Abstract
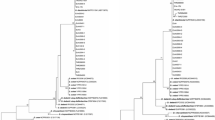
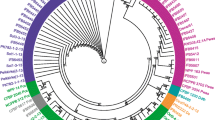
Plant pathogenic enterobacteria in the genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya (formerly classified as Erwinia) were isolated from diseased potato stems and tubers. The isolated bacteria were identified as P. atrosepticum, P. carotovorum and pathogens in the genus Dickeya with PCR tests. Furthermore, Dickeya strains were isolated from river water samples throughout the country. Phylogenetic analysis with 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer sequences suggested that the Dickeya strains could be divided into three groups, two of which were isolated from potato samples. Phylogenetic analysis with 16S rDNA sequences and growth at 39°C suggested that one of the groups corresponds to D. dianthicola, a quarantine pathogen in greenhouse cultivation of ornamentals, while two of the groups did not clearly resemble any of the previously characterised Dickeya species. Field trials with the strains indicated that D. dianthicola-like strains isolated from river samples caused the highest incidence of rotting and necrosis of potato stems, but some of the Dickeya strains isolated from potato samples also caused symptoms. The results showed that although P. atrosepticum is still the major cause of blackleg in Finland, virulent Dickeya strains were commonly present in potato stocks and rivers. This is the first report suggesting that Dickeya, originally known as a pathogen in tropical and warm climates, may cause diseases in potato in northern Europe.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrova, A. O., Hyman, L. J., Toth, R. L., & Toth, I. K. (2002). Application of amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting for taxonomy and identification of the soft rot bacteria Erwinia carotovora and Erwinia chrysanthemi. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 68, 1499–1508.
Boccara, M., Vedel, R., Lalo, D., Lebrun, M. H., & Lafay, J. F. (1991). Genetic diversity and host range in strains of Erwinia chrysanthemi. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions, 4, 293–299.
Cappaert, M. R., Powelson, M. L., Franc, G. D., & Harrison, M. D. (1988). Irrigation water as a source of inoculum of soft rot erwinias for aerial stem rot of potatoes. Phytopathology, 78, 1668–1672.
Cother, E. J., Bradley, J. K., Gillings, M. R., & Fahy, P. C. (1992). Characterization of Erwinia chrysanthemi biovars in alpine water sources by biochemical properties, GLC fatty acid analyses and genomic DNA fingerprinting. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 73, 99–107.
DeBoer, S. H., & Ward, L. J. (1995). PCR detection of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica associated with potato tissue. Phytopathology, 85, 854–858.
Dupuis, B., Michelante, D., Garcia, N., Nimal, C., & Stilman, D. (2005). Evolution of Erwinia’s potato contaminations in the Walloon Region during the seasons 2003 and 2004: Analysis of field and storage infections. Paper presented at the 16th triennial conference of the EAPR, European Association for Potato Research, Bilbao, Spain.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792–1797.
Fessehaie, A., De Boer, S. H., & Levesque, C. A. (2002). Molecular characterization of DNA encoding 16S-23S rRNA intergenic spacer regions and 16S rRNA of pectolytic Erwinia species. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 48, 387–398.
Gardan, L., Gouy, C., Christen, R., & Samson, R. (2003). Elevation of three subspecies of Pectobacterium carotovorum to species level: Pectobacterium atrosepticum sp. nov., Pectobacterium betavasculorum sp. nov. and Pectobacterium wasabiae sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 381–391.
Hasegawa, M., Kishino, H., & Yano, T. (1985). Dating the human–ape split by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 22, 160–174.
Hélias, V., Le Roux, A. C., Boishardy, M., Aujean, J. M., Copin, P., Perramant, M., et al. (2004). Erwinias causing blackleg in France: Species/subspecies and their distribution in 2003. Paper presented at the E.A.P.R. pathology section meeting, Lille, France.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Ronquist, F. (2001). MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics, 17, 754–755.
Janse, J. D., & Ruissen, M. A. (1988). Characterization and classification of Erwinia chrysanthemi strains from several hosts in the Netherlands. Phytopathology, 78, 800–808.
Lee, Y.-A., & Chen, K.-P. (2002). First report of bacterial soft rot of white flowered calla lily caused by Erwinia chrysanthemi in Taiwan. Plant Disease, 86, 1273–1273.
Littell, R. C., Milliken, G. A., Stroup, W. W., & Wolfinger, R. D. (1996). SAS system for mixed models. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
Nassar, A., Darrasse, A., Lemattre, M., Kotoujansky, A., Dervin, C., Vedel, R., et al. (1996). Characterization of Erwinia chrysanthemi by pectinolytic isozyme polymorphism and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified fragments of pel genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 2228–2235.
Norman, D. J., Yuen, J. M. F., Resendiz, R., & Boswell, J. (2003). Characterization of Erwinia populations from nursery retention ponds and lakes infecting ornamental plants in Florida. Plant Disease, 87, 193–196.
Palacio-Bielsa, A., Cambra, M. A., & Lopez, M. M. (2006). Characterisation of potato isolates of Dickeya chrysanthemi in Spain by a microtitre system for biovar determination. Annals of Applied Biology, 148, 157–164.
Pérombelon, M. C. M. (2002). Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: An overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathology, 51, 1–12.
Pérombelon, M. C. M., & Hyman, L. J. (1987). Frequency of Erwinia carotovora in the Alyth Burn in eastern Scotland and the sources of the bacterium. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 63, 281–291.
Pérombelon, M. C. M., & van der Wolf, J. M. (Eds.) (2002). Methods for the detection and quantification of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. atrosepticum) on potatoes: A laboratory manual. Invergowrie, Dundee, Scotland: Scottish Crop Research Institute.
Persson, P. (1991). Soft rot Erwinia species attacking potatoes in Sweden. Plant Protection Reports Dissertations 20. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
Pirhonen, M., & Palva, E. T. (1988). Occurrence of bacteriophage T4 receptor in Erwinia carotovora. Molecular and General Genetics, 214, 170–172.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Samson, R., Legendre, J. B., Christen, R., Fischer le Saux, M., Achouak, W., & Gardan, L. (2005). Transfer of Pectobacterium chrysanthemi (Burkholder et al. 1953) Brenner et al. 1973 and Brenneria paradisiaca to the genus Dickeya gen. nov. as Dickeya chrysanthemi comb. nov. and Dickeya paradisiaca comb. nov. and delineation of four novel species, Dickeya dadantii sp. nov., Dickeya dianthicola sp. nov., Dickeya dieffenbachiae sp. nov. and Dickeya zeae sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 55, 1415–1427.
Schaad, N. W., Jones, J. B., & Chun, W. (Eds.) (2001). Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria. St. Paul, Minnesota, USA: The American Phytopathological Society.
Toth, I. K., Avrova, A. O., & Hyman, L. J. (2001). Rapid identification and differentiation of the soft rot erwinias by 16S-23S intergenic transcribed spacer-PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 67, 4070–4076.
Toth, I. K., Bell, K. S., Holeva, M. C., & Birch, P. R. J. (2003). Soft rot erwiniae: From genes to genomes. Molecular Plant Pathology, 4, 17–30.
Waleron, M., Waleron, K., Podhajska, A. J., & Lojkowska, E. (2002). Genotyping of bacteria belonging to the former Erwinia genus by PCR-RFLP analysis of a recA gene fragment. Microbiology, 148, 583–595.
Acknowledgments
Laboratory assistants Satu Kostamo and Aila Sirén, technician Tuula Viljanen are thanked for their assistance. Dr. Ian Toth is thanked for the P. atrosepticum strains SCRI1039 and SCRI1043. We are also grateful to laboratory engineer Anneli Virta for the sequencing, to biometrician Lauri Jauhiainen for help in statistical analyses, to GIS expert Hannu Ojanen for preparing the map of the water sample sites and to Dr. Fred Stoddard for language checking and critically reading the manuscript. Finnish potato processing and seed potato companies and the Finnish Food Safety Authority Evira are thanked for samples and plant material and Finnzymes Ltd for the real-time PCR diagnostics. The present work was financially supported by the Finnish Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (4868/501/03) and MTT Agrifood Research Finland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laurila, J., Ahola, V., Lehtinen, A. et al. Characterization of Dickeya strains isolated from potato and river water samples in Finland. Eur J Plant Pathol 122, 213–225 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9274-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9274-5