Abstract
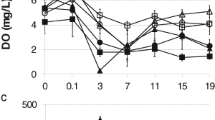
Butachlor is the most commonly used herbicide on paddy fields in Taiwan and throughout Southeast Asia. Since paddy fields provide habitat for pond breeding amphibians, we examined growth, development, time to metamorphosis, and survival of alpine cricket frog tadpoles (Fejervarya limnocharis) exposed to environmentally realistic concentrations of butachlor. We documented negative impacts of butachlor on survival, development, and time to metamorphosis, but not on tadpole growth. The 96 h LC50 for tadpoles was 0.87 mg/l, much lower than the 4.8 mg/l recommended dosage for application to paddy fields. Even given the rapid breakdown of butachlor, tadpoles would be exposed to concentrations in excess of their 96 h LC50 for an estimated 126 h. We also documented DNA damage (genotoxicity) in tadpoles exposed to butachlor at concentrations an order of magnitude less than the 4.8 mg/l recommended application rate. We did not find that butachlor depressed cholinesterase activity of tadpoles, unlike most organophosphorus insecticides. We conclude that butachlor is likely to have widespread negative impacts on amphibians occupying paddy fields with traditional herbicide application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander PS, Chang C-M, Yang C-H (1963) Reproductive variation in the female rice frog Rana limnocharis during the spring season in Taiwan. Tunghai J 5(2):19–32
Alexander PS, Alcala AC, Wu DY (1979) Annual reproductive pattern in the rice frog Rana L. limnocharis in Taiwan. J Asian Ecol 1:68–78
Ateeq B, Farsh MA, Ahmad W (2005) Detection of DNA damage by alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis in 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic-acid- and butachlor-exposed erythrocytes of Clarias batrachus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:348–354
Bambaradeniya CNB (2000) Rice field: an important man-made habitat of herpetofauna. Paper presented at the proceeding of the 4th Asian Herpetological Congress, Chengdu, China
Bambaradeniya CNB, Amarasinghe FP (2003) Biodiversity associated with the rice field agroecosystem in Asian countries: a brief review. International Water Management Institute, Columbus
Berry PY (1975) The amphibian fauna of peninsular Malaysia. Tropical Press, Kuala Lumpur
Brusick DJ, Ashby J, de Serres FJ, Lohman PHM, Matsushima T, Matter BE, Mendelsohn ML, Moore DH II, Nesnow S, Waters MD (1992) A method for combining and comparing short-term genotoxicity test data: preface: a report from ICPEMC committee 1. Mutat Res 266:1–6
Chen HW, Chien ML, Chaung YH, Lii CK, Wang TS (2004) Extracts from cigarette smoke induce DNA damage cell adhesion molecule expression through different pathway. Chem Biol Interact 150:233–241
Clements C, Ralph S, Petras M (1997) Genotoxicity of select herbicides in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles using the alkaline single-cell gel DNA electrophoresis (comet) assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 29:277–288
Del Buano D, Scarponi L, Amato RD (2005) An analytical method for the simultaneous determination of butachlor and benoxacor in wheat and soil. J Agric Food Chem 53:4326–4330
Geng BR, Yao D, Xue QQ (2005a) Acute toxicity of the pesticide dichlorvos and the herbicide butachlor of tadpoles of four anuran species. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:343–349
Geng BR, Yao D, Xue QQ (2005b) Genotoxicity of pesticide dichlorvos and herbicide butachlor in Rhacophorus megacephalus tadpoles. Acta Zool Sin 51:447–454
Gosner K (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Hsu KY, Lin HJ, Lin JK, Kuo WS, Ou YH (2005) Mutagenicity study of butachlor and its metabolites using Salmonella typhimurium. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 38:409–416
Junghans M, Backhaus T, Faust M, Scholze M, Grimme LH (2003) Predictability of combined effects of eight chloroacetanilide herbicides on algal reproduction. Pest Manag Sci 59:1101–1110
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Lohman PHM, Mendelsohn ML, Moore DH II, Waters MD, Brusick DJ, Ashby J, Lohman WJA (1992) A method for comparing and combining short-term genotoxicity test data: the basic system. Mutat Res 266:7–25
Lue KY, Tu MC, Shang G (1999) A field guide of the amphibians and reptiles of Taiwan. Great Nature Magazine Publisher, Taipei
Muthukaruppan G, Gunasekaran P (2010) Effect of butachlor herbicide on earthworm Eisenia fetida—its histology and perspicuity. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2010:1–4
Muthukaruppan G, Janardhanan S, Vijayalakshmi G (2005) Sublethal Toxicity of the herbicide butachlor on the earthworm Perionyx sansibaricus and its histological changes. J Soils Sediments 5:82–86
Panneerselvam N, Sinha S, Shanmugam G (1999) Butachlor is cytotoxic and clastogenic and induces apoptosis in mammalian cells. Indian J Exp Biol 37:888–892
Rajyalakshmi T, Srinivas T, Swamy KV, Prasad NS, Mohan PM (1996) Action of the herbicide butachlor on cholinesterases in the freshwater snail Pila globosa (Swainson). Drug Chem Toxicol 19:325–331
Ralph S, Petras M (1997) Genotoxicity monitoring of small bodies of water using two species of tadpoles and the alkaline single cell gel (comet) assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 29:418–430
Ralph S, Petras M, Pandrangi R, Vrzoc M (1996) Alkaline single cell gel (comet) assay and genotoxicity monitoring using two species of tadpoles. Environ Mol Mutagen 28:112–120
Seefeldt SS, Jensen JE, Fuerst EP (1995) Log-logistic analysis of herbicide dose-response relationships. Weed Technol 9:218–227
Senseman SA (2007) Herbicide Handbook. Weed Science Society of America, Lawrence
Shang KS, Yang YJ, Li PH (2009) Field guide to amphibians and reptiles in Taiwan. Owl Publishing House Co., Ltd, Taipei
Sinha S, Panneerselvam N, Shanmugam G (1995) Genotoxicity of the herbicide butachlor in cultured human lymphocytes. Mut Res Genet Toxicol 344:63–67
Sumida M, Kotaki M, Islam MM, Djong TH, Igawa T, Kondo Y, Matsui M, Anslem DS, Khonsue W, Nishioka M (2007) Evolutionary relationships and reproductive isolating mechanisms in the rice frog (Fejervarya limnocharis) species complex from Sri Lanka, Thailand, Taiwan and Japan, inferred from mtDNA gene sequences, allozymes, and crossing experiments. Zool Sci 24:547–562
Taiwan Agrochemical Industrial Association (1996) Domestic manufacturers production and sale of pesticides in 1995. Taipei, Taiwan
Tilak KS, Veeraiah K, Bhaskara Thathaji P, Butchiram MS (2007) Toxicity studies of butachlor to the freshwater fish Channa punctata (Bloch). J Environ Biol 28:485–487
Vaughan DA, Lu BR, Tomooka N (2008) The evolving story of rice evolution. Plant Sci 174:394–408
Vonesh JR, Buck J (2007) Pesticide alters habitat selection in gray treefrogs. Oecologia (Berl) 154:219–226
Wang YS, Jaw CG, Tang HC, Lin TS, Chen YL (1992) Accumulation and release of herbicides butachlor, thiobencarb, and chlomethoxyfen by fish, clam, and shrimp. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 48:474–480
Wells KD (2007) The ecology and behaviour of amphibians. The University of Chicago Press, Chicaga
Wilson AGE, Takei AS (2000) Summary of toxicology studies with butachlor. J Pestic Sci 25:75–83
Wu CS, Kam YC (2009) Effects of salinity on the survival, growth, development, and metamorphosis of Fejervarya limnocharis tadpoles living in brackish water. Zool Sci (Tokyo) 26:476–482
Yang YR (1998) A field guide to the frogs and toads of Taiwan. Chinese Photography Association, Taipei (in Chinese)
Yin LC, guo HR, Zhang SC, Wang J (2007) Study on the acute toxicity and genotoxicity of herbicide butachlor in flounder, Paralichihys olivaceus, and flounder gill (FG) cells. J Ocean Univ Qingdao 37:167–171
Yin XH, Li SN, Zhang L, Zhu GN (2008) Evaluation of DNA damage in Chinese toad (Bufo gargarizans) after in vivo exposure to sublethal concentration of four herbicides using the comet assay. Ecotoxicology 17:280–286
Yu KN, Qi CJ, Tang K (1993) Relationship between degradation rate of butachlor and conditions of paddy fields. Acta Sci Circumstantiae 13:169–173
Zug GR, Vitt LJ, Caldwell JP (2001) Herpetology. Academic Press, New York
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a National Science Council Grant (NSC 95-2311-B-029-006-MY3) to YCK. Joan Fellers, Patrick Kleeman, and Norm Scott provided helpful comments on the manuscript. Any use of trade, product, or firm names in this publication is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the US Government. This is contribution 417 of the US Geologic Survey, Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative (ARMI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, WY., Wang, CY., Wang, TS. et al. Impacts of the herbicide butachlor on the larvae of a paddy field breeding frog (Fejervarya limnocharis) in subtropical Taiwan. Ecotoxicology 20, 377–384 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0589-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0589-6