Summary
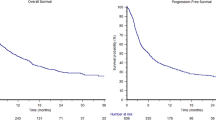
Background Sorafenib is an oral multikinase inhibitor that blocks cell proliferation via the ERK pathway and angiogenesis via the VEGF pathway. This phase II trial was conducted to determine the efficacy and tolerability of sorafenib for the treatment of patients with metastatic urothelial cancer (UC) who had not had prior chemotherapy for advanced disease. Patients and Methods Seventeen chemo-naïve UC patients with adequate performance status and organ function were treated with sorafenib 400 mg twice daily on a continuous basis until progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was objective tumor response rate as measured by RECIST criteria. Secondary endpoints included rate of prolonged stable disease (>3 months), time to progression, median and 1 yr survival and safety and tolerability. Results There were no objective responses. Only one patient had stable disease by RECIST criteria and remained on treatment more than 3 months. Three patients had stable disease by RECIST criteria but were on treatment less than 3 months due to progressive disease (PD) or adverse events (AE). Eight patients had PD by RECIST criteria as their best overall response. Two patients had symptomatic PD prior to cycle 2 evaluation, and three patients were inevaluable (1 death, 1 AE, 1 withdrew consent).The time to progression was 1.9 months (range 0.7–8.7 months) and median survival was 5.9 months. The most common grade 3+ toxicities were abdominal pain, back pain, hand-foot reaction and bladder infection. Conclusions Sorafenib does not show sufficient activity as a single agent in first-line metastatic urothelial cancer to warrant further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M (2001) Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin 51:15–36
von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Bodrogi I, Albers P, Knuth A, Lippert CM, Kerbrat P, Sanchez Rovira P, Wersall P, Cleall SP, Roychowdhury DF, Tomlin I, Visseren-Grul CM, Conte PF (2000) Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol 18:3068–3077
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y, Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE, Bollag G, Trail PA (2004) BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:7099–7109
Sridhar SS, Hedley D, Siu LL (2005) Raf kinase as a target for anticancer therapeutics. Mol Cancer Ther 4:677–685
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski RM (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:125–134
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, Douillard JY, Lathia C, Schwartz B, Taylor I, Moscovici M, Saltz LB (2006) Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24:4293–4300
McDermott DF, Sosman JA, Gonzalez R, Hodi FS, Linette GP, Richards J, Jakub JW, Beeram M, Tarantolo S, Agarwala S, Frenette G, Puzanov I, Cranmer L, Lewis K, Kirkwood J, White JM, Xia C, Patel K, Hersh E (2008) Double-blind randomized phase II study of the combination of sorafenib and dacarbazine in patients with advanced melanoma: a report from the 11715 Study Group. J Clin Oncol 26:2178–2185
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Vageli D, Kiaris H, Delakas D, Anezinis P, Cranidis A, Spandidos DA (1996) Transcriptional activation of H-ras, K-ras and N-ras proto-oncogenes in human bladder tumors. Cancer Lett 107:241–247
Viola MV, Fromowitz F, Oravez S, Deb S, Schlom J (1985) ras Oncogene p21 expression is increased in premalignant lesions and high grade bladder carcinoma. J Exp Med 161:1213–1218
Oxford G, Theodorescu D (2003) The role of Ras superfamily proteins in bladder cancer progression. J Urol 170:1987–1993
Simon R, Richter J, Wagner U, Fijan A, Bruderer J, Schmid U, Ackermann D, Maurer R, Alund G, Knonagel H, Rist M, Wilber K, Anabitarte M, Hering F, Hardmeier T, Schonenberger A, Flury R, Jager P, Fehr JL, Schraml P, Moch H, Mihatsch MJ, Gasser T, Sauter G (2001) High-throughput tissue microarray analysis of 3p25 (RAF1) and 8p12 (FGFR1) copy number alterations in urinary bladder cancer. Cancer Res 61:4514–4519
Bue P, Wester K, Sjostrom A, Holmberg A, Nilsson S, Carlsson J, Westlin JE, Busch C, Malmstrom PU (1998) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in urinary bladder cancer metastases. Int J Cancer 76:189–193
Crew JP, O’Brien T, Bradburn M, Fuggle S, Bicknell R, Cranston D, Harris AL (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a predictor of relapse and stage progression in superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Res 57:5281–5285
O’Brien T, Cranston D, Fuggle S, Bicknell R, Harris AL (1995) Different angiogenic pathways characterize superficial and invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res 55:510–513
Sonpavde G, Jian W, Liu H, Wu MF, Shen SS, Lerner SP (2009) Sunitinib malate is active against human urothelial carcinoma and enhances the activity of cisplatin in a preclinical model. Urol Oncol 27:391–399
Wu W, Shu X, Hovsepyan H, Mosteller RD, Broek D (2003) VEGF receptor expression and signaling in human bladder tumors. Oncogene 22:3361–3370
Duff SE, Jeziorska M, Rosa DD, Kumar S, Haboubi N, Sherlock D, O’Dwyer ST, Jayson GC (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factors and receptors in colorectal cancer: implications for anti-angiogenic therapy. Eur J Cancer 42:112–117
Moore MJ, Tannock IF, Ernst DS, Huan S, Murray N (1997) Gemcitabine: a promising new agent in the treatment of advanced urothelial cancer. J Clin Oncol 15:3441–3445
Stadler WM, Kuzel T, Roth B, Raghavan D, Dorr FA (1997) Phase II study of single-agent gemcitabine in previously untreated patients with metastatic urothelial cancer. J Clin Oncol 15:3394–3398
Bajorin DF, Dodd PM, Mazumdar M, Fazzari M, McCaffrey JA, Scher HI, Herr H, Higgins G, Boyle MG (1999) Long-term survival in metastatic transitional-cell carcinoma and prognostic factors predicting outcome of therapy. J Clin Oncol 17:3173–3181
Dreicer R, Li H, Stein M, DiPaola R, Eleff M, Roth BJ, Wilding G (2009) Phase 2 trial of sorafenib in patients with advanced urothelial cancer: a trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer 115:4090–4095
Bellmunt J, Maroto P, Mellado B, Carles J, Calvo E, Alcaraz A, Placer J, Villaviciencio H, Grande E, Albanell J (2008) Phase II study of sunitinib as first line treatment in patients with advanced urothelial cancer ineligible for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. In: Genitourinary Cancers Symposium. Abstract 291.
Gallagher D, Milowsky M, Gerst S, Tickoo S, Ishill N, Regazzi A, Trout A, Bajorin D (2009) A phase II study of sunitinib on a continuous dosing schedule in patients (pts) with relapsed or refractory urothelial carcinoma (UC). In: ASCO Annual Meeting. Journal of Clinical Oncology, Orlando, FL, Abstract 5072.
Hussain MH, MacVicar GR, Petrylak DP, Dunn RL, Vaishampayan U, Lara PN Jr, Chatta GS, Nanus DM, Glode LM, Trump DL, Chen H, Smith DC (2007) Trastuzumab, paclitaxel, carboplatin, and gemcitabine in advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor-2/neu-positive urothelial carcinoma: results of a multicenter phase II National Cancer Institute trial. J Clin Oncol 25:2218–2224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presentations: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) - 2008 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridhar, S.S., Winquist, E., Eisen, A. et al. A phase II trial of sorafenib in first-line metastatic urothelial cancer: a study of the PMH Phase II Consortium. Invest New Drugs 29, 1045–1049 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9408-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9408-4