Abstract
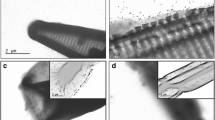
Given the demonstrated antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), and the key role that microorganisms play in performing critical ecosystem functions such as decomposition and nutrient cycling, there is growing concern that AgNP pollution may negatively impact ecosystems. We examined the response of streamwater and sediment microorganisms to commercially available 21 ± 17 nm AgNPs, and compared AgNP impacts to those of dissolved-Ag added as AgNO3. We show that in streamwater, AgNPs and AgNO3 decreased respiration in proportion to dissolved-Ag concentrations at the end of the incubation (r2 = 0.78), while in sediment the only measurable effect of AgNPs was a 14 % decrease in sulfate concentration. This contrasts with the stronger effects of dissolved-Ag additions in both streamwater and sediment. In streamwater, addition of dissolved-Ag at a level equivalent to the lowest AgNP dose led to respiration below detection, a 55 % drop in phosphatase enzyme activity, and a 10-fold increase in phosphate concentration. In sediment, AgNO3 addition at a level equivalent to the highest AgNP addition led to a 34 % decrease in respiration, a 55 % increase in microbial biomass, and a shift in bacterial community composition. The results of this study suggest that, in similar freshwater environments, the short-term biological impacts of AgNPs on microbes are attenuated by the physical and chemical properties of streamwater and sediment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin RM, Mohamed MB, Ramadan MA, Verwanger T, Krammer B (2009) Rapid and sensitive microplate assay for screening the effect of silver and gold nanoparticles on bacteria. Nanomedicine 4(6):637–643. doi:102217/nnm0950
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26(1):32–46. doi:101111/j1442-9993200101070ppx
Aruguete DM, Hochella MF (2010) Bacteria-nanoparticle interactions and their environmental implications. Environ Chem 7(1):3–9. doi:101071/en09115
Benn TM, Westerhoff P (2008) Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environ Sci Technol 42(11):4133–4139. doi:10.1021/es7032718
Bradford A, Handy RD, Readman JW, Atfield A, Muhling M (2009) Impact of silver nanoparticle contamination on the genetic diversity of natural bacterial assemblages in Estuarine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 43(12):4530–4536. doi:10.1021/es9001949
Choi O, Hu Z (2008) Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42(12):4583–4588. doi:101021/es703238h
Choi OK, Hu ZQ (2009) Nitrification inhibition by silver nanoparticles. Water Sci Technol 59(9):1699–1702. doi:102166/wst2009205
Choi O, Cleuenger TE, Deng BL, Surampalli RY, Ross L, Hu ZQ (2009) Role of sulfide and ligand strength in controlling nanosilver toxicity. Water Res 43(7):1879–1886. doi:101016/jwatres200901029
Corley E, Scheufele D, Hu Q (2009) Of risks and regulations: how leading US nanoscientists form policy stances about nanotechnology. J Nanopart Res 11(7):1573–1585. doi:101007/s11051-009-9671-5
Costerton JW (2007) The biofilm primer. Springer, Berlin
Elzey S, Grassian VH (2010) Agglomeration, isolation and dissolution of commercially manufactured silver nanoparticles in aqueous environments. J Nanopart Res 12(5):1945–1958. doi:101007/s11051-009-9783-y
Fabrega J, Fawcett SR, Renshaw JC, Lead JR (2009) Silver nanoparticle impact on bacterial growth: effect of pH, concentration, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7285–7290. doi:101021/es803259g
Fierer N, Schimel JP, Holden PA (2003) Variations in microbial community composition through two soil depth profiles. Soil Biol Biochem 35(1):167–176
Gao J, Wang Y, Hovsepyan A, Bonzongo JCJ (2011) Effects of engineered nanomaterials on microbial catalyzed biogeochemical processes in sediments. J Hazard Mater 186(1):940–945. doi:101016/jjhazmat201011084
Girvan MS, Campbell CD, Killham K, Prosser JI, Glover LA (2005) Bacterial diversity promotes community stability and functional resilience after perturbation. Environ Microbiol 7(3):301–313. doi:101111/j1462-2920200500695x
Goslee SC, Urban DL (2007) The ecodist package for dissimilarity-based analysis of ecological data. J Stat Softw 22(7):1–19
Kent RD, Vikesland PJ (2011) Controlled evaluation of silver nanoparticle dissolution using atomic force microscopy. Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1021/es203475a
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Park YK, Park YH, Hwang CY, Kim YK, Lee YS, Jeong DH, Cho MH (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 3(1):95–101
Kim B, Park CS, Murayama M, Hochella MF Jr (2010) Discovery and characterization of silver sulfide nanoparticles in final sewage sludge products. Environ Sci Technol 44(19):7509–7514
Liu J, Hurt RH (2010) Ion release kinetics and particle persistence in aqueous nano-silver colloids. Environ Sci Technol 44(6):2169–2175. doi:101021/es9035557
Liu WT, Marsh TL, Cheng H, Forney LJ (1997) Characterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(11):4516–4522
Lok C-N, Ho C-M, Chen R, He Q-Y, Yu W-Y, Sun H, Tam P, Chiu J-F, Che C-M (2006) Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. J Proteome Res 5(4):916–924
Lok C-N, Ho C-M, Chen R, He Q-Y, Yu W-Y, Sun H, Tam P, Chiu J-F, Che C-M (2007) Silver nanoparticles: partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J Biol Inorg Chem 12(4):527–534
McCune B, Grace JB (2002) Analysis of ecological communities. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach
Miao AJ, Schwehr KA, Xu C, Zhang SJ, Luo ZP, Quigg A, Santschi PH (2009) The algal toxicity of silver engineered nanoparticles and detoxification by exopolymeric substances. Environ Pollut 157(11):3034–3041. doi:101016/jenvpol200905047
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramírez JT, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16:2346
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8959–8964
Oksanen J (2010) Multivariate analysis of ecological communities in R: Vegan tutorial
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2010) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 1.17-3. Available at http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. Accessed 12 Feb 2010
Osborn AM, Moore ERB, Timmis KN (2000) An evaluation of terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis for the study of microbial community structure and dynamics. Environ Microbiol 2(1):39–50
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(6):1712–1720. doi:101128/aem02218-06
Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies (2010) Nanotechnology consumer products inventory. http://www.nanotechproject.org/inventories/consumer/. Accessed April 12 2010
Saiya-Cork KR, Sinsabaugh RL, Zak DR (2002) The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34(9):1309–1315
Schimel J, Balser TC, Wallenstein M (2007) Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function. Ecology 88(6):1386–1394. doi:10.1890/06-0219
Smetana AB, Klabunde KJ, Marchin GR, Sorensen CM (2008) Biocidal activity of nanocrystalline silver powders and particles. Langmuir 24(14):7457–7464. doi:101021/la800091y
Smith RM, Martell AE, Motekaitis RJ (1997) NIST critically selected stability constants of metal complexes database, version 4.0. NIST Standard Reference Database 46
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci 275(1):177–182
Sudduth EB, Bernhardt ES (2011) Testing the field of dreams hypothesis: functional responses to urbanization and restoration in stream ecosystems. Ecol Appl 21(6):1972–1988
Systat Software Inc. (2008) Sigmaplot, 11.0 edn, San Jose, USA
Takeno N (2005) Atlas of Eh-pH diagrams, intercomparison of thermodynamic databases. Geological Survey of Japan
Yin L, Cheng Y, Espinasse B, Colman BP, Auffan M, Wiesner M, Rose J, Liu J, Bernhardt ES (2011) More than the ions: the effects of silver nanoparticles on Lolium multiflorum. Environ Sci Technol 45:2360–2367. doi:101021/es103995x
Yoon KY, Byeon JH, Park JH, Hwang J (2007) Susceptibility constants of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to silver and copper nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 373(2–3):572–575. doi:101016/jscitotenv200611007
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sam Johnson, Medora Burke-Scoll, Brooke Hassett, Curt Richardson, Claudia Gunsch, and Christina Arnaout for their discussions and laboratory assistance. This work was funded through the Center for the Environmental Implications of Nanotechnology (CEINT), which is supported by funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NSF or the EPA. This work has not been subjected to EPA review and no official endorsement should be inferred.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colman, B.P., Wang, SY., Auffan, M. et al. Antimicrobial effects of commercial silver nanoparticles are attenuated in natural streamwater and sediment. Ecotoxicology 21, 1867–1877 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0920-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0920-5