Abstract
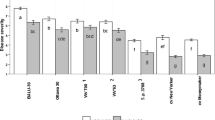
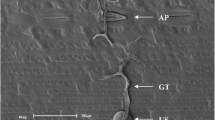
Potato and tomato are the two major hosts for Phytophthora infestans causing late blight. The susceptibility of leaves and whole plants of Solanum nigrum, S. villosum, and S. scabrum to infection by P. infestans was tested under laboratory conditions. Out of 39 plants representing 38 different S. nigrum accessions, 16 were highly resistant (seven accessions did not show any symptoms of infection, nine were highly resistant showing necrotic lesions in the place of infection), and 23 plants of S. nigrum were colonized by, at least, 1 of the 2 isolates of P. infestans (17 accessions were infected with two P. infestans isolates, and 6 accessions showed different reactions depending on the isolate used for inoculation). Three accessions of S. villosum, and one accession of S. scabrum were tested and did not show any symptoms of infection. The majority of S. nigrum accessions infected by P. infestans in a detached leaf assay were also infected in the whole plant assay. The reaction of field- and greenhouse-grown plants to inoculation with P. infestans in detached leaf assays was similar, but in some cases leaves from field-grown plants reacted as resistant in comparison with the leaves from greenhouse-grown plants, which were susceptible.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakonyi, J., Láday, M., Dula, T., & Érsek, T. (2002). Characterisation of Phytophthora infestans isolates from Hungary. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 108, 139–146.
Bectell, M. C., Smart, C. D., Haney, C. H., & Fry, W. E. (2006). Host–pathogen interactions between Phytophthora infestans and the solanaceous hosts Calibrachoa x hybridus, Petunia x hybrida, and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Disease, 90, 24–32.
Black, W., Mastenbroek, C., Mills, W. R., & Peterson, L. C. (1953). A proposal for an international nomenclature of races of Phytophthora infestans and of genes controlling immunity in Solanum demissum derivatives. Euphytica, 2, 173–178.
Carnegie, S. F., & Colhoun, J. (1982). Susceptibility of potato leaves to Phytophthora infestans in relation to plant age and leaf position. Phytopathologische Zeitschrift, 104, 157–167.
Colon, L. T., Eijlander, R., Budding, D. J., Pieters, M. M. J., Hoogendoorn, J., & Van-Ijzendoorn, M. T. (1993). Resistance to potato late blight (Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary) in Solanum nigrum, S. villosum and their sexual hybrids with S. tuberosum and S. demissum. Euphytica, 66, 55–64.
Daggett, S. S., Götz, E., & Therrien, C. D. (1993). Phenotypic changes in populations of Phytophthora infestans from Germany. Phytopathology, 83, 319–323.
Dandurand, L. M., Knudsen, G. R., & Eberlein, C. V. (2006). Susceptibility of five nightshade (Solanum) species to Phytophthora infestans. American Journal of Potato Research, 83, 205–210.
Deahl, K. L., Shaw, D. S., & Cooke, L. R. (2004). Natural occurence of Phytophthora infestans on black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) in Wales. Plant Disease, 88, 771.
Edmonds, J. M., & Chweya, J. A. (1997). Black nightshades Solanum nigrum L. and related species. Promoting the conservation and use of underutilized and neglected crops, vol. 15. Rome, Italy: Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research, Gatersleben/IPGRI.
Flier, W. G., van der Bosch, G. M. B, & Turkensteen, L. J. (2003). Epidemiological importance of Solanum sisymbriifolium, S. nigrum and S. dulcamara as alternative hosts for Phytophthora infestans. Plant Pathology, 52, 595–603.
Govers, F. (2005). Late blight: The perspective from the pathogen. In A. J. Havenkort & P.C. Struik (Eds.), Potato in progress: Science meets practice (pp. 245–254). The Netherlands: Wageningen Academic Publishers.
Heath, M. C. (2000). Non-host resistance and nonspecific plant defences. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 3, 315–319.
Hirst, J. M., & Steadman, O. J. (1960). The epidemiology of Phytophthora infestans. II. The source of infection. Annals of Applied Biology, 48, 489–517.
Horsman, K., Bergervoet, J. E. M., & Jacobsen, E. (1997). Somatic hybridization between Solanum tuberosum and species of the Solanum nigrum complex: Selection of vigorously growing and flowering plants. Euphytica, 96, 345–352.
Malcolmson, J. F., & Black, W. (1966). New R genes in Solanum demissum Lindl. and their complementary races of Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary. Euphytica, 15, 199–203.
Perez, W. G., Gamboa, J. S., Falcon, Y. V., Coca, M., Raymundo, R. M., & Nelson, R. J. (2001). Genetic structure of Peruvian populations of Phytophthora infestans. Phytopathology, 91, 956–965.
Platt, H. W. (1999). Response of solanaceous cultivated plants and weed species to inoculation with A1 or A2 mating type strains of Phytophthora infestans. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 21, 301–307.
Śliwka, J., Sobkowiak, S., Lebecka, R., Avendaño-Córcoles, A., & Zimnoch-Guzowska, E. (2007). Mating type, virulence, aggressiveness and metalaxyl resistance of isolates of Phytophthora infestans in Poland. Potato Research, 49(3), 155–166.
Stankiewicz, M., Gadomski, G., & Gawroński, W. (2001). Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships of triazine-resistant and triazine-susceptible biotypes of Solanum nigrum – analysis using RAPD markers. Weed Research, 41, 287–300.
Thordal-Christensen, H. (2003). Fresh insight into process of nonhost resistance. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6, 351–357.
Vleeshouwers, V. G. A. A., van Dooijeweert, W., Govers, F., Kamoun, S., & Colon, L. T. (2000). The hypersensitive response is associated with host and nonhost resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Planta, 210, 853–864.
Zarzycka, H. (1997). Ocena zmian zachodz1cych w polskiej populacji Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary. Biuletyn Instytutu Ziemniaka, 48, 125–135.
Zarzycka, H. (2001). Assessment of resistance to Phytophthora infestans in tuber slices and whole tubers. In IHAR Monografie i Rozprawy Naukowe 10a (pp. 78–80). Radzików, Poland: Plant Breeding and Acclimatization Institute.
Zimnoch-Guzowska, E., Lebecka, R., Kryszczuk, A., Maciejewska, U., Szczerbakowa, A., & Wielgat, B. (2003). Resistance to Phytophthora infestans in somatic hybrids of Solanum nigrum L. and diploid potato. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 107, 43–48.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the State Committee for Scientific Research, Warsaw, Poland – Grant 2 P06A 013 26, 2004–2006. It is a great pleasure to thank Ewa Zimnoch-Guzowska and Jadwiga Śliwka (IHAR, Młochów, Poland) for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebecka, R. Host–pathogen interaction between Phytophthora infestans and Solanum nigrum, S. villosum, and S. scabrum . Eur J Plant Pathol 120, 233–240 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9211-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9211-z