Abstract
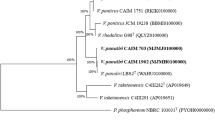
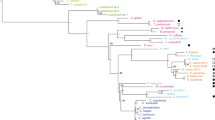
Sequence parts of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of nuclear ribosomal DNA were analysed to screen for the intraspecific variability of a non-coding genomic region in 15 Plasmopara halstedii populations of different pathotype and geographic origin. Samples revealed uniformity in a ca. 790 Bp fragment comprising of the ITS-1, 5.8S and front parts of the ITS-2. In contrast, clear differences were found in a ca. 810 Bp fragment of the ITS-2 thus allowing differentiation between populations of pathotype 100, 310 and 330 and a group of populations representing pathotypes 700, 701, 703, 710 and 730. Samples of pathotypes 700 to730 originated from Slovakia, France, and Germany, but were uniform in both ITS sequence parts, thus indicating very recent origin of these highly aggressive physiological races. The potential use of ITS sequences for pathotype differentiation and phylogenetic studies in P. halstedii is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachofer M (2004) Molekularbiologische Populationsstudien an Plasmopara halstedii, dem Falschen Mehltau der Sonnenblume Dissertation, Universität Hohenheim Germany, (pp. 1–140).
O Constantinescu J Fatehi (2002) ArticleTitlePeronospora-like fungi (Chromista, Peronosporales) parasitic to Brassicaceae and related hosts Nova Hedwigia 74 291–338 Occurrence Handle10.1127/0029-5035/2002/0074-0291
Constantinescu O, Voglmayr H, Fatehi J and Thines M (2005) The taxonomy and nomenclature of Plasmopara (Chromista, Peronosporales). Taxon 54: 813–821.
DEL Cooke A Drenth JM Duncan G Wagels CM Brasier (2000) ArticleTitleA molecular phylogeny analysis of Phytophthora and related Oomycetes Fungal Genetics and Biology 30 17–32 Occurrence Handle10955905 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtlekt78%3D Occurrence Handle10.1006/fgbi.2000.1202
DEL Cooke NA Williams B Williamson JM Duncan (2002) An ITS-based phylogenetic analysis of the relationships between Peronospora and Phytophthora PTN Spencer-Phillips U Gisi A Lebeda (Eds) Advances in Downy Mildew Research NumberInSeriesVol. 1 Kluwer Acad. Publishers Dordrecht, The Netherlands 161–165
J Felsenstein (1985) ArticleTitleConfidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using bootstrap Evolution 39 783–791 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2408678
O. Gascuel (1997) ArticleTitleBIONJ: An improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data Molecular Biology and Evolution 14 685–695 Occurrence Handle9254330 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksVahs7o%3D
M Göker A Riethmüller H Voglmayr M. Weiß F. Oberwinkler (2004) ArticleTitlePhylogeny of Hyaloperonospora based on nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer sequences Mycological Progress 3 83–176 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11557-006-0079-7
TJ Gulya (1995) Proposal of a revised system of classifying races of sunflower downy mildew Proc. 17th Sunflower Research Workshop Fargo 76–78
TJ Gulya KY Rashid SM Masirevic (1997) Sunflower diseases AA Schneiter (Eds) Sunflower Technology and Production American Soc Agronomy, Wisconsin, USA 263–379
F Intelmann O Spring (2002) ArticleTitleAnalysis of total DNA by minisatellite and simple-sequence repeat primers for the use of population studies in Plasmopara halstedi Canadian Journal of Microbiology 48 555–559 Occurrence Handle12166683 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvFersLc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1139/w02-046
K Katoh K Misawa K Kuma T Miyata (2002) ArticleTitleMAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform Nucleic Acids Research 30 3059–3066 Occurrence Handle12136088 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlslOqu7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/gkf436
MC Leclerc J Guillot M Deville (2000) ArticleTitleTaxonomic and phylogenetic analysis of Saprolegniaceae (Oomycetes) inferred from LSU rDNA and ITS sequence comparisons Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 77 369–377 Occurrence Handle10959566 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmsVSksbg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1002601211295
EE Leppik (1966) ArticleTitleOrigin and specialization of Plasmopara halstedii complex on the Compositae FAO Plant Protection Bulletin 14 72–76
JM Moncalvo HH Wang RS Hseu (1995) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic relationships in Ganoderma inferred from the internal transcribed spacers and 25S ribosomal DNA seuqences Mycologia 87 223–238 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXms12ltbY%3D
N Novotelnova (1962) ArticleTitlePlasmopara halstedii (Farl) Berl et de Toni Botanical Journal of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR 47 IssueID7 970–981
AB Petersen S Rosendahl (2000) ArticleTitlePhylogeny of the Peronosporomycetes (Oomycota) based on partial sequences of the large ribosomal subunit (LSU rDNA) Mycological Research 104 1295–1303 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXot1Cqsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0953756200003075
D Posada KA Crandall (1998) ArticleTitleModeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution Bioinformatics 14 IssueID9 817–818 Occurrence Handle9918953 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktlCltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817
D Posada TR Buckley (2004) ArticleTitleModel selection and model averaging in phylogenetics: Advantages of the AIC and Bayesian approaches over likelihood ratio tests Systematic Biology 53 793–808 Occurrence Handle15545256 Occurrence Handle10.1080/10635150490522304
A Riethmüller H Voglmayr M Göker M Weiß F Oberwinkler (2002) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic relationships of the downy mildews (Peronosporales) and related groups based on nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences Mycologia 94 834–849
P Roeckel-Drevet V Coelho J Tourvieille P Nicolas D Tourvieille de Labrouhe (1997) ArticleTitleLack of genetic variability in french identified races of Plasmopara halstedii, the cause of downy mildew in sunflower Helianthus annuus Canadian Journal of Microbiology 43 260–263 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXitFOjs7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1139/m97-036
B Rozynek O Spring (2000) ArticleTitlePathotypes of sunflower in Southern Germany Helia 23 27–34
WE Sackston (1981) Downy mildew of sunflower DM Spencer (Eds) The Downy Mildews Academic Press London 545–575
N Saitou M Nei (1987) ArticleTitleThe neighbour-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees Molecular Biology and Evolution 4 406–425 Occurrence Handle3447015 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7ovFSjsA%3D%3D
O Spring B Rozynek R Zipper (1998) ArticleTitleSingle spore infections with sunflower downy mildew Journal of Phytopathology 146 577–579
O Spring H Voglmayr A Riethmüller F Oberwinkler (2003) ArticleTitleCharacterization of a Plasmopara isolate from Helianthus × laetiflorus based on cross infection, morphological, fatty acids and molecular phylogenetic data Mycological Progress 2 163–170 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11557-006-0054-3
Swofford, DL (2002) PAUP* Phylogenetic Analysis Using parsimony (*and Other Methods) version 4b10. Sinauer Massachusetts.
DL Swofford GJ Olsen PJ Waddel DM Hillis (1996) Phylogenetic inference DM Hillis C Maritz BK Mable (Eds) Molecular Systematics Sinauer Associates Sunderland, MA, USA
M Thines H Komjati O Spring (2005) ArticleTitleExceptional length in Plasmopara halstedii ITS is due to multiple repetitions in the ITS-2 region European Journal of Plant Pathology 112 395–398 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXpsVams7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10658-005-6606-6
JN Thompson TJ Gibson F Plewniak F Jeanmougin DG Higgins (1997) ArticleTitleThe ClustalX windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools Nucleic Acid Research 25 4876–4882 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntFyntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
F Viranyi (2002) The sunflower – Plasmopara halstedii pathosystem: Natural and artificially induced coevolution PTN Spencer-Phillips U. Gisi A Lebeda (Eds) Advances in Downy Mildew Research NumberInSeriesVol. 1 Kluwer Acad. Publishers Dordrecht, The Netherlands 167–172
H Voglmayr (2003) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic study of Peronospora and realted genera based on nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences Mycological Research 107 1132–1142 Occurrence Handle14635762 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXotFWlsbo%3D Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0953756203008438
H Voglmayr A Riethmüller M Göker M Weiss F Oberwinkler (2004) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic relationships of Plasmopara, Bremia and other genera of downy mildew pathogens with pyriform haustoria based on Bayesian analysis of partial LSU rDNA sequence data Mycological Research 108 1011–1024 Occurrence Handle15506014 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXns1Onurk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0953756204000954
D Zimmer (1974) ArticleTitlePhysiological specialization between races of Plasmopara halstedii in America and Europe Phytopathology 64 1465–1467 Occurrence Handle10.1094/Phyto-64-1465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spring, O., Bachofer, M., Thines, M. et al. Intraspecific Relationship of Plasmopara halstedii Isolates Differing in Pathogenicity and Geographic Origin Based on ITS Sequence Data. Eur J Plant Pathol 114, 309–315 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-5996-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-5996-9