Summary
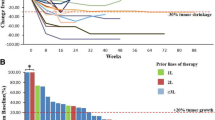
Background. Mucosal melanoma is rare and has distinct clinical and genetic features. Even with advances in targeted and immune therapies, the survival of patients with advanced or recurrent mucosal melanomas remains poor. The standard treatment remains controversial and we conducted this real-world study aimed to explore continuous intravenous recombinant human endostatin (Rh-endostatin) infusion plus chemotherapy in this population in the first-line setting. Methods. Overall, 43 patients with advanced or recurrent mucosal melanoma treated at Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center between April 2017 and August 2020 were retrospectively included. Patients received dacarbazine plus cisplatin or temozolomide plus cisplatin per the investigators’ preference. Rh-endostatin (105 mg/m2) was administered with continuous infusion for 168 h (Civ 168 h). Results. Of the 43 patients, 72.1% had metastatic disease, and the most common primary site was the gastrointestinal tract (51.2%). The most commonly observed mutations were NRAS (23.1%), BRAF (7.7%) and CKIT mutations (5.1%). An objective response was observed in 12 (30.0%) of the 40 evaluable patients, and disease control was achieved in 31 (77.5%) patients. With a median follow-up of 17.6 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 4.9 and 15.3 months, respectively. Additionally, high lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) (p = 0.023, HR 0.29, 95% CI: 0.10–0.84) and BRAF/KIT/RAS mutation (p = 0.028, HR 0.24, 95% CI: 0.07–0.86) were independently correlated with prolonged OS. Toxicity was manageable overall. Conclusion. Continuous Rh-endostatin infusion plus chemotherapy was effective and safe for the treatment of advanced or recurrent mucosal melanoma. High LMR was correlated with favorable PFS and OS in this patient population.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data of this study are available per the corresponding author’s approval.
Abbreviations
- BRAF:
-
B-raf proto-oncogene
- ORR:
-
Overall response rate
- ICIs:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung cancer
- SCLC:
-
Small-cell lung cancer
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- ECOG:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
- PS:
-
Performance status
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- NLR:
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
- LMR:
-
Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio
- AEs:
-
Adverse events
- NCI CTCAE:
-
National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events
- RECIST:
-
Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors
- CR:
-
Complete response
- PR:
-
Partial response
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- TKIs:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
References
Barth A, Wanek LA, Morton DL (1995) Prognostic factors in 1,521 melanoma patients with distant metastases. J Am Coll Surg 181(3):193–201
Lian B, Cui C-L, Zhou L, Song X, Zhang X-S, Wu D, Si L, Chi Z-H, Sheng X-N, Mao L-L, Wang X, Tang B-X, Yan X-Q, Kong Y, Dai J, Li SM, Bai X, Zheng N, Balch C-M, Guo J (2017) The natural history and patterns of metastases from mucosal melanoma: an analysis of 706 prospectively-followed patients. Annals of oncology: official J European Soc Med Oncol 28(4):868–873. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw694
D’Angelo SP, Larkin J, Sosman JA, Lebbé C, Brady B, Neyns B, Schmidt H, Hassel JC, Hodi FS, Lorigan P, Savage KJ, Miller WH Jr, Mohr P, Marquez-Rodas I, Charles J, Kaatz M, Sznol M, Weber JS, Shoushtari AN, Ruisi M, Wolchok JD (2017) Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab Alone or in Combination With Ipilimumab in Patients With Mucosal Melanoma: A Pooled Analysis. Journal of clinical oncology: Official J European Soc Med Oncol 35(2):226–235. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.67.9258
Lyu J, Wu Y, Li C, Wang R, Song RG, Guo W (2016) Mutation scanning of BRAF, NRAS, KIT, and GNAQ/GNA11 in oral mucosal melanoma: a study of 57 cases. Journal of oral pathology and medicine: official publication of the International Association of Oral Pathologists and the American Academy of Oral Pathology 45(4):295–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12358
Kuk D, Shoushtari AN, Barker CA, Panageas KS, Munhoz RR, Momtaz P, Ariyan CE, Brady MS, Coit DG, Bogatch K, Callahan MK, Wolchok JD, Carvajal RD, Postow MA (2016) Prognosis of Mucosal, Uveal, Acral, Nonacral Cutaneous, and Unknown Primary Melanoma from the Time of First Metastasis. Oncologist 21(7):848–854. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0522
McLaughlin CC, Wu XC, Jemal A, Martin HJ, Roche LM, Chen VW (2005) Incidence of noncutaneous melanomas in the U.S. Cancer 103(5):1000–1007. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20866
Chi Z, Li S, Sheng X, Si L, Cui C, Han M, Guo, J (2011) Clinical presentation, histology, and prognoses of malignant melanoma in ethnic Chinese: a study of 522 consecutive cases. BMC cancer 11(85). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-85
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88(2):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81848-6
Yoon SS, Eto H, Lin CM, Nakamura H, Pawlik TM, Song SU, Tanabe KK (1999) Mouse endostatin inhibits the formation of lung and liver metastases. Can Res 59(24):6251–6256
Kim YM, Jang JW, Lee OH, Yeon J, Choi EY, Kim KW, Lee ST, Kwon YG (2000) Endostatin inhibits endothelial and tumor cellular invasion by blocking the activation and catalytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase. Can Res 60(19):5410–5413
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’Reilly MS (1997) Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 390(6658):404–407. https://doi.org/10.1038/37126
Mendoza L, Valcárcel M, Carrascal T, Egilegor E, Salado C, Sim BK, Vidal-Vanaclocha F (2004) Inhibition of cytokine-induced microvascular arrest of tumor cells by recombinant endostatin prevents experimental hepatic melanoma metastasis. Can Res 64(1):304–310. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1829
Han B, Xiu Q, Wang H, Shen J, Gu A, Luo Y, Bai C, Guo S, Liu W, Zhuang Z, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Jiang L, Zhou J, Jin X (2011) A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy of paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with endostar for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of thoracic oncology: official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. 6(6):1104–1109.https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182166b6b
Zhou Z-T, Zhou F-X, Wei Q, Zou L-Y, Qin B-F, Peng X-S (2011) Phase II study of cisplatin/etoposide and endostar for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68(4):1027–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-011-1576-1
Lu S, Li L, Luo Y, Zhang L, Wu G, Chen Z, Huang C, Guo S, Zhang Y, Song X, Yu Y, Zhou C, Li W, Liao M, Li B, Xu L, Chen P, Hu C, Hu C (2015) A multicenter, open-label, randomized phase II controlled study of rh-endostatin (Endostar) in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. Journal of thoracic oncology: official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 10(1):206–211. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000343
Yang H, Sui Y, Guo X, Tan X, Li Y, Wang M (2018) Endostar continuous intravenous infusion combined with S-1 and oxaliplatin chemotherapy could be effective in treating liver metastasis from gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 14(Supplement):S1148–S1151. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.204880
Zhou J-F, Bai C-M, Wang Y-Z, Li X-Y, Cheng Y-J, Chen S-C (2011) Endostar combined with chemotherapy for treatment of metastatic colorectal and gastric cancer: a pilot study. Chin Med J 124(24):4299–4303
Jia Y, Liu M, Huang W, Wang Z, He Y, Wu J, Ren S, Ju Y, Geng R, Li Z (2012) Recombinant human endostatin endostar inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in a mouse xenograft model of colon cancer. Pathology oncology research: POR 18(2):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9447-y
Su A, Zhang J, Pan Z-H, Zhou Q-M, Lv X (2013) Salvage therapy of gemcitabine plus endostar significantly improves progression-free survival (PFS) with platinum-resistant recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP 14(3):1841–1846. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.3.1841
Jin T, Jiang F, Jin Q-F, Piao Y-F, Chen X-Z (2018) Endostar Combined with Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Chemotherapy for Patients with Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: an Update. Translational oncology 11(2):286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2018.01.002
Guan Y, Li A, Xiao W, Liu S, Chen B, Lu T, Zhao C, Han F (2015) The efficacy and safety of Endostar combined with chemoradiotherapy for patients with advanced, locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 6(32):33926–33934. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5271
Li Y, Tian Y, Jin F, Wu W, Long J, Ouyang J, Zhou Y (2020) A phase II multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare standard chemoradiation with or without recombinant human endostatin injection (Endostar) therapy for the treatment of locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Long-term outcomes update. Curr Probl Cancer 44(1):100492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2019.06.007
Cui C, Mao L, Chi Z, Si L, Sheng X, Kong Y, Li S, Lian B, Gu K, Tao M, Song X, Lin T, Ren X, Qin S, Guo J (2013) A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial of Endostar in patients with metastatic melanoma. Molecular therapy: the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 21(7):1456–1463. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2013.79
Carvajal RD, Spencer SA, Lydiatt W (2012) Mucosal melanoma: a clinically and biologically unique disease entity. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network: JNCCN 10(3):345–356. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2012.0034
Middleton MR, Grob JJ, Aaronson N, Fierlbeck G, Tilgen W, Seiter S, Gore M, Aamdal S, Cebon J, Coates A, Dreno B, Henz M, Schadendorf D, Kapp A, Weiss J, Fraass U, Statkevich P, Muller M, Thatcher N (2000) Randomized phase III study of temozolomide versus dacarbazine in the treatment of patients with advanced metastatic malignant melanoma. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 18(1):158–166. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2000.18.1.158
Eggermont AM, Kirkwood JM (2004) Re-evaluating the role of dacarbazine in metastatic melanoma: what have we learned in 30 years. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England:1990) 40(12):1825–1836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2004.04.030
Postow MA, Hamid O, Carvajal RD (2012) Mucosal melanoma: pathogenesis, clinical behavior, and management. Curr Oncol Rep 14(5):441–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-012-0244-x
Ma H-L, Hui Z-G, Peng F, Zhao LJ, Li D-M, Xu Y-J, Bao Y, Xu L-M, Zhai Y-R, Hu X, Wang J, Kong Y, Wang L-H, Chen M (2020) Different administration routes of recombinant human endostatin combined with concurrent chemoradiotherapy might lead to different efficacy and safety profile in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer: Updated follow-up results from two phase II trials. Thoracic cancer 11(4):898–906. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13333
Cui CL, Lu S, Chi ZH, Sheng XN, Mao LL, Wang X, Lian B, Yan XQ, Guo J (2015) Preliminary results of a phase II trial with continuous intravenous infusion of rh-endostatin in combination with dacarbazine as the first-line therapy for metastatic acral melanoma. Anticancer Res 35(7):4350–4351
Si L, Zhang X-S, Shu Y-Q, Pan H-M, Wu D, Liu JW, Lou F, Mao L-L, Wang X, Wen XZ, Gu YH, Zhu LJ, Lan SJ, Cai X, Diede SJ, Zhou Y, Ge J, Li JF, Wu HY, Guo J (2019) A Phase Ib Study of Pembrolizumab as Second-Line Therapy for Chinese Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Melanoma (KEYNOTE-151). Translational oncology 12(6):828–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2019.02.007
Tang B, Chi Z, Chen Y, Liu X, Wu D, Chen J, Song X, Wang W, Dong L, Song H, Wu H, Feng H, Yao S, Qin S, Zhang X, Guo J (2020) Safety, Efficacy, and Biomarker Analysis of Toripalimab in Previously Treated Advanced Melanoma: Results of the POLARIS-01 Multicenter Phase II Trial. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 26(16):4250–4259. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3922
Sheng X, Yan X, Chi Z, Si L, Cui C, Tang B, Li S, Mao L, Lian B, Wang X, Bai X, Zhou L, Kong Y, Dai J, Wang K, Tang X, Zhou H, Wu H, Feng H, Yao S, Guo J (2019) Axitinib in Combination With Toripalimab, a Humanized Immunoglobulin G4 Monoclonal Antibody Against Programmed Cell Death-1, in Patients With Metastatic Mucosal Melanoma: An Open-Label Phase IB Trial. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 37(32):2987–2999. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00210
Si L, Sheng XN, Mao LL, Li CL, Wang X, Bai X, Qi Z, Chi ZH, Cui CL, Lian B, Tang BX, Yan XQ, Zhou L, Li SM, Duan R (2020) A phase II study of vorolanib (CM082) in combination with toripalimab (JS001) in patients with advanced mucosal melanoma. J Clin Oncol 38(15_suppl):10040–10040
Ma J-Y, Liu Q (2018) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in patients with gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. International journal of surgery (London, England) 50:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.002
Mao Y, Chen D, Duan S, Zhao Y, Wu C, Zhu F, Chen C, Chen Y (2018) Prognostic impact of pretreatment lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in advanced epithelial cancers: a meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int 18:201. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0698-5
Nishijima TF, Muss HB, Shachar SS, Tamura K, Takamatsu Y (2015) Prognostic value of lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev 41(10):971–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.10.003
Lacono D, Basile D, Gerratana L, Vitale MG, Pelizzari G, Cinausero M, Poletto E, Puglisi F, Fasola G, Minisini AM (2019) Prognostic role of disease extent and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio in advanced melanoma. Melanoma Res 29(5):510–515. https://doi.org/10.1097/CMR.0000000000000584
Leontovich AA, Dronca RS, Nevala WK, Thompson M, Kottschade LA, Ivanov LV, Markovic SN, Melanoma Study Group of the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center (2017) Effect of the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio on the clinical outcome of chemotherapy administration in advanced melanoma patients. Melanoma Res 27(1):32–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/CMR.0000000000000290
Minowa T, Kato J, Hida T, Horimoto K, Sato S, Sawada M, Uhara H (2018) Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte and lymphocyte to monocyte ratios in advanced melanoma treated with anti-programmed death-1. European journal of dermatology: EJD 28(5):705–707. https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2018.3381
Wang Y, Zhang H, Yang Y, Zhang T, Ma X (2019) Prognostic Value of Peripheral Inflammatory Markers in Preoperative Mucosal Melanoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Front Oncol 9:995. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00995
Amit M, Tam S, Abdelmeguid AS, Roberts DB, Takahashi Y, Raza SM, Su SY, Kupferman ME, DeMonte F, Hanna EY (2017) Mutation status among patients with sinonasal mucosal melanoma and its impact on survival. Br J Cancer 116(12):1564–1571. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.125
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. (Grant No. 2016D01C091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SYJ, XWZ and FJ drafted the manuscript. ZGL and XL supervised and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Jin, F., Jiang, S. et al. Rh-endostatin combined with chemotherapy in patients with advanced or recurrent mucosal melanoma: retrospective analysis of real-world data. Invest New Drugs 40, 453–460 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01172-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01172-9