Abstract
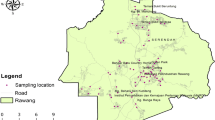
Dust samples were collected from roads of five distinct types of land use zones (National Highway, residential areas, sensitive areas, mining areas, and busy traffic areas) of Dhanbad to determine the pollution characteristics, health risk, and identifying the source of trace elements. The dust samples were segregated into ≤ 60 µm and trace elements like Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn were analysed. Concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, and Mn were observed highest in the mining areas, whereas Ni, Pb, and Zn presented higher concentration values at National Highway and busy traffic zones. Cd showed highest geo-accumulation index (Igeo), contamination factor (Cf), and ecological risk (ER) among all the trace elements. The health risk assessment model was performed to assess the health effects of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic pollutants caused due to multi-elemental exposure on adults and children. The significantly higher HQ (Hazard Quotient) and HI (Hazard Index) values posed by Cr, Fe, and Mn indicated potential non-carcinogenic risks to the people of Dhanbad. Similarly, values of CR (Cancer Risk) for Cd, Cr and Ni were within the range of 10–6–10–4, which indicated to cause carcinogenic risk to the population by the exposure of road dust. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Pearson correlation showed that coal mining activities in Jharia coalfield, coal-based industries like coke-oven plants, coal washeries and heavy vehicular load in the roads of Dhanbad were the major causes of emission of these trace elements.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Acosta, J. A., Faz, A., Kalbitz, K., Jansen, B., & Martínez-Martínez, S. (2014). Partitioning of heavy metals over different chemical fraction in street dust of Murcia (Spain) as a basis for risk assessment. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144, 298–305.
Adachi, K., & Tainosho, Y. (2004). Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environment International, 30(8), 1009–1017.
Ali, M. U., Liu, G., Yousaf, B., Abbas, Q., Ullah, H., Munir, M. A. M., & Fu, B. (2017). Pollution characteristics and human health risks of potentially (eco)toxic elements (PTEs) in road dust from metropolitan area of Hefei, China. Chemosphere, 181, 111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.061.
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2004). Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak Industrial Estate Jordan. Atmospheric Environment, 38(39), 6803–6812.
Alloway, B. J. (Ed.). (2013). Heavy metals in soils: Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer.
Apeagyei, E., Bank, M. S., & Spengler, J. D. (2011). Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmospheric Environment, 45(13), 2310–2323.
Atiemo, M., Ofosu, G., Kuranchie-Mensah, H., Tutu, A., Palm, N., & Blankson, S. (2011). Contamination assessment of heavy metals in road dust from selected roads in Accra, Ghana. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 3(5), 473–480.
Bini, C., & Bech, J. (Eds.). (2014). PHEs environment and human health. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Bourliva, A., Kantiranis, N., Papadopoulou, L., Aidona, E., Christophoridis, C., Kollias, P., et al. (2018). Seasonal and spatial variations of magnetic susceptibility and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in road dusts of Thessaloniki city, Greece: A one-year monitoring period. Science of The Total Environment, 639, 417–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.170.
Chen, H., Teng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2015). Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Science of The Total Environment, 512–513, 143–153.
Cheyns, K., Nkulu, B. L. C., Ngombe, L. K., Asosa, J. N., Haufroid, V., De Putter, T., et al. (2014). Pathways of human exposure to cobalt in Katanga, a mining area of the D.R Congo. Science of The Total Environment, 490, 313–321.
Danielsson, B., Hassoun, E., & Dencker, L. (1982). Embryotoxicity of chromium: Distribution in pregnant mice and effects on embryonic cells in vitro. Archives of Toxicology, 51(3), 233–245.
Dhanbad City Pollution Census. https://www.census2011.co.in/census/district/96-dhanbad. Accessed 26 Aug 2018.
Du, Y., Gao, B., Zhou, H., Ju, X., Hao, H., & Yin, S. (2013). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in urban parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 18, 299–309.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Wong, C. S. C., Aydin, A., Song, Z., You, M., & Li, X. D. (2006). Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou SE China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28(4), 375–391.
Eqani, S. A. M. A. S., Kanwal, A., Bhowmik, A. K., Sohail, M., Ullah, R., Ali, S. M., et al. (2016). Spatial distribution of dust–bound trace elements in Pakistan and their implications for human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 213, 213–222.
Faiz, Y., Tufail, M., Javed, M. T., & ChaudhryNaila-Siddique, M. M. (2009). Road dust pollution of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad expressway Pakistan. Microchemical Journal, 92(2), 186–192.
Ferreira-Baptista, L., & De Miguel, E. (2005). Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 39(25), 4501–4512.
Flora, G., Gupta, D., & Tiwari, A. (2012). Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 5(2), 47–58. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10102-012-0009-2.
Fujiwara, F., Rebagliati, R. J., Dawidowski, L., Gómez, D., Polla, G., Pereyra, V., & Smichowski, P. (2011). Spatial and chemical patterns of size fractionated road dust collected in a megacitiy. Atmospheric Environment, 45(8), 1497–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.12.053.
Gabarrón, M., Faz, A., & Acosta, J. A. (2018). Use of multivariable and redundancy analysis to assess the behavior of metals and arsenic in urban soil and road dust affected by metallic mining as a base for risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Management, 206, 192–201.
Ghahremanzadeh, H., Noori, R., Baghvand, A., & Nasrabadi, T. (2018). Evaluating the main sources of groundwater pollution in the southern Tehran aquifer using principal component factor analysis. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(4), 1317–1328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0058-8.
Ghosh, S. P., & Maiti, S. K. (2018). Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in roadside deposited sediments and road surface runoff: A case study. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(7), 267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7370-1.
Gobba, N. A. E. K., Hussein Ali, A., El Sharawy, D. E., & Hussein, M. A. (2018). The potential hazardous effect of exposure to iron dust in Egyptian smoking and nonsmoking welders. Archives of Environmental and Occupational Health, 73(3), 189–202.
Gope, M., Masto, R. E., George, J., & Balachandran, S. (2018). Tracing source, distribution and health risk of potentially harmful elements (PHEs) in street dust of Durgapur, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 154, 280–293.
Gope, M., Masto, R. E., George, J., Hoque, R. R., & Balachandran, S. (2017). Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 231–241.
Grigoratos, T., & Martini, G. (2015). Brake wear particle emissions: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(4), 2491–2504.
Gunawardana, C., Goonetilleke, A., Egodawatta, P., Dawes, L., & Kokot, S. (2012). Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere, 87(2), 163–170.
Hamzah, N. A., MohdTamrin, S. B., & Ismail, N. H. (2016). Metal dust exposure and lung function deterioration among steel workers: An exposure-response relationship. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health, 22(3), 224–232.
Han, N. M. M., Latif, M. T., Othman, M., Dominick, D., Mohamad, N., Juahir, H., & Tahir, N. M. (2014). Composition of selected heavy metals in road dust from Kuala Lumpur city centre. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(3), 849–859.
Ibanez, Y., Le Bot, B., & Glorennec, P. (2010). House-dust metal content and bioaccessibility: A review. European Journal of Mineralogy, 22(5), 629–637. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2010/0022-2010.
ICMR. (2009). Nutrient Requirements and Recommended Dietary Allowances For Indians- A Report of the Expert Group of the Indian Council of Medical Research. National Institute of Nutrition.
Iijima, S., Matsumoto, N., & Lu, C.-C. (1983). Transfer of chromic chloride to embryonic mice and changes in the embryonic mouse neuroepithelium. Toxicology, 26(3–4), 257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(83)90086-0.
Jena, S., & Singh, G. (2017). Human health risk assessment of airborne trace elements in Dhanbad, India. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(3), 490–502.
Jena, S., Perwez, A., & Singh, G. (2019). Trace element characterization of fine particulate matter and assessment of associated health risk in mining area, transportation routes and institutional area of Dhanbad, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41(6), 2731–2747.
Johri, N., Jacquillet, G., & Unwin, R. (2010). Heavy metal poisoning: The effects of cadmium on the kidney. BioMetals, 23(5), 783–792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9328-y.
Jose, J., & Srimuruganandam, B. (2020). Investigation of road dust characteristics and its associated health risks from an urban environment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(9), 2819–2840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00521-6.
Kamani, H., Mirzaei, N., Ghaderpoori, M., Bazrafshan, E., Rezaei, S., & Mahvi, A. H. (2018). Concentration and ecological risk of heavy metal in street dusts of Eslamshahr Iran. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 24(4), 961–970.
Keshavarzi, B., Tazarvi, Z., Rajabzadeh, M. A., & Najmeddin, A. (2015). Chemical speciation, human health risk assessment and pollution level of selected heavy metals in urban street dust of Shiraz Iran. Atmospheric Environment, 119, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.001.
Khadem, M., Golbabaei, F., & Rahmani, A. (2017). Occupational exposure assessment of chromium (VI): A review of environmental and biological monitoring. International Journal of Occupational Hygiene, 9, 118–131.
Konstantinova, E., Minkina, T., Konstantinov, A., Sushkova, S., Antonenko, E., Kurasova, A., & Loiko, S. (2020). Pollution status and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban street dust of Tyumen city. Russia: Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00692-2.
Koukoulakis, K. G., Chrysohou, E., Kanellopoulos, P. G., Karavoltsos, S., Katsouras, G., Dassenakis, M., et al. (2019). Trace elements bound to airborne PM10 in a heavily industrialized site nearby Athens: Seasonal patterns, emission sources, health implications. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 10(4), 1347–1356.
Kowalska, J. B., Mazurek, R., Gąsiorek, M., & Zaleski, T. (2018). Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(6), 2395–2420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0106-z.
Krupnova, T. G., Rakova, O. V., Gavrilkina, S. V., Antoshkina, E. G., Baranov, E. O., & Yakimova, O. N. (2020). Road dust trace elements contamination, sources, dispersed composition, and human health risk in Chelyabinsk Russia. Chemosphere, 261, 127799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127799.
Kumar, M., Furumai, H., Kurisu, F., & Kasuga, I. (2013). Tracing source and distribution of heavy metals in road dust, soil and soakaway sediment through speciation and isotopic fingerprinting. Geoderma, 211, 8–17.
Laidlaw, M. A. S., & Filippelli, G. M. (2008). Resuspension of urban soils as a persistent source of lead poisoning in children: A review and new directions. Applied Geochemistry, 23(8), 2021–2039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.05.009.
Lee, D.-H., & Jacobs, D. R. (2004). Serum markers of stored body iron are not appropriate markers of health effects of iron: A focus on serum ferritin. Medical Hypotheses, 62, 442–445.
Li, F., Li, X., Hou, L., & Shao, A. (2018). Impact of the coal mining on the spatial distribution of potentially toxic metals in farmland tillage soil. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 14925.
Li, F., Zhang, J., Huang, J., Huang, D., Yang, J., Song, Y., & Zeng, G. (2016). Heavy metals in road dust from Xiandao district, Changsha city, China: Characteristics, health risk assessment, and integrated source identification. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(13), 13100–13113.
Lin, M., Gui, H., Wang, Y., & Peng, W. (2017). Pollution characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk of heavy metals in street dust of Suzhou China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(2), 1987–1998.
Liu, S., Wu, Q., Cao, X., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Cai, D., et al. (2016). Pollution assessment and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soils of coal mining area in Longkou city. Huan Jing KeXue = HuanjingKexue, 37(1), 270–279.
Liu, X., Jiang, J., Yan, Y., Dai, Y., Deng, B., Ding, S., et al. (2018). Distribution and risk assessment of metals in water, sediments, and wild fish from Jinjiang river in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere, 196, 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.135.
Loganathan, P., Vigneswaran, S., & Kandasamy, J. (2013). Road-deposited sediment pollutants: A critical review of their characteristics, source apportionment, and management. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 43(13), 1315–1348.
Ma, Z., Chen, K., Li, Z., Bi, J., & Huang, L. (2016). Heavy metals in soils and road dusts in the mining areas of Western Suzhou, China: A preliminary identification of contaminated sites. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(1), 204–214.
Mahanta, M. J., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2011). Total concentrations, fractionation and mobility of heavy metals in soils of urban area of Guwahati India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1–4), 221–240.
Mancuso, T.F. (1975). International conference on heavy metals in the environment. Canada, Toronto, Ontario (Cited in U.S. EPA, 1991; and in U.S. EPA, 1984a).
Manno, E., Varrica, D., & Dongarrà, G. (2006). Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela Sicily. Atmospheric Environment, 40(30), 5929–5941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.020.
Masto, R. E., George, J., Rout, T. K., & Ram, L. C. (2017). Multi element exposure risk from soil and dust in a coal industrial area. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176, 100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.12.009.
Matsumoto, N., Iijima, S., & Katsunuma, H. (1976). Placental transfer of chromic chloride and its teratogenic potential in embryonic mice. The Journal of Toxicological Sciences, 1(2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.1.2_1.
Men, C., Liu, R., Xu, F., Wang, Q., Guo, L., & Shen, Z. (2018). Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Science of The Total Environment, 612, 138–147.
MirzaeiAminiyan, M., Baalousha, M., Mousavi, R., MirzaeiAminiyan, F., Hosseini, H., & Heydariyan, A. (2018). The ecological risk, source identification, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in road dust: A case study in Rafsanjan, SE Iran. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(14), 13382–13395.
Mohmand, J., Eqani, S. A. M. A. S., Fasola, M., Alamdar, A., Mustafa, I., Ali, N., et al. (2015). Human exposure to toxic metals via contaminated dust: Bio-accumulation trends and their potential risk estimation. Chemosphere, 132, 142–151.
Mondal, S., Singh, G., & Jain, M. K. (2020). Spatio-temporal variation of air pollutants around the coal mining areas of Jharia Coalfield India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(6), 405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08324-z.
Morman, S. A., & Plumlee, G. S. (2013). The role of airborne mineral dusts in human disease. Aeolian Research, 9, 203–212.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
Najmeddin, A., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., & Lahijanzadeh, A. (2018). Source apportionment and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in road dust from urban industrial areas of Ahvaz megacity Iran. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(4), 1187–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0035-2.
Nazzal, Y., Rosen, M. A., & Al-Rawabdeh, A. M. (2013). Assessment of metal pollution in urban road dusts from selected highways of the Greater Toronto area in Canada. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(2), 1847–1858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2672-3.
Ogbeibu, A. E., Omoigberale, M. O., Ezenwa, I. M., Eziza, J. O., & Igwe, J. O. (2014). Using pollution load index and geoaccumulation index for the assessment of heavy metal pollution and sediment quality of the Benin river Nigeria. Natural Environment, 2(1), 1.
Padoan, E., Romè, C., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2017). Bioaccessibility and size distribution of metals in road dust and roadside soils along a peri-urban transect. Science of The Total Environment, 601–602, 89–98.
Pandey, B., Agrawal, M., & Singh, S. (2016). Ecological risk assessment of soil contamination by trace elements around coal mining area. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(1), 159–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1173-8.
Pang, W. P., Qin, F. X., Lyu, Y. C., Li, Y. J., Li, G., & Li, X. L. (2016). Chemical speciations of heavy metals and their risk assessment in agricultural soils in a coal mining area from Xingren county, Guizhou province China. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(5), 1468–1478.
Rastmanesh, F., Moore, F., KharratiKopaei, M., Keshavarzi, B., & Behrouz, M. (2011). Heavy metal enrichment of soil in Sarcheshmeh copper complex, Kerman Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(2), 329–336.
Roy, D., Singh, G., & Seo, Y. C. (2019). Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks from PM10-and PM2. 5-Bound metals in a critically polluted coal mining area. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 10(6), 1964–1975.
Santamaria, A. B. (2008). Manganese exposure, essentiality and toxicity. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 128(4), 484–500.
Santos-Burgoa, C., Rios, C., Mercado, L. A., Arechiga-Serrano, R., Cano-Valle, F., Eden-Wynter, R. A., et al. (2001). Exposure to manganese: Health effects on the general population, a pilot study in Central Mexico. Environmental Research, 85(2), 90–104.
Selonen, V., Varjonen, R., & Korpimäki, E. (2015). Immediate or lagged responses of a red squirrel population to pulsed resources. Oecologia, 177(2), 401–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-3148-7.
Shabbaj, I., Alghamdi, M., Shamy, M., Hassan, S., Alsharif, M., & Khoder, M. (2018). Risk assessment and implication of human exposure to road dust heavy metals in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1), 36.
Siddiqui, A. U., Jain, M. K., & Masto, R. E. (2020). Pollution evaluation, spatial distribution, and source apportionment of trace metals around coal mines soil: The case study of eastern India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(10), 10822–10834.
Singh, A. K. (2011). Elemental chemistry and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in road dust from Dhanbad and Bokaro regions India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(7), 1447–1459.
Soltani, N., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Tavakol, T., Lahijanzadeh, A. R., Jaafarzadeh, N., & Kermani, M. (2015). Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis Iran. Science of The Total Environment, 505, 712–723.
Srivastava, A. K., Jerai, M. C., & Lal, J. K. (2019). Nutrient status of Dhanbad district soils. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, SP2, 137–140.
Subba Rao, N., Sunitha, B., Adimalla, N., & Chaudhary, M. (2020). Quality criteria for groundwater use from a rural part of Wanaparthy district, Telangana state, India, through ionic spatial distribution (ISD), entropy water quality index (EWQI) and principal component analysis (PCA). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(2), 579–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00393-5.
Taghavi, S. N., Kamani, H., Dehghani, M. H., Nabizadeh, R., Afshari, N., & Mahvi, A. H. (2019). Assessment of heavy metals in street dusts of Tehran using enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index. Health Scope, 8(1), 9.
Tang, R., Ma, K., Zhang, Y., & Mao, Q. (2013). The spatial characteristics and pollution levels of metals in urban street dust of Beijing, China. Applied Geochemistry, 35, 88–98.
Tang, Z., Chai, M., Cheng, J., Jin, J., Yang, Y., Nie, Z., et al. (2017). Contamination and health risks of heavy metals in street dust from a coal-mining city in eastern China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 83–91.
Taylor, S. R. (1964). Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: A new table. GeochimicaetCosmochimicaActa, 28(8), 1273–1285.
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. (2012). Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In A. Luch (Ed.), Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology (Vol. 101, pp. 133–164). Basel: Springer Basel.
Trujillo-González, J. M., Torres-Mora, M. A., Keesstra, S., Brevik, E. C., & Jiménez-Ballesta, R. (2016). Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Science of The Total Environment, 553, 636–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.101.
US EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). (1984). Health Assessment Document for Arsenic. Office of Health and Environmental Assessment. Environmental Criteria and Assessment Office, Research Triangle Park, NC. EPA 600/8- 32–021F. Acessed September 10, 2020
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (1989). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Vol. I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (EPA/540/1–89/002). Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C. Acessed June 28, 2019
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (2001). Risk assessment guidance for Superfund: volume III — part A, process for conducting probabilistic risk assessment. EPA 540-R-02–002. Washington, D.C. Acessed June 28, 2019
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (2002). Child specific exposure factors handbook. EPA-600-P-00–002B.Washington, DC: National Center for Environmental Assessment. Acessed June 28, 2019
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (2011). Exposure factors handbook 2011 edition. EPA/600/R-09/052 F.Washington, D.C.: National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; 20460. Acessed June 28, 2019
Verma, S. K., Masto, R. E., Gautam, S., Choudhury, D. P., Ram, L. C., Maiti, S. K., & Maity, S. (2015). Investigations on PAHs and trace elements in coal and its combustion residues from a power plant. Fuel, 162, 138–147.
Wahab, M. I. A., Razak, W. M. A. A., Sahani, M., & Khan, M. F. (2020). Characteristics and health effect of heavy metals on non-exhaust road dusts in Kuala Lumpur. Science of The Total Environment, 703, 135535.
Wei, B., & Yang, L. (2010). A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchemical Journal, 94(2), 99–107.
Yuan, G.-L., Sun, T.-H., Han, P., Li, J., & Lang, X.-X. (2014). Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: Typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 136, 40–47.
Yuen, J. Q., Olin, P. H., Lim, H. S., Benner, S. G., Sutherland, R. A., & Ziegler, A. D. (2012). Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in road deposited sediments in residential and light industrial neighborhoods of Singapore. Journal of Environmental Management, 101, 151–163.
Zhang, J., Hua, P., & Krebs, P. (2017). Influences of land use and antecedent dry-weather period on pollution level and ecological risk of heavy metals in road-deposited sediment. Environmental Pollution, 228, 158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.029.
Zheng, N., Liu, J., Wang, Q., & Liang, Z. (2010a). Heavy metals exposure of children from stairway and sidewalk dust in the smelting district, Northeast of China. Atmospheric Environment, 44(27), 3239–3245.
Zheng, N., Liu, J., Wang, Q., & Liang, Z. (2010b). Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast of China. Science of The Total Environment, 408(4), 726–733.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Indian Institute Technology (Indian School of Mines) Dhanbad for providing all the necessary laboratory facilities during the research work.
Funding
No funding was received by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.S. supervised the work. S.M. performed the analysis and calculations. S.M. wrote the manuscript in consultation with G.S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, S., Singh, G. Pollution evaluation, human health effect and tracing source of trace elements on road dust of Dhanbad, a highly polluted industrial coal belt of India. Environ Geochem Health 43, 2081–2103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00785-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00785-y