Abstract
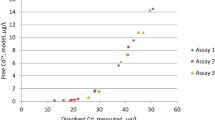
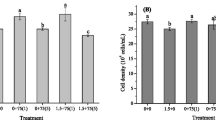
During the time-course of ecotoxicity tests with algae and chronic (reproductive) toxicity tests with daphnids, in which algae are present as a food source, pH can dramatically increase due to photosynthetic activity. As pH changes can significantly affect metal speciation and thus its bioavailability, it may be necessary to buffer the pH of the exposure medium. One class of buffers (Good’s N-subtituted aminosulfonic acids) are increasingly being used in biological and chemical applications, including ecotoxicity testing. However, the potential effect of these buffers on metal toxicity has, so far, scarcely been examined. In this study we investigated if MOPS (3-N morpholino propane sulfonic acid) affected the toxicity of copper and zinc to two standard test organisms: the cladoceran Daphnia magna and the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. First, we demonstrate that up to a concentration of 750 mg l−1 (which proved to be sufficient for pH buffering) MOPS did not affect 21-day net reproduction of D. magna or the 72-h population growth of P. subcapitata. Second, we conducted bioassays in copper and zinc spiked standard media for the pH range 6 – 8. For D. magna the possible effect of 750 mg l−1 MOPS on acute copper and zinc toxicity was investigated by performing parallel 48-h toxicity tests in NaHCO3 and MOPS buffered test media. Seventy-two hour growth inhibition assays with P. subcapitata were performed in parallel in MOPS and NaHCO3 buffered test media and in test media with daily manual pH adjustment with HCl. For daphnids no significant differences in copper and zinc toxicity were observed between MOPS or NaHCO3 buffered test media. For algae no significant differences in metal toxicity were observed between MOPS and HCl buffered media, but in test media buffered with NaHCO3 an increased copper and zinc toxicity was observed as a consequence of pH increases during the test. Clearly, the results of this study demonstrate the importance of pH buffering in metal toxicity testing and the suitability of the MOPS buffer for that purpose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.A.C. De Schamphelaere C.R. Janssen (2002) ArticleTitleA biotic ligand model predicting acute copper toxicity for Daphnia magna: the effect of calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium and pH Environ. Sci. Technol. 36 48–54 Occurrence Handle11817370 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXoslSgtbY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/es000253s
B.P. Elendt W.R. Bias (1990) ArticleTitleTrace nutrient deficiency in daphnia magna cultured in standard medium for toxicity testing, effects of the optimization of culture conditions on life history parameters of D magna. Water Res 24 1157–1167 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhvFSgsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(90)90180-E
W.J. Ferguson (1980) ArticleTitleHydrogen ion buffers for biological research Anal. biochem. 104 300–310 Occurrence Handle7446957 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXksVSquro%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2697(80)90079-2
N.M. Franklin J.L. Stauber S.J. Markich R.P. Lim (2000) ArticleTitlepH-dependent toxicity of copper and uranium to a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.) Aquat. Toxicol. 48 275–289 Occurrence Handle10686332 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXht1Kqtrw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00042-9
N.E. Good S. Izawa (1972) ArticleTitleHydrogen ion buffers Method Enzymol. 24 53–68 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0076-6879(72)24054-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXhtlCjug%3D%3D
N.E. Good G.D. Winget W. Winter T.N. Connolly S. Izawa R.M.M. Singh (1966) ArticleTitleHydrogen ion buffers for biological research Biochemistry 5 467–477 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF28XltlKhuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle5942950 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi00866a011
L. Haanstra P. Doelman J.H. Oude Voshaar (1985) ArticleTitleThe use of sigmoidal dose-response curves in soil ecotoxicological research Plant Soil 84 293–297 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXks1Khsr8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02143194
M.A. Hamilton R.C. Russo R.V. Thurston (1977) ArticleTitleTrimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays Environ. Sci. Technol. 11 714–719 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXksl2it7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/es60130a004
D.G. Heijerick K.A.C. De Schamphelaere C.R. Janssen (2002) ArticleTitlePredicting acute zinc toxicity for Daphnia magna as a function of key water chemistry characteristics: development and validation of a Biotic Ligand Model Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 21 1309–1315 Occurrence Handle12069319 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xktleru7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1897/1551-5028(2002)021<1309:PAZTFD>2.0.CO;2
D.G. Heijerick C.R. Janssen W.M. De Coen (2003) ArticleTitleThe Combined Effects of Hardness, pH, and Dissolved Organic Carbon on the Chronic Toxicity of Zn to D. magna: development of a Surface Response Model. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 44 210–217 Occurrence Handle12520393 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjsF2ntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00244-002-2010-9
ISO. (1989). Water Quality–Fresh water algal growth inhibition test with Scenedesmus subspicatus and Raphidocelis subcapitata. ISO-8692, International Organisation for Standardisation, Geneva, Switzerland.
InstitutionalAuthorNameISO (1996) Water quality - Determination of the inhibition of the mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea) - Acute toxicity test ISO-6341 International Organisation for Standardisation, Geneva, Switzerland
A. Kandegedara D.B. Rorabacher (1999) ArticleTitleNoncomplexing tertiary amines as ‘better’ buffers covering the range of pH 3-11. Temperature dependence of their acid dissociation constants. Anal. Chem. 71 3140–3144 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjvFams7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/ac9902594
O.M. Lage M.T.S.D. Vasconcelos H.M.V.M. Soares J.M. Osswald F. Sansonetty A.M. Parente R. Salema (1996) ArticleTitleSuitability of the pH buffers 3-[‘N-N-bis(hydroxyethyl)amino ]-2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid and N-2-hydroxyethyl piperazine-N’-2-ethanesulfonic acid for in vitro copper toxicity studies Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31 273–281 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00212366
S.M. Macfie Y. Tarmohamed P.M. Welboum (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of cadmium, cobalt, copper and nickel on growth of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: the influence of cell wall and pH Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27 454–458 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmvFCltLs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00214835
J.P. Meador (1991) ArticleTitleThe interaction of pH, dissolved organic carbon and total copper in the determination of ionic copper and toxicity Aquat. Toxicol. 19 13–32 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtFKmu7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0166-445X(91)90025-5
C. Nalewajko B. Colman M. Olaveson (1997) ArticleTitleEffects of pH on growth, photosynthesis, respiration and copper tolerance of three scenedesmus strains Environ. Exp. Bot. 37 153–160 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntlygt74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0098-8472(96)01029-5
N. Nyholm T. Källqvist (1989) ArticleTitleMethods for growth inhibition tests with freshwater algae Environ. Toxicol. 8 689–703 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXltFSgtbY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1897/1552-8618(1989)8[689:MFGITT]2.0.CO;2
OECD. (1984a). Alga growth inhibition test, Test Guideline No. 201. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
OECD. (1984b). Daphnia sp., acute immobilisation test. Test Guideline No. 202. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
OECD. (1998). Daphnia magna reproduction test. Test Guideline No. 211. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
M.K. Schubauer-Berigan J.R. Dierkes P.D. Monson G.T. Ankley (1993) ArticleTitlepH-dependent toxicity of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn to Ceriodaphnia dubia, Pimephales promelas, Hyalella azteca, and Lumbriculus variegatus Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12 1261–1266 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXks1Ght74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1897/1552-8618(1993)12[1261:PTOCCN]2.0.CO;2
R.C. Santore R. Mathew P.R. Paquin D. Di Toro (2002) ArticleTitleApplication of the biotic ligand model to predicting zinc toxicity to rainbow trout, fathead minnow and Daphnia magna Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C 133 271–285
W. Stumm J.J. Morgan (1996) Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters John Wiley & Sons New York
US EPA. (1991). Methods for aquatic toxicity identification evaluation. Phase I Toxicity characterisation procedures (second edition). EPA/600/6-91/003, United States Environmental Protection Agency
M.T.S.D. Vasconcelos C.M.R. Almeida O.M. Lage F. Sansonetty (2000) ArticleTitleInfluence of zwitterionic pH buffers on the bioavailability and toxicity of copper to the alga Amphidinium carterae Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19 2542–2550 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntVakurc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1897/1551-5028(2000)019<2542:IOZPBO>2.3.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Schamphelaere, K.A.C., Heijerick, D.G. & Janssen, C.R. Comparison of the Effect of Different pH Buffering Techniques on the Toxicity of Copper and Zinc to Daphnia Magna and Pseudokirchneriella Subcapitata . Ecotoxicology 13, 697–705 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-003-4429-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-003-4429-9