Abstract
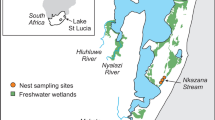
Generally crocodilians have received little attention with regard to the effects of lead toxicity despite their trophic status as apex, generalist predators that utilize both aquatic and terrestrial habitats, thereby exposing them to a potentially wide range of environmental contaminants. During July–October 2010 we collected whole blood from 34 sub-adult and adult free-ranging Nile crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus) from three separate populations in northeastern South Africa in order to analyze their blood lead concentrations (BPb). Concentrations ranged from below detectability (<3 μg/dL, n = 8) to 960 μg/dL for an adult male at the Lake St Lucia Estuary. Blood lead concentrations averaged 8.15 μg/dL (SD = 7.47) for females and 98.10 μg/dL (SD = 217.42) for males. Eighteen individuals (53 %) had elevated BPbs (≥10 μg/dL). We assessed 12 general linear models using Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) and found no significant statistical effects among the parameters of sex, crocodile size and population sampled. On average, crocodiles had higher BPbs at Lake St Lucia than at Ndumo Game Reserve or Kosi Bay, which we attribute to lead sinker ingestion during normal gastrolith acquisition. No clinical effects of lead toxicosis were observed in these crocodiles, even though the highest concentration (960 μg/dL) we report represents the most elevated BPb recorded to date for a free-ranging vertebrate. Although we suggest adult Nile crocodiles are likely tolerant of elevated Pb body burdens, experimental studies on other crocodilian species suggest the BPb levels reported here may have harmful or fatal effects to egg development and hatchling health. In light of recent Nile crocodile nesting declines in South Africa we urge further BPb monitoring and ecotoxicology research on reproductive females and embryos.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almi B, Mwase M, Sivertsen T, Musonda MM, Flaoyen A (2005) Hepatic and renal concentrations of 10 trace elements in crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus) in Kafue and Luangwa Rivers in Zambia. Sci Total Environ 337:75–82
Botha H, van Hoven W, Guillette LJ (2011) The decline of the Nile crocodile population in Loskop Dam, Olifants River, South Africa. Water SA 1:103–108
Botha AB, Haldorsen S, Porat N (2013) Geological history. In: Perissinotto R, Stretch DD, Taylor RH (eds) Ecology and conservation of estuarine ecosystems: Lake St Lucia as a global model. Cambridge University Press, Barcelona, pp 46–61
Brazaitis PJ (1968) The determination of sex in living crocodilians. Br J Herpetol 4:54–58
Buekers J, Redeker ES, Smolder E (2009) Lead toxicity to wildlife: derivation of a critical blood concentration for wildlife monitoring based on literature data. Sci Total Environ 407:3431–3438
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Calverley PM, Downs CT (2014a) Population status of Nile crocodiles in Ndumo Game Reserve, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa (1971-2012). Herpetologica 70:417–425
Calverley PM, Downs CT (2014b) Habitat use by Nile crocodiles in Ndumo Game Reserve, South Africa: a naturally patchy environment. Herpetologica 70:426–438
Campbell KR (2003) Ecotoxicology of crocodilians. Appl Herpetol 1:45–163
Camus AC, Mitchell MM, Williams JF, Jowett PLH (1998) Elevated lead levels in farmed American alligators Alligator mississippiensis consuming nutria Myocastor coypus meat contaminated by lead bullets. J World Aquac Soc 29:370–376
Chiasson RB (1962) Laboratory anatomy of the alligator. Wm C Brown Co, Dubuque
Combrink X (2014) Spatial and reproductive ecology and population status of the Nile Crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) in the Lake St Lucia estuarine system, South Africa. Ph.D. thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
Combrink X, Korrubel JL, Kyle R, Taylor R, Ross P (2011) Evidence of a declining Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) population at Lake Sibaya, South Africa. S Afr J Wildl Res 41:145–157
Combrink X, Warner JK, Hofmeyr M, Govender D, Ferreira SM (2012) Standard operating procedure for the monitoring, capture and sampling of Nile Crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus). South African National Parks, Skukuza, South Africa, unpublished report, pp 1–14
Combrink X, Warner J, Taylor R, Downs CT (2013) Nile crocodiles. In: Perissinotto R, Stretch DD, Taylor RH (eds) Ecology and conservation of estuarine ecosystems: Lake St Lucia as a global model. Cambridge University Press, Barcelona, pp 333–353
Cook R, Behler J, Braezitis P, Dolensek E (1988) A survey of blood lead levels in crocodilians. In: Stoskopf MK (ed) International association for aquatic animal medicine proceedings, vol 19. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 149–150
Ferreira SM, Pienaar D (2011) Degradation of the crocodile population in the Olifants River Gorge of Kruger National Park, South Africa. Aquat Conserv 21:155–164
Fisher IJ, Pain DJ, Thomas VG (2006) A review of lead poisoning from ammunition sources in terrestrial birds. Biol Conserv 131:421–432
Franson JC (1996) Interpretation of tissue lead residues in birds other than waterfowl. In: Beyer WN, Heinz GH, Redmon-Norwood AW (eds) Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentrations. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Grillitsch B, Schiesari L (2010) The ecotoxicology of metals in reptiles. In: Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest SK (eds) Ecotoxicology of reptiles and amphibians. CRC Press, New York
Hammerton KM, Jayasinghe N, Jeffree RA, Lim RP (2003) Experimental study of blood lead kinetics in estuarine crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus) exposed to ingested lead shot. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:390–398
Heinz GH, Percival HF, Jenning ML (1991) Contaminants in America alligator eggs from Lake Apopka, Lake Griffin, and Lake Okeechobee, Florida. Environ Monit Assess 16:277–285
Jeffree RA, Markich SJ, Twining JR (2001) Element concentrations in the flesh and osteoderms of estuarine crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus) from the Alligator Rivers Region, northern Australia: biotic and geographic effects. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:236–245
Kyle R (1999) Gillnetting in nature reserves: a case study from the Kosi Lakes, South Africa. Biol Conserv 88:183–192
Lambertucci SA, Donázar JA, Huertas AD, Jiménez B, Sáez M, Sanchez-Zapata JA, Hiraldo F (2011) Widening the problem of lead poisoning to a South American top scavenger: lead concentrations in feathers of wild Andean condors. Biol Conserv 144:1464–1471
Lance VA, Horn TR, Elsey RM, de Peyster A (2006) Chronic incidental lead ingestion in a group of captive-reared alligators (Alligator mississippiensis): possible contribution to reproductive failure. Comp Biochem Physiol C 142:30–35
Ma WC (1996) Lead in mammals. In: Beyer WN, Heinz GH, RedmonNorwood AW (eds) Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentrations. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Manolis SC, Webb GJW, Britton AR, Jeffree RA, Markich SJ (2002) Trace element concentrations of wild saltwater crocodile eggs. In: Makich SJ, Jefree RA (eds) The Finniss River, a natural laboratory of mining impacts—past, present and future. ANSTO, Sydney, pp 58–61
Marais J (2014) Crocodylus niloticus (Laurenti, 1768). In: Bates MF, Branch WR, Bauer AM, Burger M, Marais J, Alexander GJ, de Villiers (eds) Atlas and Red List of the Reptiles of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland. Suricata 1. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria
Milnes MR, Guillette LJ Jr (2008) Alligator tales: new lessons about environmental contaminants from a sentinel species. Bioscience 58:1027–1036
Myburgh JG, Kirberger RM, Steyl JCA, Soley JT, Booyse DG, Huchzermeyer FW, Lowers RH, Guillette LJ (2014) The post-occipital spinal venous sinus of the Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus): its anatomy and use for blood sample collection and intravenous infusions. J S Afr Vet Assoc 85:965. doi:10.4102/jsava.v85i1.965
Nadjafzadeh M, Hofer H, Krone O (2013) The link between feeding ecology and lead poisoning in white-tailed eagles. J Wildl Manag 77:48–57
Naidoo V, Wolter K, Espie I, Kotze A (2012) Lead toxicity: consequences and interventions in an intensively managed (Gyps coprotheres) vulture colony. J Zoo Wildl Med 43:573–578
Pain DJ (1996) Lead in waterfowl. In: Beyer WN, Heinz GH, Redmon-Norwood AW (eds) Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentrations. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Perkin-Elmer (1996) Analytical methods for atomic absorption spectroscopy. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, p 300
Phelps RJ, Focardi S, Fossi C, Leonzio C, Renzoni A (1986) Chlorinated hydrocarbons and heavy metals in crocodile eggs from Zimbabwe. Trans Zimb Sci Assoc 63:8–15
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online at http://www.R-project.org/
Rainwater TR, Wu TH, Finger AG, Canas JE, Yu L, Reynolds KD, Coimbatore G, Barr B, Platt SG, Cobb GP, Anderson TA, McMurry ST (2007) Metals and organochlorine pesticides in caudal scutes of crocodiles from Belize and Costa Rica. Sci Total Environ 373:146–156
Rumbold DG, Fink LE, Laine KA, Niemezyk SL, Chandrasekhar T, Wankel SD, Kendall C (2002) Levels of mercury in alligators (Alligator mississippiensis) collected along a transect through the Florida Everglades. Sci Total Environ 297:239–252
Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest SK (2010) Ecotoxicology of reptiles and amphibians. CRC Press, New York
Stretch D, Chrystal CP, Chrystal RA, Maine CM, Pringle JJ (2013) Estuary and lake hydrodynamics. In: Perissinotto R, Stretch DD, Taylor RH (eds) Ecology and conservation of estuarine ecosystems: Lake St Lucia as a global model. Cambridge University Press, Barcelona, pp 112–149
Swanepoel D, Boomker J, Kriek NPJ (2000) Selected chemical parameters in the blood and metals in the organs of the Nile crocodile Crocodylus niloticus, in the Kruger National Park. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 67:141–148
Thomas TG (1997) Attitudes and issues preventing bans on toxic lead shot and sinkers in North America and Europe. Environ Values 6:185–199
Twinning JR, Markich SJ, Prince KE, Jeffree RA (1999) Osteoderms of estuarine crocodiles record their enhanced Pb exposure in Kakadu National Park. Envrion Sci Technol 33:4396–4400
Wallace KM, Leslie AJ (2008) Diet of the Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. J Herpetol 42:361–368
Warner JK (2015) Morphometrics, ecotoxicology and stable isotope ecology of Nile crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus) in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Ph.D. thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG (2009) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife and Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise
Xu Q, Fang S, Wang Z, Wang Z (2006) Heavy metal distribution in tissues and eggs of Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:580–586
Zinterhofer LJM, Jatlow PI, Fappiano A (1971) Atomic absorption determination of lead in blood and urine in the presence of EDTA. J Lab Clin Med 78:664
Acknowledgments
We thank R. Taylor, P. Calverley, G. Champion, F. Myburgh, S. Kyle and family, the many volunteers who assisted with fieldwork, M. Dreslik for statistical guidance, Ezemvelo KwaZulu-Natal Widlife and the iSimangaliso Wetland Park Authority. The Ford Wildlife Foundation and the South African Water Research Commission are thanked for their vehicle/financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
There were no human subjects, thus informed consent is not applicable for this study.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Warner, J.K., Combrink, X., Myburgh, J.G. et al. Blood lead concentrations in free-ranging Nile crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus) from South Africa. Ecotoxicology 25, 950–958 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1652-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1652-8