Abstract
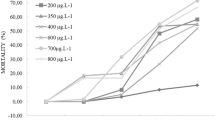
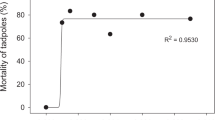
The study of the effects of the insecticide cypermethrin (CY) technical grade and its Sherpa® commercial formulation on Hypsiboas pulchellus tadpoles assessing lethality, behavior, growth, and abnormalities under standardized laboratory conditions is reported. Observed behaviors were identified and categorized by means of a ranking system according to the loss of mobility. Results of acute lethal effects indicate higher potency for Sherpa® at this level of assessment. All effects on behavior showed an increasing degree of injury as insecticide concentration increased. Organisms exposed to technical grade CY showed lower body length with respect to controls from 3.44 µg CY/L to higher concentrations, whereas those exposed to Sherpa® exhibited lower growth from 0.83 µg CY/L. Both forms of the tested insecticide caused abnormalities between 0.34 and 4.18 µg CY/L, but 100% of malformed individuals was detected from 34.4 µg CY/L for those exposed to the technical grade CY, and from 8.36 µg CY/L for those exposed to Sherpa®. This study proposes the use of easily identifiable and distinguishable sublethal end-points. The high input loads of CY in natural environments, the detected concentrations in the field, in addition to the low levels of this insecticide required to induce sublethal effects (which could eventually lead to death), allow for the conclusion that the insecticide is a risk factor for amphibians inhabiting agroecosystems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini MG, Natale GS, Ronco AE (2009) Impact of endosulphan and cypermethrin mixture on amphibians under field use forbiotech soya bean production. Int J Environ Health 3(4):379–389
Alford RA, Harris RN (1988) Effects of larval growth history on anuran metamorphosis. Am Nat 131:91–106
Bantle JA, Dumont JN, Finch RA, Linder G, Fort DJ (1996) Atlas of abnormalities. A guide for the performance of FETAX, 2nd edn. Oklahoma State University, Stillwater
Beebee TJC, Griffiths RA (2005) The amphibian decline crisis: a watershed for conservation biology? Biol Conserv 125:271–285
Berril M, Bertram S, Wilson A, Louis S, Brigham D, Stromberg C (1993) Lethal and sublethal impact of pyrethroid insecticides on amphibian embryos and tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:525–539
Bindraban PS, Franke AC, Ferraro DO, Ghersa CM, Lotz LAP, Nepomuceno A, Smulders MJM, van de Wiel CCM (2009) GM-related sustainability: agro-ecological impacts, risks and opportunities of soy production in Argentina and Brazil. Plant Research International B.V, Wageningen
Blaunstein AR, Kiesecker JM (2002) Complexity in conservation: lessons from the global decline of amphibian populations. Ecol Lett 57:21–43
Bridges CM (2000) Long-term effects of pesticide exposure al various life stages of the southern leopard frog (Rana sphenocephala). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:91–96
Cabagna M, Lajmanovich RC, Peltzer PM, Attademo M, Ale E (2006) Induction of micronucleus in tadpoles of Odontophrynus americanus (Amphibia: Leptodactylidae) by the pyrethroid insecticide cypermethrin. Toxicol Environ Chem 88:729–737
Campana MA, Panzeri AM, Moreno VJ, Dulout FN (2003) Micronuclei induction in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles by the pyrethroid insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin. Genet Mol Biol 26:99–103
Carriquiriborde P, Diaz J, Mugni H, Bonetto C, Ronco EA (2007) Impact of cypermethrin on stream fish populations under field-use in biotech-soybean production. Chemosphere 68:613–621
CASAFE (2007) Guía de productos fitosanitarios. Cámara de Sanidad Agropecuaria y Fertilizantes, Buenos Aires
Cei JM (1980) Amphibians of Argentina. Monit Zool Italiano, Ital J Zool Monogr 2
Crossland NO (1982) Aquatic toxicology of cypermethrin. II. Fate and biological effects in pond experiments. Aquat Toxicol 2:205–222
Edwards R, Millburn P, Hutson DH (1986) Comparative toxicity of cis-cypermetrhrin in Rainbow trout, frog, mouse and quail. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 84:512–522
Emerson SB (1986) Heterochony and frogs: the relationship of a life history trait to morphological form. Am Nat 127:167–183
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis. Cambridge University Press, London
Gammon DW, Brown MA, Casida JE (1981) Two classes of pyrethroid action in the cockroach. Pestic Biochem Physiol 15:181–191
Gosner KL (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetology 16:183–190
Greulich K, Pflugmacher S (2003) Differences in susceptibility of various life stages on amphibians to pesticide exposure. Aquat Toxicol 65:329–336
Harris RN (1999) The biology of anuran larvae. In: McDiarmid RW, Altig R (eds) Tadpoles. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 279–294
Hensley FR (1993) Ontogenetic loss of phenotypic plasticity of age at metamorphosis in tadpoles. Ecology 74:2405–2412
Houlahan JE, Findlay CS, Schmidt BR, Meyers AH, Kusmin SL (2000) Quantitative evidence for global amphibians population declines. Environ Pollution 82:277–288
Izaguirre MF, Lajmanovich RC, Peltzer PM, Soler AP, Casco VH (2000) Cypermethrin-induced apoptosis in the telencephalon of Physalaemus biligonigerus tadpoles (Anura: Leptodactylidae). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 65:501–507
Jergentz S, Mugni H, Bonetto C, Schulz R (2005) Assessment of insecticide contamination in runoff and stream water of small agricultural streams in the main soybean area of Argentina. Chemosphere 61:817–826
Johansson M, Piha H, Kylin H, Merilä J (2006) Chemistry toxicity of six pesticides to common frog (Rana temporaria) tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:3164–3170
Jolly AL, Avault JW (1978) Acute toxicity of permethrin to several aquatic animals. Trans Am Fish Soc 107:825–827
Khan MZ, Tabassum R, Naqvi SNH, Shah EZ, Tabassum F, Ahmad I, Fatima F (2003) Effect of cypermethrin and permethrin on cholinesterase activity and protein contents in Rana tigrina (Amphibia). Turk J Zool 27:243–246
Mann RM, Bidwell JR (1999) The toxicity of glyphosate and several glyphosate formulations to four species of southwestern Australian frogs. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:193–199
Mann RM, Hyne RV, Choung CB, Wilson SP (2009) Amphibians and agricultural chemicals: review of the risks in a complex environment. Environ Pollut 157(11):2903–2927
Marino D, Ronco EA (2005) Cypermethrin and chlorpyrifos concentration levels in surface water bodies of the Pampa Ondulada, Argentina. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:820–826
Materna EJ, Rabeni CF, LaPoint TW (1995) Effect of the synthetic pyrethroid insecticide esfenvalerate on larval leopard frog (Rana spp.). Environ Toxicol Chem 14:613–622
Natale GS (2006) Análisis Ecotoxicológico de una Comunidad de Anuros de la Región Pampeana: Efecto del Cr(VI) Sobre Embriones y Larvas de Distintas Especies de una Taxocomunidad, PhD Thesis, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Buenos Aires
Natale GS, Basso NG, Ronco AE (2000) Effect of Cr(VI) on early life stages of three species of hylid frogs (Amphibia, Anura) from South America. Environ Toxicol 15:509–512
Natale GS, Ammassari LL, Basso NG, Ronco AE (2006) Acute and chronic effects of Cr(VI) on Hypsiboas pulchellus embryos and tadpoles. Dis Aquat Org 72:261–267
Paulov S (1990) Potential impact of pyrethroids (cypermethrin) on the model amphibians (Rana temporaria). Biologia (Bratislava) 45:133–139
Pechman JH, Wake DB (1997) Declines and disappearances of amphibian populations. In: Meffe GK, Carrol CR (eds) Principles of conservation biology, 2nd edn. Sinauer, Sunderland, pp 135–137
Polat H, Erkoç FÜ, Viran R, Koçak O (2002) Investigation of acute toxicity of beta-cypermethrin on guppies Poecilia reticulata. Chemosphere 49:39–44
Pough FH, Kamel F (1984) Post-metamorphic change in activity metabolism of anurans in relation to life history. Oecologia 65:138–144
Relyea RA (2009) A cocktail of contaminants: how mixtures of pesticides at low concentrations affect aquatic communities. Oecologia 159:363–376
Ronco EA, Carriquiriborde P, Natale GS, Martin ML, Mugni H, Bonetto C (2008) Integrated approach for the assessment of biotech soybean pesticides impact on low order stream ecosystems of the Pampasic Region. In: Chen J, Guo C (eds) Ecosystem ecology research trends. Nova Science, Hauppauge, pp 209–239
Saha S, Kaviraj A (2008) Acute toxicity of synthetic pyrethroid cypermethrin to some freshwater organisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:49–52
Salibián A (1992) Effects of deltamethrin on the South American toad, Bufo arenarum, tadpoles. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 48:616–621
Sparling DW, Fellers GM, McConnell L (2001) Pesticides and amphibian population declines in California, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1591–1595
Stephenson RR (1982) Aquatic toxicology of cypermethrin. I. Acute toxicology to some freshwater fish and invertebrates in laboratory tests. Aquat Toxicol 2:175–185
Stuart SN, Chanson JS, Cox NA, Young BE, Rodriguez ASL, Fischman DL, Waller RW (2004) Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinction worldwide. Science 306:1591–1595
Taigen TL, Pough FH (1985) Metabolic correlates of anuran behavior. Am Zool 25:987–997
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1999) http://www.epa.gov/scripoly/sap/1999/february/pyreth.pdf. Accessed 28 December 2009
Vijverberg HPM, Van Der Bercken J (1982) Action of pyrethroid insecticides on the vertebrate nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 8:421–440
Willbur HM, Collins JP (1973) Ecological aspect of amphibian metamorphosis. Science 182:1305–1314
Word Health Organization (WHO) (1992) Alpha-cypermethrin. Environmental Health Criteria
Zar JH (2010) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. N. G. Basso for allowing use of instrumentation, Dr. D. Marino for chemical analysis of samples, CIMA-Grupo Anfibio for assistance in the experiments, and C. Knipp for editorial suggestions. This study was funded by the ANPCyT PICT project 38350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agostini, M.G., Natale, G.S. & Ronco, A.E. Lethal and sublethal effects of cypermethrin to Hypsiboas pulchellus tadpoles. Ecotoxicology 19, 1545–1550 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0539-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0539-3