Abstract
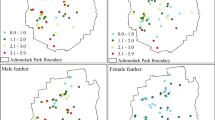
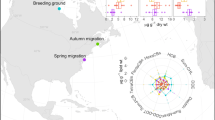
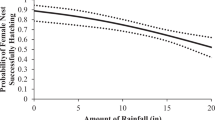
Much of the Laurentian Great Lakes region is a mercury-sensitive landscape, in which atmospheric deposition and waterborne sources of mercury (Hg) have led to high concentrations of bioavailable methylmercury (MeHg) in predatory fish and piscivorous wildlife. Efforts since the early 1990s have established the common loon (Gavia immer) as the primary avian indicator for evaluating the exposure and effects of MeHg in North America. A regional Hg dataset was compiled from multiple loon tissue types and yellow perch (Perca flavescens), a preferred prey fish species for loons. Hg exposure in loons and perch was modeled to develop male and female loon units (MLU and FLU, respectively), standardized metrics that represent the estimated blood Hg exposure of a male or female loon for a given loon territory or water body. Using this common endpoint approach to assess loon Hg exposure, the authors demonstrate spatial trends in biotic Hg concentrations, examine MeHg availability in aquatic ecosystems of the Great Lakes region in relation to landscape-level characteristics, and identify areas with potentially significant adverse reproductive impacts to loons and other avian piscivores. Based on 8,101 MLUs, seven biological Hg hotspots were identified in the Great Lakes region. Policy-relevant applications are presented.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RM, Twiss MR, Driscoll CT (2009) Patterns of mercury accumulation among seston in lakes of the Adirondack Mountains, New York. Environ Sci Technol 43:4836–4842
Anderson MR, Scruton DA, Williams UP, Curtis LR (1995) Mercury in the fish in the Smallwood reservoir, Labrador, 21 years after impoundment. Water Air Soil Pollut 80:927–930
Barr JF (1986) Population dynamics of the common loon (Gavia immer) associated with mercury-contaminated waters in northwestern Ontario. Occ Paper 56, Can Wildl Serv, Ottawa Ontario
Barr JF (1996) Aspects of common loon (Gavia immer) feeding biology on its breeding ground. Hydrobiology 32:119–144
Bergquist BA, Blum JD (2007) Mass-dependent and -independent fractionation of Hg isotopes by photoreduction in aquatic systems. Science 318:417–420
Bhavsar SP, Gewurtz SB, McGoldrick DJ, Keir MJ, Backus SM (2010) Changes in mercury levels in Great Lakes fish between 1970s and 2007. Environ Sci Technol 44:3273–3279
Blum JD, Bergquist BA (2007) Reporting of variations in the natural isotopic composition of mercury. Anal Bioanal Chem 388:353–359
Bodaly RA, Heckey RE, Fudge RJP (1994) Increases in fish mercury in lakes flooded by the Churchill River diversion, northern Manitoba. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 41:682–691
Burgess NM, Hobson KA (2006) Bioaccumulation of mercury in Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens) and Common Loons (Gavia immer) in relation to lake chemistry in Atlantic Canada. Hydrobiology 567:275–282
Burgess NM, Meyer MW (2008) Methylmercury exposure associated with reduced productivity in common loons. Ecotoxicology 17:83–91
Burgess NM, Evers DC, Kaplan JD, Duggan M, Kerekes JJ (1998) Mercury and reproductive success of Common Loons breeding in the Maritimes. In: Mercury in Atlantic Canada: a progress report, Environ Canada, Sackville, NB, pp 104–109
Burgess NM, Evers DC, Kaplan JD (2005) Mercury and other contaminants in common loons breeding in Atlantic Canada. Ecotoxicology 14:193–222
Chen CY, Folt C (2005) High plankton densities reduce mercury biomagnification. Environ Sci Technol 39:115–121
Chen CY, Stemberger R, Klauje B, Blum J, Pickhardt P, Folt C (2000) Accumulation of heavy metals across a gradient of lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 45:1525–1536
Clarkson TW, Magos L (2006) The toxicology of mercury and its chemical compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol 36:609–662
Compeau GC, Bartha R (1985) Sulfate-reducing bacteria: principal methylators of mercury in anoxic estuarine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:498–502
Cope WG, Wiener JG, Rada RG (1990) Mercury accumulation in yellow perch in Wisconsin seepage lakes: relation to lake characteristics. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:931–940
Dittman JA, Driscoll CT (2009) Factors influencing changes in mercury concentrations in lake water and yellow perch (Perca flavescens) in Adirondack lakes. Biogeochem 93:179–196
Dittman JA, Shanley JB, Driscoll CT, Aiken GR, Chalmers AT, Towse JE (2009) Ultraviolet absorbance as a proxy for total dissolved mercury in streams. Environ Pollut 157:1953–1956
Driscoll CT, Han YJ, Chen CY, Evers DC, Lambert KF, Holsen TM, Kamman NC, Munson R (2007) Mercury contamination in remote forest and aquatic ecosystems in the northeastern US: sources, transformations and management options. BioSci 57:17–28
Engstrom DR, Swain EB (1997) Recent declines in atmospheric mercury deposition in the Upper Midwest. Environ Sci Technol 31:960–967
Environment Canada (2010) National pollutant release inventory (NPRI). http://www.ec.gc.ca/inrp-npri/default.asp?lang=en&n=0EC58C98. Accessed 9 Dec 2010
ESRI (2010) ArcInfo v.10. Redlands, California, USA
Evers DC (2006) Loons as biosentinels of aquatic integrity. Environ Bioindic 1:18–21
Evers DC (2007) Status assessment and conservation plan for the common loon in North America. US Fish Wildl Serv Tech Rept Series, Denver, Colorado
Evers DC, Kaplan JD, Meyer MW, Reaman PS, Major A, Burgess N, Braselton WE (1998) Bioavailability of environmental mercury measured in Common Loon feathers and blood across North America. Environ Tox Chem 17:173–183
Evers DC, Taylor KM, Major A, Taylor RJ, Poppenga RH, Scheuhammer AM (2003) Common Loon eggs as indicators of methylmercury availability in North America. Ecotoxicology 12:69–81
Evers DC, Lane OP, Savoy L, Goodale W (2004) Assessing the impacts of methylmercury on piscivoress using a wildlife criterion value based on the common loon, 1998–2003. Report BRI 2004–2005, submitted to the Maine Dept Environ Protection, BioDiversity Res Inst, Falmouth, Maine. http://www.briloon.org/pub/doc/2004-05baseline.pdf
Evers DC, Han YJ, Driscoll CT, Kamman NC, Goodale MW, Lambert KF, Holsen TM, Chen CY, Clair TA, Butler T (2007) Biological mercury hotspots in the Northeastern United States and Southeastern Canada. BioSci 57:29–43
Evers DC, Savoy L, DeSorbo CR, Yates D, Hanson W, Taylor KM, Siegel L, Cooley JH, Bank M, Major A, Munney K, Vogel HS, Schoch N, Pokras M, Goodale W, Fair J (2008) Adverse effects from environmental mercury loads on breeding common loons. Ecotoxicology 17:69–81
Evers DC, Paruk JD, Mcintyre JW, Barr JF (2010) Common loon (Gavia immer). In: Poole A (ed) The birds of North America. http://bna.birds.cornell.edu/bna/species/313. Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, New York
Fitzgerald WF, Engstrom DR, Mason RP, Nater EA (1998) The case for atmospheric mercury contamination in remote areas. Environ Sci Technol 32:1–7
Fournier F, Karasov WH, Kenow KP, Meyer MW, Hines RK (2002) The oral bioavailability and toxicokinetics of methylmercury in common loon (Gavia immer) chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A 133:703–714
Freund RF, Littell RC, Creighton L (2003) Regression using JMP. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, North Carolina
Gilmour CC, Henry EA, Mitchell R (1992) Sulfate stimulation of mercury methylation in freshwater sediments. Environ Sci Technol 26:2281–2287
Gratz LE, Keeler GJ, Blum JD, Sherman LS (2010) Isotopic composition and fractionation of mercury in Great Lakes precipitation and ambient air. Environ Sci Technol 44:7764–7770
Grear JS, Meyer MW, Cooley JH, Kuhn A, Piper WH, Mitro MG, Vogel HS, Taylor KM, Kenow KP, Craig SM, Nacci DE (2009) Population growth and demography of common loons in the northern United States. J Wildl Manag 73:1108–1115
Hammerschmidt CR, Fitzgerald WF (2005) Methylmercury in mosquitoes related to atmospheric mercury deposition and contamination. Environ Sci Technol 39:3034–3039
Hammerschmidt CR, Fitzgerald WF (2006) Methylmercury in freshwater fish linked to atmospheric mercury deposition. Environ Sci Technol 40:7764–7770
Hammerschmidt CR, Sandheinrich MB (2005) Maternal diet during oogenesis is the major source of methylmercury in fish embryos. Environ Sci Technol 39:3580–3584
Harris R, Krabbenhoft DP, Mason RP, Murray MW, Reash R, Saltman T (eds) (2007) Ecosystem responses to mercury contamination: indicators of change. SETAC. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Heinz GH (1979) Methylmercury: reproductive and behavioral effects on three generations of Mallard ducks. J Wildl Manag 43:394–401
Heinz GH, HoffmanDJ KlimstraJD, Stebbins KR (2010) Predicting mercury concentrations in mallard eggs from mercury in the diet or blood of adult females and from duckling down feathers. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:389–392
Hutcheson MS, Smith CM, Wallace GT, Rose J, Eddy B, Sullivan J, Pancorbo O, West CR (2008) Freshwater fish mercury concentrations in a regionally high mercury deposition area. Water Air Soil Pollut 191:15–31
Institute Inc SAS (2010) JMP version 9.0.0. Cary, North Carolina
Kamman NC, Lorey PM, Driscoll CT, Estabrook R, Major A, Pientka B, Glassford E (2004) Assessment of mercury in waters, sediments and biota of New Hampshire and Vermont lakes sampled using a geographically randomized design. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1172–1186
Keeler GJ, Landis MS, Norris GA, Christianson EM, Dvonch JT (2006) Sources of mercury wet deposition in Eastern Ohio, USA. Environ Sci Technol 40:5874–5881
Kelly CA, Rudd JWM, Bodaly RA, Roulet NP, St. Louis VL, Heyes A, Moore TR, Schiff S, Aravena R, Scott KJ, Dyck B, Harris R, Warner B, Edwards G (1997) Increases in fluxes of greenhouse gases and methyl mercury following flooding of an experimental reservoir. Environ Sci Technol 31:1334–1344
Kenow KP, Gutretuer S, Hines RK, Meyer MW, Fournier F, Karasov WH (2003) Effects of methyl mercury exposure on the growth of juvenile common loons. Ecotoxicology 12:171–182
Kenow KP, Meyer MW, Rossmann R, Gendron-Fitzpatrick A, Gray BR (2011) Effects of injected methylmercury on the hatching of common loon (Gavia immer) eggs. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0743-9
Kerfoot WC, Harting S, Rossmann R, Robbins JA (1999) Anthropogenic copper inventories and mercury profiles from Lake Superior: evidence for mining impacts. J Great Lakes Res 25:663–682
Krabbenhoft DP, Benoit JM, Babiarz CL, Hurley JP, Andren AW (1995) Mercury cycling in the Allequash Creek watershed, northern Wisconsin. Water Air Soil Pollut 80:425–433
Kramar D, Goodale WM, Kennedy LM, Carstensen LW, Kaur T (2005) Relating land cover characteristics and common loon mercury levels using geographic information systems. Ecotoxicology 14:253–262
Lamborg CH, Fitzgerald WF, Damman AWH, Benoit JM, Balcom PH, Engstrom DR (2002) Modern and historic atmospheric mercury fluxes in both hemispheres: global and regional mercury cycling implications. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16:1104
Lockhart WL, Wilkinson P, Billeck BN, Danell RA, Hunt RV, De Laronde J, Brunskill GJ, St Louis V (1998) Fluxes of mercury to lake sediments in central and northern Canada inferred from dated sediment cores. Biogeochem 40:163–173
Lorey P, Driscoll CT (1999) Historical trends of mercury deposition in Adirondack lakes. Environ Sci Technol 33:718–722
Mason RP, Sullivan KA (1997) Mercury in Lake Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 31:942–947
Mason RP, Abbot ML, Bodaly RA, Bullock OR, Driscoll CT, Evers DC, Lindberg SE, Murray M, Swain EB (2005) Monitoring the response to changing mercury deposition. Environ Sci Technol 39:14A–22A
Mergler D, Anderson HA, Chan LHM, Mahaffey KR, Murray M, Sakamoto M, Stern AH (2007) Methylmercury exposure and health effects in humans: a worldwide concern. Ambio 36:3–11
Merrill EH, Hartigan JJ, Meyer MW (2005) Does prey biomass of mercury exposure affect loon chick survival in Wisconsin? J Wildl Manag 69:57–67
Meyer MW, Evers DC, Daulton T (1995) Common loons nesting on acidified lakes in northern Wisconsin have elevated mercury exposure. Water Air Soil Pollut 80:871–880
Meyer MW, Evers DC, Hartigan JJ, Rasmussen PS (1998) Patterns of common loon (Gavia immer) mercury exposure reproduction and survival in Wisconsin, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:184–190
Meyer MW, Rasmussen PW, Watras CJ, Fevold BM, Kenow KP (2011) Bi-phasic trends in mercury concentrations in blood of Wisconsin common loons during 1992–2010. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0759-1
Mitro MG, Evers DC, Meyer MW, Piper WH (2008) Common loon survival rates and mercury in New England and Wisconsin. J Wildl Manag 72:665–673
Monson BA (2009) Trend reversal of mercury concentrations in piscivorous fish from Minnesota Lakes: 1982–2006. Environ Sci Technol 43:1750–1755
Monson BA, Staples DF, Bhavsar SP, Holsen TM, Schrank CS, Moses SK, McGoldrick DJ, Backus SM, Williams KA (2011) Spatiotemporal trends of mercury in walleye and largemouth bass from the Laurentian Great Lakes region. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0715-0
Morrison HA (2011) The Canadian clean air regulatory agenda mercury science program. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0714-1
Munthe J, Bodaly RA, Branfireun B, Driscoll C, Gilmour C, Harris R, Horvat M, Lucotte M, Malm O (2007) Recovery of mercury-contaminated fisheries. Ambio 36:33–44
Nacci D, Pelletier M, Lake J, Bennett R, Nichols J, Haebler R, Grear J, Kuhn A, Copeland J, Nicholson M, Walters S, Munns WR Jr (2005) An approach to predict risks to wildlife populations from mercury and other stressors. Ecotoxicology 14:283–293
National Atlas of the United States, US Geological Survey, Statistics Canada (2004) Hydroply.sdc ESRI base layer: US National Atlas Water Feature Areas and Canadian Data Bundle 2002. ESRI Data and Maps, Redlands, CA. http://dataviewer.atdd.noaa.gov/website/noaadata/arcmap/ESRI%20USA%20Data/hydro/hydroply.sdc.xml. Accessed 20 January 2011
Nocera J, Taylor P (1998) In situ behavioral response of common loons associated with elevated mercury exposure. Conserv Ecol 2(2):10
NRC (2000) Toxicological effects of methylmercury national research council committee on the toxicological effects of methylmercury. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Pacyna EG, Pacyna JM, Steenhuisen F, Wilson S (2006) Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000. Atmos Environ 40:4048–4063
Pickhardt PC, Folt CL, Chen CY, Klaue B, Blum JD (2002) Algal blooms reduce the uptake of toxic methylmercury in freshwater food webs. Proc Nat Acad Sci 99:4419–4423
Rasmussen PE, Villard DJ, Gardner HD, Fortescue JAC, Schiff SL, Shilts WW (1998) Mercury in lake sediments of the Precambrian Shield near Huntsville, Ontario, Canada. Environ Geol 33:170–182
Rasmussen PW, Schrank CS, Campfield PA (2007) Temporal trends of mercury concentrations in Wisconsin walleye (Sander vitreus), 1982–2005. Ecotoxicology 16:541–550
Rimmer C, McFarland K, Evers DC, Miller EK, Aubry Y, Busby D, Taylor R (2005) Mercury levels in Bicknell’s Thrush and other insectivorous passerine birds in montane forests of northeastern United States and Canada. Ecotoxicology 14:223–240
Rolfhus KR, Sakamoto HE, Cleckner LB, Stoor RW, Babiarz CL, Back RC, Manolopoulos H, Hurley JP (2003) Distribution and fluxes of total and methylmercury in Lake Superior. Environ Sci Technol 37:865–872
Sandheinrich MB, Wiener JG (2011) Methylmercury in fish—advances in assessing toxicity of environmentally relevant exposures. In: Beyer WN, Meador JP (eds) Environmental contaminants in biota: interpreting tissue concentrations, 2nd edition edn. CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 161–182
Scheuhammer AM, Blancher PB (1994) Potential risk to common loons (Gavia immer) from methylmercury exposure in acidified lakes. Hydrobiology 279–280:445–455
Scheuhammer AM, Atchison CM, Wong AHK, Evers DC (1998) Mercury exposure in breeding common loons (Gavia immer) in central Ontario, Canada. J Environ Toxicol Chem 17:191–196
Scheuhammer AM, Perrault JA, Bond DE (2001) Mercury, methylmercury and selenium concentrations in eggs of Common Loons (Gavia immer) from Canada. Environ Monitor Assess 72:79–84
Scheuhammer AM, Meyer MW, Sandheinrich MB, Murray MW (2007) Effects of environmental methylmercury on the health of wild birds mammals and fish. Ambio 36:12–18
Schmeltz D, Evers DC, Driscoll CT, Artz R, Cohen M, Gay D, Haeuber R, Krabbenhoft DP, Mason R, Morris K, Wiener JG (2011) MercNet: a national monitoring network to assess responses to changing mercury emissions in the United States. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0756-4
Shanley JB, Moore R, Smith RA, Miller EK, Simcox A, Kamman N, Nacci D, Robinson K, Johnston JM, Hughes M, Johnston C, Evers DC, Williams KA, Graham J, King S. MERGANSER—An empirical model to predict fish and loon mercury in New England lakes. Environ Sci Technol (Submitted)
Simonin HA, Loukmas JJ, Skinner LC, Roy KM (2008) Lake variability: key factors controlling mercury concentrations in New York State fish. Environ Pollut 154:107–115
Sorensen JA, Kallemeyn LW, Sydor M (2005) Relationship between mercury accumulation in young-of-the-year yellow perch and water level fluctuations. Environ Sci Technol 39:9237–9243
St Louis VL, Rudd JWM, Kelly CA, Beaty KG, Bloom NS, Flett RJ (1994) Importance of wetlands as sources of methyl mercury to boreal forest ecosystems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:1065–1076
St Louis VL, Rudd JWM, Kelly CA, Bodaly RA, Paterson MJ, Beaty KG, Hesslein RH, Heyes A, Majewski AR (2004) The rise and fall of mercury methylation in an experimental reservoir. Environ Sci Technol 38:1348–1358
Statistics Canada (2006) 2006 Agricultural Ecumene Census Divisions of Canada. http://app.databasin.org/app/pages/datasetPage.jsp?id=70c195f3ae224908ad2125a05bfebd07. Accessed 19 January 2011
Stemberger RS, Chen CY (1998) Fish tissue metals and zooplankton assemblages of northeastern US lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 2:339–352
Swain EB, Engstrom DR, Brigham ME, Henning TA, Brezonik PL (1992) Increasing rates of atmospheric mercury deposition in midcontinental North America. Science 257:784–787
Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat (2010) Federal Contaminated Sites Inventory. http://www.tbs-sct.gc.ca/fcsi-rscf/home-accueil-eng.aspx. Accessed 15 Dec 2010
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2002) NEI v.3 facility summary (2007) http://www.epa.gov/ttn/chief/eiinformation.html. Accessed 20 April 2010
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2008) MercNet: establishing a comprehensive national mercury monitoring network. http://nadp.sws.uiuc.edu/mercnet/MercNetFinalReport.pdf. 2008 Workshop report, US EPA Report EP-W-08-018, Washington, D.C
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2010) National priorities list (NPL). http://www.epa.gov/superfund/sites/npl/index.htm. Accessed 14 Dec 2010
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) Office of Water (2009) 2008 Biennial national listing of fish advisories. http://water.epa.gov/scitech/swguidance/fishshellfish/fishadvisories/upload/2009_09_16_fish_advisories_tech2008-2.pdf. Fact Sheet EPA-823-F-09-007, Washington, D.C. Accessed 18 January 2011
US National Library of Medicine (2010) http://toxmap.nlm.nih.gov/toxmap/combo/mapControls.do. Accessed 14 Dec 2010
Wang W, Driscoll CT (1995) Patterns of total mercury concentrations in Onondaga Lake, New York. Environ Sci Technol 29:2261–2266
Watras CJ, Morrison KA (2008) The response of two remote, temperate lakes to changes in atmospheric mercury deposition, sulfate, and the water cycle. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 65:100–116
Wiener JG, Krabbenhoft DP, Heinz GH, Scheuhammer AM (2003) Ecotoxicology of mercury. In: Hoffman DJ, Rattner BA, Burton GA Jr, Cairns J Jr (eds) Handbook of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 409–463
Wiener JG, Knights C, Sandheinrich MB, Jeremiason JD, Brigham ME, Engstrom DR, Woodruff LG, Cannon WF, Balogh SJ (2006) Mercury in soils, lakes and fish in Voyageurs National Park (Minnesota): importance of atmospheric deposition and ecosystem factors. Environ Sci Technol 40:6261–6268
Wiener JG, Evers DC, Gay DA, Morrison HA, Williams KA (2011) Mercury contamination in the Laurentian Great Lakes region: introduction and overview. Environ Pollut (in press)
Wolfe MF, Atkeson T, Bowerman W, Burger K, Evers DC, Murray MW, Zillioux E (2007) Wildlife indicators. In: Harris R, Krabbenhoft DP, Mason R, Murray MW, Reash R, Saltman T (eds) Ecosystem response to mercury contamination: indicators of change SETAC. CRC Press, Webster, New York, pp 123–189
Yu X, Driscoll CT, Montesdeoca M, Evers DC, Duron M, Williams KA, Schoch N, Kamman NC (2011) Spatial patterns of mercury in biota of Adirondack, New York lakes. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0717-y
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Wildlife Conservation Society, Natural History Museum of the Adirondacks, and Audubon International, as well as NYSERDA and NYS DEC. The authors also thank ESRI for their software donation, which facilitated the compilation and analysis of data at the Biodiversity Research Institute. Sources for perch data include the Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission, Indiana Department of Environmental Management, Michigan Department of Environmental Quality, Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, New York State Energy Research and Development Authority, Ohio Environmental Protection Agency, Ontario Ministry of the Environment, and the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evers, D.C., Williams, K.A., Meyer, M.W. et al. Spatial gradients of methylmercury for breeding common loons in the Laurentian Great Lakes region. Ecotoxicology 20, 1609–1625 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0753-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0753-7