and nucleic acid-associated proteins from infected and control leaves were examined using two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis. The majority of proteins had a similar abundance in control and infected leaves; however, several proteins were altered in abundance and twelve were found to have increased significantly in the latter. These proteins were selected for either matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry or electro-spray ionisation quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry analysis following trypsin digestion, with sequence identity being assigned to eight of the proteins. These included the ABR17 stress-response protein, the pathogen-induced PI176 protein, three photosynthetic proteins, a glycine-rich RNA binding protein and two glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenases (cytosolic and chloroplastic) which can be induced by a range of abiotic and biotic stresses in many plant species. The possible roles of these proteins in the response of the pea plant during P. viciae infection are discussed. This study represents the first proteomic analysis of downy mildew infection of pea leaves, and provides the basis for further work to elucidate molecular mechanisms of compatibility in P. viciae infections.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-D DIGE:
-
two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis
- dpi:
-
days post-inoculation
- ESI Q-TOF MS/MS:
-
electro-spray ionisation quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- MALDI-TOF MS:
-
matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry
References
Amey, R. C., & Spencer-Phillips, P. T. N. (2006). Towards developing diagnostics for downy mildew diseases. Outlooks on Pest Management, 17, 4–8.
Aneeta Sanan-Mishra, N., Tuteja, N., & Sopory, S. K. (2002). Salinity- and ABA-induced up-regulation and light-mediated modulation of mRNA encoding glycine-rich RNA-binding protein from Sorghum bicolor. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 296, 1063–1068.
Bantignies, B., Seguin, J., Muzac, I., Dedaldechamp, F., Gulick, P., & Ibrahim, R. (2000). Direct evidence of ribonucleolytic activity of a PR-10-like protein from white lupin roots. Plant Molecular Biology, 42, 871–881.
Baudo, M. M., Meza-Zepeda, L. A., Palva, E. T., & Heino, P. (1999). Isolation of a cDNA corresponding to a low temperature- and ABA-responsive gene encoding a putative glycine-rich RNA-binding protein from Solanum commersonii. Journal of Experimental Botany, 50, 1867–1868.
Beranova-Giorgianni, S. (2003). Proteome analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry: strengths and limitations. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 22, 273–281.
Bergeron, D., Beauseigle, D., & Bellemare, G. (1993). Sequence and expression of a gene encoding a protein with RNA-binding and glycine-rich domains in Brassica napus. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1216, 123–125.
Bestel-Corre, G., Dumas-Gaudot, E., Poinsot, V., Dieu, M., Dierick, J. F., van Tuinen, D., et al. (2002). Proteome analysis and identification of symbiosis-related proteins from Medicago truncatula Gaertn. by two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis, 23, 122–137.
Beyer, K., Jiménez, S., Randall, T. A., Lam, S., Binder, A., Boller, T., et al. (2002). Characterization of Phytophthora infestans genes regulated during the interaction with potato. Molecular Plant Pathology, 3, 473–485.
Biesiadka, J., Bujacz, G., Sikorski, M. M., & Jaskolski, M. (2002). Crystal structures of two homologous pathogenesis-related proteins from yellow lupine. Journal of Molecular Biology, 319, 1223–1234.
Carpenter, C. D., Kreps, J. A., & Simon, A. E. (1994). Genes encoding glycine-rich Arabidopsis thaliana proteins with RNA-binding motifs are influenced by cold treatment and an endogenous circadian rhythm. Plant Physiology, 104, 1015–1025.
Castillejo, M. Á., Amiour, N., Dumas-Gaudot, E., Rubiales, D., & Jorrín, J. V. (2004). A proteomic approach to studying plant response to crenate broomrape (Orobanche crenata) in pea (Pisum sativum). Phytochemistry, 65, 1817–1828.
Chang, M. M., Chiang, C. C., Martin, M. W., & Hadwiger, L. A. (1993). Expression of a pea disease resistance response gene in the potato cultivar Shepody. American Potato Journal, 70, 635–647.
Chivasa, S., Ndimba, B. K., Simon, W. J., Robertson, D., Yu, X. L., Knox, J. P., et al. (2002). Proteomic analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana cell wall. Electrophoresis, 23, 1754–1765.
Chuisseu Wandji, J. L., Amey, R. C., Butt, E., Harrison, J., Macdonald, H., & Spencer-Phillips, P. T. N. (2007). Towards proteomic analysis of Peronospora viciae conidiospores. In A. Lebeda, & P. T. N. Spencer-Phillips (Eds.), Advances in Downy Mildew Research (vol. 3, pp. 95–100). Kostelec na Hane (Czech Republic): Palacky University in Olomouc and JOLA.
Clark, J. S. C., & Spencer-Phillips, P. T. N. (2000). Downy Mildews. In J. Lederberg, M. Alexander, B. R. Bloom, D. Hopwood, R. Hull, B. H. Inglearski, A. I. Laskia, S. G. Oliver, M. Schaechter, & W. C. Summers (Eds.), Encyclopaedia of microbiology (vol. 2, pp. 117–129). San Diego: Academic.
Clark, J. S. C., & Spencer-Phillips, P. T. N. (2004). The compatible interaction in downy mildew infections. In P. T. N. Spencer-Phillips, & M. J. Jeger (Eds.), Advances in downy mildew research (vol. 2, pp. 1–34). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Colditz, F., Nyamsuren, O., Niehaus, K., Eubel, H., Braun, H-P., & Krajinski, F. (2004). Proteomic approach: identification of Medicago truncatula proteins induced in roots after infection with the pathogenic oomycete Aphanomyces euteiches. Plant Molecular Biology, 55, 109–120.
Corbett, M., Virtue, S., Bell, K., Birch, P., Burr, T., Hyman, L., et al. (2005). Identification of a new quorum-sensing-control led virulence factor in Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica secreted via the type II targeting pathway. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 18, 334–342.
Coulthurst, S. J., Lilley, K. S., & Salmond, G. P. C. (2006). Genetic and proteomic analysis of the role of luxS in the enteric phytopathogen, Erwinia carotovora. Molecular Plant Pathology, 7, 31–45.
Curto, M., Camafeita, E., Lopez, J. A., Maldonado, A. M., Rubiales, D., & Jorrín, J. V. (2006). A proteomic approach to study pea (Pisum sativum) responses to powdery mildew (Erysiphe pisi). Proteomics, 6, S163–S174.
Dangl, J. L., & Jones, J. D. G. (2001). Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature, 411, 826–833.
Djordjevic, M. A., Chen, H. C., Netera, S., Van Noorden, G., Menzel, C., Taylor, S., et al. (2003). A global analysis of protein expression profiles in Sinorhizobium meliloti: discovery of new genes for nodule occupancy and stress adaptation. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 16, 508–524.
Dubos, C., & Plomion, C. (2001). Drought differentially affects expression of a PR-10 protein in needles of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.) seedlings. Journal of Experimental Botany, 52, 1143–1144.
Ebstrup, T., Saalbach, G., & Egsgaard, H. (2005). A proteomics study of in vitro cyst germination and appressoria formation in Phytophthora infestans. Proteomics, 5, 2839–2848.
El-Gariani, N. K., & Spencer-Phillips, P. T. N. (2004). Isolation of viable Peronospora viciae hyphae from infected Pisum sativum leaves and accumulation of nutrients in vitro. In P. T. N. Spencer-Phillips, & M. J. Jeger (Eds.), Advances in downy mildew research: Volume 2 (pp. 249–264). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Fristensky, B., Horovitz, D., & Hadwiger, L. A. (1988). cDNA sequences for pea disease resistance response genes. Plant Molecular Biology, 11, 713–715.
Geri, C., Cecchini, E., Giannakou, M. E., Covey, S. N., & Milner, J. J. (1999). Altered patterns of gene expression in Arabidopsis elicited by Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) infection and by a CaMV gene VI transgene. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 12, 377–384.
Giavalisco, P., Nordhoff, E., Lehrach, H., Gobom, J., & Klose, J. (2003). Extraction of proteins from plant tissues for two-dimensional electrophoresis analysis. Electrophoresis, 24, 207–216.
Gomez, J., Sanchez-Martinez, D., Stiefel, V., Rigau, J., Puigdomènech, P., & Pagès, M. (1988). A gene induced by the plant hormone abscisic acid in response to water stress encodes a glycine-rich protein. Nature, 344, 262–264.
Grenville-Briggs, L. J., Avrova, A. O., Bruce, C. R., Williams, A., Whisson, S. C., Birch, P. R. J., et al. (2005). Elevated amino acid biosynthesis in Phytophthora infestans during appressorium formation and potato infection. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 42, 244–256.
Gygi, S. P., Rochon, Y., Franza, B. R., & Abersold, R. (1999). Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Molecular Cell Biology, 19, 1720–1730.
Hancock, J. T., Henson, D., Nyirenda, M., Desikan, R., Harrison, J., Lewis, M., et al. (2005). Proteomic identification of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase as an inhibitory target of hydrogen peroxide in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 43, 828–835.
Hopkins, W. G., & Hüner, N. P. A. (2004). Introduction to plant physiology. New York: Wiley.
Kamoun, S., Hraber, P., Sobral, B., Nuss, D., & Govers, F. (1999a). Initial assessment of gene diversity for the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans based on expressed sequences. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 28, 94–106.
Kamoun, S., Huitema, E., & Vleeshouwers, V. G. A. A. (1999b). Resistance to oomycetes: a general role for the hypersensitive response. Trends in Plant Science, 4, 196–200.
Kav, N. N. V., Srivastava, S., Goonewardene, L., & Blade, S. F. (2004). Proteome-level changes in the roots of Pisum sativum in response to salinity. Annals of Applied Biology, 145, 217–230.
Kim, Y-O., Kim, J. S., & Kang, H. (2005). Cold-inducible zinc finger-containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein contributes to the enhancement of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal, 42, 890–900.
Laberge, S., Castonguay, Y., & Vezina, L. P. (1993). New cold- and drought-regulated gene from Medicago sativa. Plant Physiology, 101, 1411–1412.
Laxalt, A. M., Cassia, R. O., Sanllorenti, P. M., Madrid, E. A., Andreu, A. B., Daleo, G. R., et al. (1996). Accumulation of cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA under biological stress conditions and elicitor treatments in potato. Plant Molecular Biology, 30, 961–972.
Liu, J. J., Ekramoddoullah, A. K. M., & Yu, X. S. (2003). Differential expression of multiple PR10 proteins in western white pine following wounding, fungal infection and cold-hardening. Physiologia Plantarum, 119, 544–553.
Lucas, J. A. (1998). Plant pathology and plant pathogens. Oxford: Blackwell.
Luo, M., Lin, L., Hill, R. D., & Mohapatra, S. S. (1991). Primary structure of an environmental stress and abscisic acid-inducible alfalfa protein. Plant Molecular Biology, 17, 1267–1269.
Luo, M., Liu, J-H., Mohapatra, S., Hill, R. D., & Mohapatra, S. S. (1992). Characterization of a gene family encoding abscisic acid- and environmental stress-inducible proteins of alfalfa. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 15367–15374.
Matton, D. P., & Brisson, N. (1989). Cloning, expression, and sequence conservation of pathogenesis-related gene transcripts of potato. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 2, 325–331.
McDowell, J. M., & Dangl, J. L. (2000). Signal transduction in the plant immune response. Trends in Biochemical Science, 25, 79–82.
McGee, J. D., Hamer, J. E., & Hodges, T. K. (2001). Characterization of a PR-10 pathogenesis-related gene family induced in rice during infection with Magnaporthe grisea. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 14, 877–886.
Mence, M. J., & Pegg, G. F. (1971). The biology of Peronospora viciae on pea: factors affecting the susceptibility of plants to local infection and systemic colonisation. Annals of Applied Biology, 67, 297–308.
Mitchell, H. J., Kovac, K. A., & Hardham, A. R. (2002). Characterisation of Phytophthora nicotianae zoospore and cyst membrane proteins. Mycological Research, 106, 1211–1223.
Moiseyev, G. P., Beintema, J. J., Fedoreyeva, L. I., & Yakovlev, G. I. (1994). High sequence similarity between a ribonuclease from ginseng calluses and fungus-elicited proteins from parsley indicates that intracellular pathogenesis-related proteins are ribonucleases. Planta, 193, 470–472.
Moons, A., Bauw, G., Prinsen, E., van Montagu, M., & van der Straeten, D. (1995). Molecular and physiological responses to abscisic acid and salts in roots of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant Indica rice varieties. Plant Physiology, 107, 177–186.
Moons, A., Prinsen, E., Bauw, G., & Van Montagu, M. (1997). Antagonistic effects of abscisic acid and jasmonates on salt-stress inducible transcripts in rice roots. Plant Cell, 9, 2243–2259.
Moore, B. D. (2004). Bifunctional and moonlighting enzymes: lighting the way to regulatory control. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 221–228.
Mousavi, A., & Hotta, Y. (2005). Glycine-rich proteins – a class of novel proteins. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 120, 169–174.
Naqvi, S. M. S., Park, K.-S., Yi, S.-Y., Lee, H.-W., Bok, S. H., & Choi, D. (1998). A glycine-rich RNA-binding protein gene is differentially expressed during acute hypersensitive response following Tobacco mosaic virus infection in tobacco. Plant Molecular Biology, 37, 571–576.
Nyamsuren, O., Colditz, F., Rosendahl, S., Tamasloukht, M., Bekel, T., Meyer, F., et al. (2003). Transcriptional profiling of Medicago truncatula roots after infection with Aphanomyces euteiches (oomycota) identifies novel genes upregulated during this pathogenic interaction. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 63, 17–26.
Park, C.-J., Kim, K.-J., Shin, R., Park, J. M., Shin, Y.-C., & Paek, K.-H. (2004). Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper functions as a ribonuclease in an antiviral pathway. Plant Journal, 37, 186–198.
Pinto, P. M., & Ricardo, C. P. P. (1995). Lupinus albus L. pathogenesis-related proteins that show similarity to PR10 proteins. Plant Physiology, 109, 1345–1351.
Pfender, W. F. (1989). Aphanomyces root rot. In D. J. Hagedorn (Ed.), Compendium of pea diseases (pp. 25–28). St. Paul: American Phytopathological Society.
Qutob, D., Hraber, P. T., Sobral, B. W. S., & Gijzen, M. (2000). Comparative analysis of expressed sequences in Phytophthora sojae. Plant Physiology, 123, 243–253.
Repetto, O., Bestel-Corre, G., Dumus-Gaudot, B. G., Gianinazzi-Pearson, V., & Gianinazzi, S. (2003). Targeted proteomics to identify calcium-induced protein modifications in Glomus mossae-inoculated pea roots. New Phytologist, 157, 555–567.
Richard, S., Drevet, C., Jouanin, L., & Séguin, A. (1999). Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding a putative white spruce glycine-rich RNA binding protein. Gene, 240, 379–388.
Ruiz-Lozano, J. M., Roussel, H., Gianinazzi, S., & Gianinazzi-Pearson, V. (1999). Defense genes are differentially induced by a mycorrhizal fungus and Rhizobium sp. in wild-type and symbiosis-defective pea genotypes. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 12, 976–984.
Schmelzer, E., Kruger-Lebus, S., & Hahlbrok, K. (1989). Temporal and spatial patterns of gene expression around sites of attempted fungal infection in parsley leaves. Plant Cell, 1, 993–1001.
Scholes, J. D. (1992). Photosynthesis: cellular and tissue aspects in diseased leaves. In P. G. Ayres (Ed.), Pests and pathogens: plant responses to foliar attack (pp. 85–106). Oxford: BIOS Scientific.
Shepherd, S. J., van West, P., & Gow, N. A. R. (2003). Proteomic analysis of asexual development of Phytophthora palmivora. Mycological Research, 107, 395–400.
Showalter, A. M. (1993). Structure and function of plant cell wall proteins. Plant Cell, 5, 9–23.
Somssich, I. E., Schmelzer, E., Kawalleck, P., & Hahlbrook, K. (1988). Gene structure and in situ transcript localization of pathogenesis-related protein 1 in parsley. Molecular and General Genetics, 213, 93–98.
Stafstrom, J. P., Ripley, B. D., Devitt, M. L., & Drake, B. (1998). Dormancy-associated gene expression in pea axillary buds. Planta, 205, 547–552.
Swoboda, I., Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K., O’Ríordáin, G., Scheiner, O., Heberle-Bors, E., & Vicente, O. (1996). Bet v1 proteins, the major birch pollen allergens and members of a family of conserved pathogenesis-related proteins, show ribonuclease activity in vitro. Physiologia Plantarum, 96, 433–438.
Ünlü, M., Morgan, M. E., & Minden, J. S. (1997). Difference gel electrophoresis: a single gel method for detecting changes in protein extracts. Electrophoresis, 18, 2071–2077.
Utriainen, M., Kokko, H., Auriola, S., Sarrazin, O., & Karenlampi, S. (1998). PR-10 protein is induced by copper stress in roots and leaves of a Cu/Zn tolerant clone of birch, Betula pendula. Plant Cell and Environment, 21, 821–828.
Velasco, R., Salamini, F., & Bartels, D. (1994). Dehydration and ABA increase mRNA levels and enzyme activity of cytosolic GAPDH in the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantineum. Plant Molecular Biology, 26, 541–546.
von Heijne, G. (1985). Signal sequences. The limits of variation. Journal of Molecular Biology, 184, 99–105.
Walter, M. H., Liu, J.-W., Grand, C., Lamb, C. J., & Hess, D. (1990). Bean pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins deduced from elicitor-induced transcripts are members of a ubiquitous new class of conserved PR proteins including pollen allergens. Molecular and General Genetics, 222, 353–360.
Wan, J., Torres, M., Ganapathy, A., Thelen, J., DaGue, B. B., Mooney, B., et al. (2005). Proteomic analysis of soybean root hairs after infection by Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 18, 458–467.
Wang, C. S., Huang, J. C., & Hu, J. H. (1999a). Characterization of two subclasses of PR-10 transcripts in lily anthers and induction of their genes through separate signal transduction pathways. Plant Molecular Biology, 40, 807–814.
Wang, Y. P., Nowak, G., Culley, D., Hadwiger, L. A., & Fristensky, B. (1999b). Constitutive expression of pea defense gene DRR206 confers resistance to blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) disease in transgenic canola (Brassica napus). Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 12, 410–418.
Warner, S. A. J., Scott, R., & Draper, J. (1992). Characterisation of a wound-induced transcript from the monocot asparagus that shares similarity with a class of intracellular pathogenesis-related PR10 proteins. Plant Molecular Biology, 19, 555–561.
Warner, S. A. J., Scott, R., & Draper, J. (1993). Isolation of an asparagus intracellular PR gene (AoPR1) wound-responsive promoter by the inverse polymerase chain reaction and its characterization in transgenic tobacco. Plant Journal, 3, 191–201.
Wienkoop, S., & Saalbach, G. (2003). Proteome analysis. Novel protein identified at the peribacteroid membrane from Lotus japonicus root nodules. Plant Physiology, 131, 1080–1090.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by DEFRA grant HH3216SFV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amey, R.C., Schleicher, T., Slinn, J. et al. Proteomic analysis of a compatible interaction between Pisum sativum (pea) and the downy mildew pathogen Peronospora viciae . Eur J Plant Pathol 122, 41–55 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9313-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9313-2