Abstract
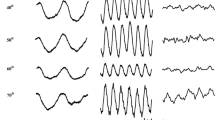
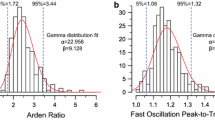
The relative number of L- and M-cones varies greatly between individuals. Differences in the relative number of L- and M-cones may also contribute to the sex difference in the ERG response amplitude reported several times. We therefore investigated the relative number of L- and M-cones and its impact on sex differences in ERG amplitudes. Multifocal ERG (mfERG) and multifocal oscillatory potentials (mfOP) combined with a cone silent substitution technique were used to investigate outer and inner retinal signals recorded from 7 female and 7 male trichromats. L:M ratios were estimated from peak amplitude as well as from area under curve (AUC) analysis. For mfERGs the L:M ratios estimates were independent of the method of analysis, while for mfOPs, differences were found which are possibly due to an artefact in the calculation of ratios for small responses. There was a tendency for lower L:M ratios in female than in male subjects for both analysis of mfERG and mfOP responses. The (L+M)-response amplitudes at both sites were slightly higher and the L:M ratios were lower for female than for male observers. Because the magnitude of the ERG amplitude differences is larger than could be explained by L:M-ratio and axial length differences, we conclude that it may be due to a direct effect of sex hormones on ion channel function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nathans J, Thomas D, Hogness DS (1986) Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science 232:193–202
Curcio CA, Allen KA, Sloan KR, Lerea CL, Hurley JB, Klock IB, Milam AH (1991) Distribution and morphology of human cone photoreceptors stained with anti-blue opsin. J Comp Neurol 312:610–624
De Vries H (1946) The heredity of the relative numbers of red and green receptors in the human eye. Genetica 24:199–212
Jacobs GH, Neitz J (1991) Electrophysiological estimates of individual variation in the L/M cone ratio. Color Vision Deficiencies XI:107–112
Kremers J, School HPN, Knau H, Berendschot TTJM, Usui T, Sharpe LT (2000) L/M cone ratios in human trichromats assessed by psychophysics, electroretinography, and retinal densitometry. J Opt Soc Am A 17:517–526
Pokorny J, Smith VC (1987) L/M Cone Ratios and the Null Point of the Perceptual Red/Green Opponent System. Die Farbe 34:53–57
Carroll J, McMahon C, Neitz M, Neitz J (2000) Flicker-photometric electroretinogram estimates of L:M cone photoreceptor ratio in men with photopigment spectra derived from genetics. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis 17:499–509
Hagstrom SA, Neitz J, Neitz M (1998) Variations in cone populations for red-green color vision examined by analysis of mRNA. Neuroreport 9:1963–1967
Deeb SS, Diller LC, Williams DR, Dacey DM (2000) Interindividual and topographical variation of L:M cone ratios in monkey retinas. J Opt Soc Am 17:538–544
Sutter EE, Tran D (1992) The Field Topography of ERG Components in Man-I. The Photopic Luminance Response. Vision Res 32:433–446
Estèvez O, Spekreijse H (1982) The “Silent Substitution” Method in Visual Research. Vision Res 22:681–691
Albrecht J, Jägle H, Hood DC, Sharpe LT (2002) The multifocal electrogram (mfERG) and cone isolating stimuli: Variation in L- and M-cone driven signal across the retina. J Vision 2(8):543–558
Kurtenbach A, Heine J, Jägle H (2004) The multifocal electroretinogram in trichromat and dichromat observers under cone isolating conditions. Vis Neurosci 21(3):249–255
Zeidler I (1959) The clinical electroretinogram, IX: the normal electroretinogram: value of the b-potential in different age groups and its difference in men and women. Arch Ophthalmol 37:294–301
Birch DG, Anderson JL (1992) Standardized full-field electroretinography. Normal values and their variation with age. Arch Ophthalmol 110(11):1571–1576
Nagy AL, MacLeod DI, Heyneman NE, Eisner A (1981) Four cone pigments in women heterozygous for color deficiency. J Opt Soc Am 71:719–22
Jordan G, Mollon JD (1993) A study of women heterozygous for colour deficiencies. Vision Res 33:1495–1508
Stockman A, Sharpe LT (2000) The spectral sensitivities of the middle- and long-wavelength-sensitive cones derived from measurements in observers of known genotype. Vision Res 40:1711–1737
Wu S, Sutter EE (1995) A topographic study of oscillatory potentials in man. Vis Neurosci 1013–1025
Hood DC, Frishman LJ, Saszik S, Viswanathan S (2002) Retinal origins of the primate multifocal ERG: implications for the human response. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1673–1685
Hagstrom SA, Neitz M, Neitz J (2000) Cone pigment gene expression in individual photoreceptors and the chromatic topography of the retina. J Opt Soc Am A 17:527–537
Vimal RL, Pokorny J, Smith VC, Shevell SK (1989) Foveal cone thresholds. Vision Res 29:61–78
Heynen H, Wachtmeister L, van Norren D (1985) Origin of the oscillatory potentials in the primate retina. Vision Res 25:1365–1373
Hare WA, Ton H (2002) Effects of APB, PDA, and TTX on ERG responses recorded using both multifocal and conventional methods in monkey. Effects of APB, PDA, and TTX on monkey ERG responses. Doc Ophthalmol 105:189–222
Rangaswamy NV, Hood DC, Frishman LJ (2003) Regional Variations in Local Contributions to the Primate Photopic Flash ERG: Revealed Using the Slow-Sequence mfERG. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3233–3247
Martin DA, Heckenlively JR (1982) The normal electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 31:135–144
Peterson H (1968) The normal b-potential in the single-flash clinical electroretinogram. Acta Ophthalmol 99:5–77
Kawabata H, Adachi-Usami E (1997) Multifocal electroretinogram in myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 38:2844–2851
Chan H, Mohidin N (2003) Variation of multifocal electroretinogram with axial length. Ophthal Physiol Opt 23:133–140
Stenström S (1946) Untersuchungen über die Variation und Kovariation der optischen Elemente des menschlichen Auges. Acta Ophthalmol, suppl 26
Gupta PD, Johar K, Nagpal K, Vasavada AR (2005) Sex hormone receptors in the human eye. Surv Ophthalmol 50:274–284
Ogueta SB, Schwartz SD, Yamashita CK, Farber DB (1999) Estrogene receptors in the human eye: influence of gender and age on gene expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:1906–1911
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants SFB430 (TP A6) and JA997/5-1 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Bonn-Bad Godesberg, Germany) and fortüne 1128-0-0 of the fortüne program of the University Tübingen awarded to H.J.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jägle, H., Heine, J. & Kurtenbach, A. L:M-cone ratio estimates of the outer and inner retina and its impact on sex differences in ERG amplitudes. Doc Ophthalmol 113, 105–113 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-006-9019-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-006-9019-8