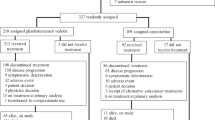
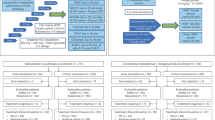
Summary
Background HER3/EGFR heterodimers have been implicated as a mode of resistance to EGFR-directed therapies. Methods This Phase 1 trial assessed the tolerability, maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of the HER-3 antibody seribantumab in combination with cetuximab (Part I) or cetuximab and irinotecan (Part II) in patients with EGFR-dependent cancers. In Part I, escalating doses of seribantumab and cetuximab were administered. In Part II of the trial, escalating doses of seribantumab/cetuximab were combined with irinotecan 180 mg/m2 administered every two weeks. Results 34 patients were enrolled in Part I (seribantumab/cetuximab) and 14 patients were enrolled in Part II (seribantumab/cetuximab/irinotecan). Common toxicities of seribantumab/cetuximab included acneiform rash, diarrhea, stomatitis, and paronychia. The MTD of Part I was seribantumab 40 mg/kg bolus, then 20 mg/kg weekly combined with cetuximab 400 mg/m2 bolus, then 250 mg/m2 IV weekly. Common toxicities reported in the seribantumab/cetuximab/irinotecan combination were similar to the Part I portion. However, toxicities were more frequent and severe with the triplet combination. There was one treatment-related death in Part II secondary to Grade 4 neutropenia and grade 3 diarrhea. Other dose-limiting toxicities in Part II were Grade 3 mucositis and Grade 3 diarrhea. A cholangiocarcinoma patient, previously untreated with EGFR-directed therapy, had a confirmed partial response (PR). One colorectal cancer patient, previously treated with EGFR-directed therapy, had an unconfirmed PR. Conclusions Seribantumab/cetuximab was well tolerated and patients experienced toxicities typical to EGFR inhibition. Unlike the seribantumab/cetuximab doublet, seribantumab/cetuximab/irinotecan was difficult to tolerate in this heavily pretreated population. There was limited efficacy of the combination therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351(4):337–345. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa033025
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar E, Kawecki A, Rottey S, Erfan J, Zabolotnyy D, Kienzer H-R, Cupissol D, Peyrade F, Benasso M, Vynnychenko I, De Raucourt D, Bokemeyer C, Schueler A, Amellal N, Hitt R (2008) Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 359(11):1116–1127. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0802656
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, Ove R, Kies MS, Baselga J, Youssoufian H, Amellal N, Rowinsky EK, Ang KK (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354(6):567–578. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa053422
Van Cutsem E, Köhne C-H, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien C-R, Makhson A, D'Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G, Roh JK, Folprecht G, Ruff P, Stroh C, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Nippgen J, Rougier P (2009) Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 360(14):1408–1417. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0805019
Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Siena S, Humblet Y, Hendlisz A, Neyns B, Canon J-L, Van Laethem J-L, Maurel J, Richardson G, Wolf M, Amado RG (2007) Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(13):1658–1664. doi:10.1200/jco.2006.08.1620
Misale S, Di Nicolantonio F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S, Bardelli A (2014) Resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer: from heterogeneity to convergent evolution. Cancer Discov 4(11):1269–1280. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-14-0462
Sacher AG, Jänne PA, Oxnard GR (2014) Management of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 120(15):2289–2298. doi:10.1002/cncr.28723
Boeckx C, Baay M, Wouters A, Specenier P, Vermorken JB, Peeters M, Lardon F (2013) Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: focus on potential molecular mechanisms of Drμg resistance. Oncologist 18(7):850–864. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0013
Prewett MC, Hooper AT, Bassi R, Ellis LM, Waksal HW, Hicklin DJ (2002) Enhanced antitumor activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody IMC-C225 in combination with irinotecan (CPT-11) against human colorectal tumor xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 8(5):994–1003
Ma J, Lyu H, Huang J, Liu B (2014) Targeting of erbB3 receptor to overcome resistance in cancer treatment. Mol Cancer 13(1):105
Gala K, Chandarlapaty S (2014) Molecular pathways: HER3 targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res 20(6):1410–1416. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-1549
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, Blair J, Hann B, Shokat KM, Moasser MM (2007) Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 445 (7126):437–441. doi:http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v445/n7126/suppinfo/nature05474_S1.html
Wheeler DL, Huang S, Kruser TJ, Nechrebecki MM, Armstrong EA, Benavente S, Gondi V, Hsu KT, Harari PM (2008) Mechanisms of acquired resistance to cetuximab: role of HER (ErbB) family members. Oncogene 27(28):3944–3956
Jain A, Penuel E, Mink S, Schmidt J, Hodge A, Favero K, Tindell C, Agus DB (2010) HER kinase Axis receptor dimer partner switching occurs in response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition despite failure to block cellular proliferation. Cancer Res 70(5):1989–1999. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-3326
Garrido G, Rabasa A, Garrido C, Lopez A, Chao L, Garcia-Lora AM, Garrido F, Fernandez LE, Sanchez B (2014) Preclinical modeling of EGFR-specific antibody resistance: oncogenic and immune-associated escape mechanisms. Oncogene 33(24):3129–3139. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.288
Kawakami H, Okamoto I, Yonesaka K, Okamoto K, Shibata K, Shinkai Y, Sakamoto H, Kitano M, Tamura T, Nishio K, Nakagawa K (2014) The anti-HER3 antibody patritumab abrogates cetuximab resistance mediated by heregulin in colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget 5(23):11847–11856. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2663
Jiang N, Wang D, Hu Z, Shin HJC, Qian G, Rahman MA, Zhang H, Amin ARMR, Nannapaneni S, Wang X, Chen Z, Garcia G, MacBeath G, Shin DM, Khuri FR, Ma J, Chen ZG, Saba NF (2014) Combination of anti-HER3 antibody MM-121/SAR256212 and cetuximab inhibits tumor growth in preclinical models of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 13(7):1826–1836. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-13-1093
Huang S, Li C, Armstrong EA, Peet CR, Saker J, Amler LC, Sliwkowski MX, Harari PM (2013) Dual targeting of EGFR and HER3 with MEHD7945A overcomes acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and radiation. Cancer Res 73(2):824–833. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-12-1611
Iida M, Brand T, Starr M, Huppert E, Luthar N, Bahrar H, Coan J, Pearson H, Salgia R, Wheeler D (2014) Overcoming acquired resistance to cetuximab by dual targeting HER family receptors with antibody-based therapy. Mol Cancer 13(1):242
Schoeberl B, Faber AC, Li D, Liang M-C, Crosby K, Onsum M, Burenkova O, Pace E, Walton Z, Nie L, Fulgham A, Song Y, Nielsen UB, Engelman JA, Wong K-K (2010) An ErbB3 antibody, MM-121, is active in cancers with ligand-dependent activation. Cancer Res 70(6):2485–2494. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-3145
Denlinger CS, Keedy VL, Cleary JM, Kubasek W, Onsum M, Moulis S, Garcia G, Schoeberl B, MacBeath G, Nering R, Murray J, Moyo V, Wong K-K, Shapiro G (2011) Abstract LB-410: Phase I dose escalation study of MM-121, a fully human monoclonal antibody to ErbB3, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res 71(8 Supplement):LB–410. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.am2011-lb-410
Jackman D, Pao W, Riely GJ, Engelman JA, Kris MG, Jänne PA, Lynch T, Johnson BE, Miller VA (2010) Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non–small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(2):357–360. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.24.7049
Huang J, Wang S, Lyu H, Cai B, Yang X, Wang J, Liu B (2013) The anti-erbB3 antibody MM-121/SAR256212 in combination with trastuzumab exerts potent antitumor activity against trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 12:134
Yu HA, Riely GJ, Lovly CM (2014) Therapeutic strategies utilized in the setting of acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 20(23):5898–5907. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-2437
Bertotti A, Migliardi G, Galimi F, Sassi F, Torti D, Isella C, Corà D, Di Nicolantonio F, Buscarino M, Petti C, Ribero D, Russolillo N, Muratore A, Massucco P, Pisacane A, Molinaro L, Valtorta E, Sartore-Bianchi A, Risio M, Capussotti L, Gambacorta M, Siena S, Medico E, Sapino A, Marsoni S, Comoglio PM, Bardelli A, Trusolino L (2011) A molecularly annotated platform of patient-derived xenografts (“Xenopatients”) identifies HER2 as an effective therapeutic target in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov 1(6):508–523. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-11-0109
Yonesaka K, Zejnullahu K, Okamoto I, Satoh T, Cappuzzo F, Souglakos J, Ercan D, Rogers A, Roncalli M, Takeda M, Fujisaka Y, Philips J, Shimizu T, Maenishi O, Cho Y, Sun J, Destro A, Taira K, Takeda K, Okabe T, Swanson J, Itoh H, Takada M, Lifshits E, Okuno K, Engelman JA, Shivdasani RA, Nishio K, Fukuoka M, Varella-Garcia M, Nakagawa K, Jänne PA (2011) Activation of ERBB2 Signaling Causes Resistance to the EGFR-Directed Therapeutic Antibody Cetuximab. Sci Transl Med 3(99):99ra86. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002442
Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I, Wang Y, Agrawal N, Bartlett BR, Wang H, Luber B, Alani RM, Antonarakis ES, Azad NS, Bardelli A, Brem H, Cameron JL, Lee CC, Fecher LA, Gallia GL, Gibbs P, Le D, Giuntoli RL, Goggins M, Hogarty MD, Holdhoff M, Hong S-M, Jiao Y, Juhl HH, Kim JJ, Siravegna G, Laheru DA, Lauricella C, Lim M, Lipson EJ, Marie SKN, Netto GJ, Oliner KS, Olivi A, Olsson L, Riggins GJ, Sartore-Bianchi A, Schmidt K, Shih l-M, Oba-Shinjo SM, Siena S, Theodorescu D, Tie J, Harkins TT, Veronese S, Wang T-L, Weingart JD, Wolfgang CL, Wood LD, Xing D, Hruban RH, Wu J, Allen PJ, Schmidt CM, Choti MA, Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Diaz LA (2014) Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Early- and Late-Stage Human Malignancies. Sci Transl Med 6(224):224ra224. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007094
Misale S, Arena S, Lamba S, Siravegna G, Lallo A, Hobor S, Russo M, Buscarino M, Lazzari L, Sartore-Bianchi A, Bencardino K, Amatu A, Lauricella C, Valtorta E, Siena S, Di Nicolantonio F, Bardelli A (2014) Blockade of EGFR and MEK Intercepts Heterogeneous Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapies in Colorectal Cancer. Sci Transl Med 6(224):224ra226. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007947
Andersen JB, Spee B, Blechacz BR, Avital I, Komuta M, Barbour A, Conner EA, Gillen MC, Roskams T, Roberts LR, Factor VM, Thorgeirsson SS (2012) Genomic and Genetic Characterization of Cholangiocarcinoma Identifies Therapeutic Targets for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Gastroenterology 142(4):1021–1031 . doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.005e1015
Ross JS, Wang K, Gay L, Al-Rohil R, Rand JV, Jones DM, Lee HJ, Sheehan CE, Otto GA, Palmer G, Yelensky R, Lipson D, Morosini D, Hawryluk M, Catenacci DVT, Miller VA, Churi C, Ali S, Stephens PJ (2014) New routes to targeted therapy of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas revealed by next-generation sequencing. Oncologist 19(3):235–242. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0352
Yang X, Wang W, Wang C, Wang L, Yang M, Qi M, Su H, Sun X, Liu Z, Zhang J, Qin X, Han B (2014) Characterization of EGFR family gene aberrations in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 32(2):700–708. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3261
Nakamura H, Arai Y, Totoki Y, Shirota T, Elzawahry A, Kato M, Hama N, Hosoda F, Urushidate T, Ohashi S, Hiraoka N, Ojima H, Shimada K, Okusaka T, Kosuge T, Miyagawa S, Shibata T (2015) Genomic spectra of biliary tract cancer. Nat Genet 47(9):1003–1010. doi:10.1038/ng.3375 http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/v47/n9/abs/ng.3375.html#supplementary-information
Chong DQ, Zhu AX (2016) The landscape of targeted therapies for cholangiocarcinoma: current status and emerging targets 2016
Lubner SJ, Mahoney MR, Kolesar JL, LoConte NK, Kim GP, Pitot HC, Philip PA, Picus J, Yong W-P, Horvath L, Van Hazel G, Erlichman CE, Holen KD (2010) Report of a multicenter phase II trial testing a combination of biweekly bevacizumab and daily erlotinib in patients with Unresectable biliary cancer: a phase II consortium study. J Clin Oncol 28(21):3491–3497. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.28.4075
Borbath I, Ceratti A, Verslype C, Demols A, Delaunoit T, Laurent S, Deleporte A, Vergauwe P, Van Maanen A, Sempoux C, Van Cutsem E, Van Laethem JL (2013) Combination of gemcitabine and cetuximab in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma: a phase II study of the Belgian Group of Digestive Oncology. Ann Oncol 24(11):2824–2829. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt337
Role of the sponsor
Merrimack Pharmaceuticals was involved in the study design, data collection, data analysis, and preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
JC reports research funding to his institution from Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, Taiho Oncology, Merck, Roche, Abbvie, Precision Biologics, and Bristol Myers Squib. He was a paid consultant with Agios Pharmaceuticals. GI was a paid consultant for Lilly, GI Therapeutics, EMD Serono, Chugai, and Millennium. He has also received research funding from Pfizer. ST reports research funding to her institution from Genentech/Roche, Merck, Exelixis, Pfizer, Lilly, and Novartis. SM, RN, GM, JK and AC are all employees of Merrimack Pharmaceuticals. WMK is a paid consultant for Merrimack Pharmaceuticals. AM, BO, and SS report no conflicts of interest.
Funding support
This study was sponsored by Merrimack Pharmaceuticals.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Funding source
Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cleary, J.M., McRee, A.J., Shapiro, G.I. et al. A phase 1 study combining the HER3 antibody seribantumab (MM-121) and cetuximab with and without irinotecan. Invest New Drugs 35, 68–78 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0399-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0399-7