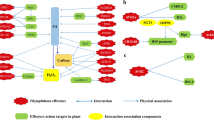
Abstract
Several plant pathogenic oomycetes have been under investigation using modern molecular approaches. Genome sequencing and annotations are underway or near to completion for some of the species. Pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules (PAMPs) and effector molecules perform inter- and intracellular tasks as adaptation factors and manipulators of the defence network. Hundreds of secreted putative effectors have been discovered and conserved molecular patterns such as RXLR and EER motifs have been identified and used for classifications. PAMPs and effectors are recognized directly or indirectly by the pattern recognition receptors at the cell surface including receptor-like kinases and receptor-like proteins, and/or by nucleotide binding site–leucine rich repeat proteins within the cytoplasm. The current knowledge of effectors, immune receptors and the defence network, will help us understand the ‘intricate genetic dance’ between the oomycete pathogens and their hosts. This review concentrates on the recent findings in oomycete-plant interactions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitch, R. B., Janjusevic, R., Stebbins, C. E., & Martin, G. B. (2006). Type III effector AvrPtoB requires intrinsic E3 ubiquitin ligase activity to suppress plant cell death and immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 2851–2856.
Agrios, G. N. (1997). Plant pathology. San Diego: Academic.
Allen, R. L., Bittner-Eddy, P. D., Grenville-Briggs, L. J., Meitz, J. C., Rehmany, A. P., Rose, L. E., et al. (2004). Host-parasite coevolutionary conflict between Arabidopsis and downy mildew. Science, 306, 1957–1960.
Altenbach, D., & Robatzek, S. (2007). Pattern recognition receptors: From the cell surface to intracellular dynamics. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 20, 1031–1039.
Armstrong, M. R., Whisson, S. C., Pritchard, L., Bos, J. I., Venter, E., Avrova, A. O., et al. (2005). An ancestral oomycete locus contains late blight avirulence gene Avr3a, encoding a protein that is recognized in the host cytoplasm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 7766–7771.
Ballvora, A., Ercolano, M. R., Weiss, J., Meksem, K., Bormann, C. A., Oberhagemann, P., et al. (2002). The R1 gene for potato resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) belongs to the leucine zipper/NBS/LRR class of plant resistance genes. Plant Journal, 30, 361–371.
Bhattacharjee, S., Hiller, N. L., Liolios, K., Win, J., Kanneganti, T. D., Young, C., et al. (2006). The malarial host-targeting signal is conserved in the Irish potato famine pathogen. PLoS Pathogens, 2, e50.
Birch, P. R., Rehmany, A. P., Pritchard, L., Kamoun, S., & Beynon, J. L. (2006). Trafficking arms: Oomycete effectors enter host plant cells. Trends in Microbiology, 14, 8–11.
Bittner-Eddy, P. D., Allen, R. L., Rehmany, A. P., Birch, P., & Beynon, J. L. (2003). Use of suppression subtractive hybridization to identify downy mildew gene expressed during infection of Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular Plant Pathology, 4, 501–507.
Borhan, M. H., Holub, E. B., Beynon, J. L., Rozwadowski, K., & Rimmer, S. R. (2004). The Arabidopsis TIR-NB-LRR gene RAC1 confers resistance to Albugo candida (white rust) and is dependent on EDS1 but not PAD4. Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions, 17, 711–719.
Bos, J. I., Kanneganti, T. D., Young, C., Cakir, C., Huitema, E., Win, J., et al. (2006). The C-terminal half of Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR3a is sufficient to trigger R3a-mediated hypersensitivity and suppress INF1-induced cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Journal, 48, 165–176.
Brunner, F., Rosahl, S., Lee, J., Rudd, J. J., Geiler, C., Kauppinen, S., et al. (2002). Pep-13, a plant defense-inducing pathogen-associated pattern from Phytophthora transglutaminases. EMBO Journal, 21, 6681–6688.
Catanzariti, A. M., Dodds, P. N., Lawrence, G. J., Ayliffe, M. A., & Ellis, J. G. (2006). Haustorially expressed secreted proteins from flax rust are highly enriched for avirulence elicitors. Plant Cell, 18, 243–256.
Catanzariti, A. M., Dodds, P. N., & Ellis, J. G. (2007). Avirulence proteins from haustoria-forming pathogens. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 269, 181–188.
Chisholm, S. T., Dahlbeck, D., Krishnamurthy, N., Day, B., Sjolander, K., & Staskawicz, B. J. (2005). Molecular characterization of proteolytic cleavage sites of the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrRpt2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 2087–2089.
Chisholm, S. T., Coaker, G., Day, B., & Staskawicz, B. J. (2006). Host-microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell, 124, 803–814.
Cooper, A. J., Woods-Tör, A., & Holub, E. B. (2002). Albugo candida (White rust) suppresses resistance to downy mildew pathogens in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings 6th Conference of EFPP, Plant Protection Science, 38 (Special issue), 474–476.
Dangl, J. L. (2007). Plant science. Nibbling at the plant cell nucleus. Science, 315, 1088–1089.
Daxberger, A., Nemak, A., Mithofer, A., Fliegmann, J., Ligterink, W., Hirt, H., et al. (2007). Activation of members of a MAPK module in beta-glucan elicitor-mediated non-host resistance of soybean. Planta, 225, 1559–1571.
Ellis, J., Catanzariti, A. M., & Dodds, P. (2006). The problem of how fungal and oomycete avirulence proteins enter plant cells. Trends in Plant Science, 11, 61–63.
Eulgem, T., Tsuchiya, T., Wang, X. J., Beasley, B., Cuzick, A., Tör, M., et al. (2007). EDM2 is required for RPP7-dependent disease resistance in Arabidopsis and affects RPP7 transcript levels. Plant Journal, 49, 829–839.
Fritz-Laylin, L. K., Krishnamurthy, N., Tör, M., Sjolander, K. V., & Jones, J. D. (2005). Phylogenomic analysis of the receptor-like proteins of rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 138, 611–623.
Felix, G., Duran, J. D., Volko, S., & Boller, T. (1999). Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant Journal, 18, 265–276.
Gaulin, E., Jauneau, A., Villalba, F., Rickauer, M., Esquerre-Tugaye, M. T., & Bottin, A. (2002). The CBEL glycoprotein of Phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae is involved in cell wall deposition and adhesion to cellulosic substrates. Journal of Cell Science, 115, 4565–4575.
Gaulin, E., Drame, N., Lafitte, C., Torto-Alalibo, T., Martinez, Y., Ameline-Torregrosa, C., et al. (2006). Cellulose binding domains of a Phytophthora cell wall protein are novel pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Plant Cell, 18, 1766–1777.
Gouget, A., Senchou, V., Govers, F., Sanson, A., Barre, A., Rouge, P., et al. (2006). Lectin receptor kinases participate in protein–protein interactions to mediate plasma membrane–cell wall adhesions in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 40, 81–90.
Göker, M., Reithmuller, A., Voglmayr, H., Weiss, M., & Oberwinkler, F. (2004). Phylogeny of Hyaloperonospora based on nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer sequences. Mycological Progress, 3, 83–94.
Grenville-Briggs, L. J., & van West, P. (2005). The biotrophic stages of oomycete-plant interactions. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 57, 217–243.
Guo, J., Jiang, R. H., Kamphuis, L. G., & Govers, F. (2006). A cDNA-AFLP based strategy to identify transcripts associated with avirulence in Phytophthora infestans. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 43, 111–123.
Guttman, D. S., Gropp, S. J., Morgan, R. L., & Wang, P. W. (2006). Diversifying selection drives the evolution of the type III secretion system pilus of Pseudomonas syringae. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 2342–2354.
Hahn, M. G. (1996). Microbial elicitors and their receptors in plants. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 34, 387–412.
Hahn, M., & Mendgen, K. (2001). Signal and nutrient exchange at biotrophic plant fungus interfaces. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 4, 322–327.
Hardham, A. R. (2007). Cell biology of plant–oomycete interactions. Cellular Microbiology, 9, 31–39.
Hiller, N. L., Bhattacharjee, S., van Ooij, C., Liolios, K., Harrison, T., Lopez-Estrano, C., et al. (2004). A host-targeting signal in virulence proteins reveals a secretome in malarial infection. Science, 306, 1934–1937.
Holub, E. B. (2001). The arms race is ancient history in Arabidopsis, the wildflower. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2, 516–527.
Holub, E. B. (2006). Evolution of parasitic symbioses between plants and filamentous microorganisms. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 9, 397–405.
Holub, E. B. (2008). Natural history of Arabidopsis thaliana and oomycete symbioses. European Journal of Plant Pathology, (in press).
Huang, S., van der Vossen, E. A., Kuang, H., Vleeshouwers, V. G., Zhang, N., Borm, T. J., et al. (2005). Comparative genomics enabled the isolation of the R3a late blight resistance gene in potato. Plant Journal, 42, 251–261.
Ingle, R. A., Carstens, M., & Denby, K. J. (2006). PAMP recognition and the plant–pathogen arms race. Bioessays, 28, 880–889.
Jones, J. D., & Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature, 444, 323–329.
Kamoun, S. (2003). Molecular genetics of pathogenic oomycetes. Eukaryotic Cell, 2, 191–199.
Kamoun, S. (2006). A catalogue of the effector secretome of plant pathogenic oomycetes. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 44, 41–60.
Kamoun, S. (2007). Groovy times: Filamentous pathogen effectors revealed. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 10, 358–365.
Kemmerling, B., Schwedt, A., Rodriguez, P., Mazzotta, S., Frank, M., Qamar, S. A., et al. (2007). The BRI1-associated kinase 1, BAK1, has a brassinolide-independent role in plant cell-death control. Current Biology, 17, 1116–1122.
Lee, S. W., Han, S. W., Bartley, L. E., & Ronald, P. C. (2006). Colloquium review. Unique characteristics of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae AvrXa21 and implications for plant innate immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 18395–18400.
Lotze, M. T., Zeh, H. J., Rubartelli, A., Sparvero, L. J., Amoscato, A. A., Washburn, N. R., et al. (2007). The grateful dead: Damage associated molecular pattern molecules and reduction/oxidation regulate immunity. Immunological Reviews, 220, 60–82.
Medzhitov, R. (2007). Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature, 449, 819–826.
Medzhitov, R., & Janeway, C. A. (2002). Decoding the patterns of self and non-self by the innate immune system. Science, 296, 298–300.
Meyers, B. C., Kozik, A., Griego, A., Kuang, H., & Michelmore, R. W. (2003). Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 15, 809–834.
Mithofer, A., Fliegmann, J., Daxberger, A., Ebel, C., Neuhaus-Url, G., Bhagwat, A. A., et al. (2001). Induction of H(2)O(2) synthesis by beta-glucan elicitors in soybean is independent of cytosolic calcium transients. FEBS Letters, 508, 191–195.
Morgan, W., & Kamoun, S. (2007). RXLR effectors of plant pathogenic oomycetes. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 10, 332–338.
Mudgett, M. B., & Staskawicz, B. J. (1998). Protein signaling via type III secretion pathways in phytopathogenic bacteria. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 1, 109–114.
Nishimura, M. T., Stein, M., Hou, B. H., Vogel, J. P., Edwards, H., & Somerville, S. C. (2003). Loss of a callose synthase results in salicylic acid-dependent disease resistance. Science, 301, 969–972.
Nurnberger, T., Nennstiel, D., Jabs, T., Sacks, W. R., Hahlbrock, K., & Scheel, D. (1994). High affinity binding of a fungal oligopeptide elicitor to parsley plasma membranes triggers multiple defense responses. Cell, 78, 449–460.
O’Connell, R. J., & Panstruga, R. (2006). Tete a tete inside a plant cell. Establishing compatibility between plants and biotrophic fungi and oomycetes. New Phytologist, 171, 699–718.
Pieterse, C. M., van West, P., Verbakel, H. M., Brasse, P. W., van den Berg-Velthuis, G. C., & Govers, F. (1994). Structure and genomic organization of the ipiB and ipiO gene clusters of Phytophthora infestans. Gene, 138, 67–77.
Qutob, D., Kamoun, S., & Gijzen, M. (2002). Expression of a Phytophthora sojae necrosis-inducing protein occurs during transition from biotrophy to necrotrophy. Plant Journal, 32, 361–373.
Qutob, D., Kemmerling, B., Brunner, F., Kufner, I., Engelhardt, S., Gust, A. A., et al. (2006). Phytotoxicity and innate immune responses induced by Nep1-like proteins. Plant Cell, 18, 3721–3744.
Rehmany, A. P., Gordon, A., Rose, L. E., Allen, R. L., Armstrong, M. R., Whisson, S. C., et al. (2005). Differential recognition of highly divergent downy mildew avirulence gene alleles by RPP1 resistance genes from two Arabidopsis lines. Plant Cell, 17, 1839–1850.
Robatzek, S. (2007). Vesicle trafficking in plant immune responses. Cellular Microbiology, 9, 1–8.
Robatzek, S., Chinchilla, D., & Boller, T. (2006). Ligand-induced endocytosis of the pattern recognition receptor FLS2 in Arabidopsis. Genes and Development, 20, 537–542.
Senchou, V., Weide, R., Carrasco, A., Bouyssou, H., Pont-Lezica, R., Govers, F., et al. (2004). High affinity recognition of a Phytophthora protein by Arabidopsis via an RGD motif. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 61, 502–509.
Shan, W., Cao, M., Leung, D., & Tyler, B. M. (2004). The Avr1b locus of Phytophthora sojae encodes an elicitor and a regulator for avirulence on soybean plants carrying resistance gene Rps1b. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 17, 394–403.
Sharp, J. K., Valent, B., & Albersheim, P. (1984). Purification and partial characterization of a beta-glucan fragment that elicits phytoalexin accumulation in soybean. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 259, 11312–11320.
Shen, Q. H., & Schulze-Lefert, P. (2007). Rumble in the nuclear jungle: Compartmentalization, trafficking, and nuclear action of plant immune receptors. EMBO Journal, 26, 4293–4301.
Shen, K. A., Chin, D. B., Arroyo-Garcia, R., Ochoa, O. E., Lavelle, D. O., Wroblewski, T., et al. (2002). Dm3 is one member of a large constitutively expressed family of nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat encoding genes. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 15, 251–61.
Shen, Q. H., Saijo, Y., Mauch, S., Biskup, C., Bieri, S., Keller, B., et al. (2007). Nuclear activity of MLA immune receptors links isolate-specific and basal disease-resistance responses. Science, 315, 1098–1101.
Shiu, S. H., Karlowski, W. M., Pan, R., Tzeng, Y. H., Mayer, K. F., & Li, W. H. (2004). Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell, 16, 1220–1234.
Sinapidou, E., Williams, K., Nott, L., Bahkt, S., Tör, M., Bittner-Eddy, P., et al. (2004). Two TIR:NB:LRR genes are required to specify resistance to Peronospora parasitica isolate Cala2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal, 38, 898–909.
Sohn, K. H., Lei, R., Nemri, A., & Jones, J. D. (2007). The downy mildew effector proteins ATR1 and ATR13 promote disease susceptibility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell, 19, 4077–4090. DOI 10.1105/tpc.107.054262.
Takahashi, Y., Nasir, K. H., Ito, A., Kanzaki, H., Matsumura, H., Saitoh, H., et al. (2007). A high-throughput screen of cell-death-inducing factors in Nicotiana benthamiana identifies a novel MAPKK that mediates INF1-induced cell death signaling and non-host resistance to Pseudomonas cichorii. Plant Journal, 49, 1030–1040.
Tör, M., Holub, E. B., Brose, E., Musker, R., Gunn, N., Can, C., et al. (1994). Map positions of three loci in Arabidopsis thaliana associated with isolate-specific recognition of Peronospora parasitica (downy mildew). Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions, 7, 214–222.
Tör, M., Gordon, P., Cuzick, A., Eulgem, T., Sinapidou, E., Mert, F., et al. (2002). Arabidopsis SGT1b is required for defence signaling conferred by several downy mildew (Peronospora parasitica) resistance genes. Plant Cell, 14, 993–1003.
Tör, M., Yemm, A., & Holub, E. (2003). Role of proteolysis in R-gene mediated defence in plants. Molecular Plant Pathology, 4, 287–296.
Tyler, B. M., Tripathy, S., Zhang, X., Dehal, P., Jiang, R. H., Aerts, A., et al. (2006). Phytophthora genome sequences uncover evolutionary origins and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science, 313, 1261–1266.
Umemoto, N., Kakitani, M., Iwamatsu, A., Yoshikawa, M., Yamaoka, N., & Ishida, I. (1997). The structure and function of a soybean beta-glucan-elicitor-binding protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94, 1029–1034.
Van Damme, M., Andel, A., Huibers, R. P., Panstruga, R., Weisbeek, P. J., & Van den Ackerveken, G. (2005). Identification of Arabidopsis loci required for susceptibility to the downy mildew pathogen Hyaloperonospora parasitica. Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions, 18, 583–592.
Van den Ackerveken, G., Marois, E., & Bonas, U. (1996). Recognition of the bacterial avirulence protein AvrBs3 occurs inside the host plant cell. Cell, 87, 1307–1316.
van der Biezen, E. A., Juwana, H., Parker, J. E., & Jones, J. D. G. (2000). cDNA-AFLP display for the isolation of Peronospora parasitica genes expressed during infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 13, 895–898.
Voegele, R. T., & Mendgen, K. (2003). Rust haustoria: Nutrient uptake and beyond. New Phytologist, 159, 93–100.
Voegele, R. T, Struck, C., Hahn, M., & Mendgen K. (2001). The role of haustoria in sugar supply during infection of broad bean by the rust fungus Uromyces fabae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 8133–8138.
Vogel, J., & Somerville, S. (2000). Isolation and characterization of powdery mildew-resistant Arabidopsis mutants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 1897–1902.
Vogel, J. P., Raab, T. K., Schiff, C., & Somerville, S. C. (2002). PMR6, a pectate lyase-like gene required for powdery mildew susceptibility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 14, 2095–2106.
Whisson, S. C., Boevink, P. C., Moleleki, L., Avrova, A. O., Morales, J. G., Gilroy, E. M., et al. (2007). A translocation signal for delivery of oomycete effector proteins into host plant cells. Nature, 450, 115–118.
Win, J., Morgan, W., Bos, J., Krasileva, K. V., Cano, L. M., Chaparro-Garcia, A., et al. (2007). Adaptive evolution has targeted the C-Terminal domain of the RXLR effectors of plant pathogenic oomycetes. Plant Cell, 19, 2349–2369.
Wroblewski, T., Piskurewicz, U., Tomczak, A., Ochoa, O., & Michelmore, R. W. (2007). Silencing of the major family of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in lettuce results in the loss of multiple resistance specificities. Plant Journal, 51, 803–818.
Xiao, F., Giavalisco, P., & Martin, G. B. (2007). Pseudomonas syringae type III effector AvrPtoB is phosphorylated in plant cells on serine 258, promoting its virulence activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 30737–30744.
Yamamizo, C., Kuchimura, K., Kobayashi, A., Katou, S., Kawakita, K., Jones, J. D., et al. (2006). Rewiring mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by positive feedback confers potato blight resistance. Plant Physiology, 140, 681–692.
Zipfel, C., & Felix, G. (2005). Plants and animals: A different taste for microbes. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 8, 353–360.
Zipfel, C., Kunze, G., Chinchilla, D., Caniard, A., Jones, J. D., Boller, T., et al. (2006). Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell, 125, 749–760.
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to colleagues in the oomycete field for invigorating discussions. I would like to thank Prof Eric Holub and Dr. Alison-Woods Tör for critically reading the manuscript and three anonymous referees for their constructive suggestions. Related research in my laboratory has been supported by grants BB/D000750/1, BB/C509490/1 and BB/E02484X/1 from the UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tör, M. Tapping into molecular conversation between oomycete plant pathogens and their hosts. Eur J Plant Pathol 122, 57–69 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9288-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9288-z