Abstract
Background
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities on the pathological damage of acute pancreatitis. However, its molecular mechanism on severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) remains unknown.
Aims
To evaluate the influence of CGRP-mediated p38MAPK signaling pathway in rats with SAP.
Methods
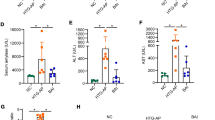
SD rats were randomly divided into Sham group, SAP group, CGRP group (SAP rats injected with CGRP), SB203580 group (rats injected with p38MAPK pathway inhibitor SB203580), and CGRP8-37 group (SAP rats injected with CGRP8-37). Serum amylase and lipase activities were determined. Histopathological observations were evaluated, and the expression of inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress-related indexes were measured.
Results
Compared with Sham group, SAP rats were increased in the activities of serum amylase and lipase, the pathologic assessment of pancreatic tissue, the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, the content of MDA and MPO, and the expressions of CGRP, and p-p38MAPK protein, but they were decreased in SOD activity and GSH content. The above alterations were aggravated in the CGRP8-37 group when compared with SAP group. Besides, in comparison with SAP group, rats in the CGRP and SB203580 groups presented a reduction in the activities of serum amylase and lipase, the levels of inflammatory cytokines, the content of MDA and MPO, and the expressions of p-p38MAPK protein, while showed an elevation in SOD activity and GSH content.
Conclusion
Pretreatment with CGRP alleviated oxidative stress and inflammatory response of SAP rats possibly by suppressing the activity of p38MAPK pathway, and thereby postponing the disease progression.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 March 2019
The original version of the article unfortunately contained errors in Materials and Methods section, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
References
Piao X, Liu B, Guo L, Meng F, Gao L. Picroside ii shows protective functions for severe acute pancreatitis in rats by preventing nf-kappab-dependent autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7085709.
Deng W, Abliz A, Xu S, et al. Severity of pancreatitis associated intestinal mucosal barrier injury is reduced following treatment with the nadph oxidase inhibitor apocynin. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14:3525–3534.
Wang G, Qu FZ, Li L, Lv JC, Sun B. Necroptosis: a potential, promising target and switch in acute pancreatitis. Apoptosis. 2016;21:121–129.
Yamaguchi I, Hamada K, Yoshida M, Isayama H, Kanazashi S, Takeuchi K. Risperidone attenuates local and systemic inflammatory responses to ameliorate diet-induced severe necrotic pancreatitis in mice: it may provide a new therapy for acute pancreatitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;328:256–262.
Takei M, Kobayashi M, Herndon DN, Pollard RB, Suzuki F. Glycyrrhizin inhibits the manifestations of anti-inflammatory responses that appear in association with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (sirs)-like reactions. Cytokine. 2006;35:295–301.
Rau B, Baumgart K, Kruger CM, Schilling M, Beger HG. Cc-chemokine activation in acute pancreatitis: Enhanced release of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in patients with local and systemic complications. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29:622–629.
Pereda J, Sabater L, Aparisi L, et al. Interaction between cytokines and oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:2775–2787.
Malon JT, Cao L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical hypersensitivity through ccl5 and p38 pathways. J Neuroimmunol. 2016;297:68–75.
Minamiyama M, Katsuno M, Adachi H, et al. Naratriptan mitigates cgrp1-associated motor neuron degeneration caused by an expanded polyglutamine repeat tract. Nat Med. 2012;18:1531–1538.
Wick EC, Pikios S, Grady EF, Kirkwood KS. Calcitonin gene-related peptide partially mediates nociception in acute experimental pancreatitis. Surgery. 2006;139:197–201.
Liu HS, Pan CE, Liu QG, Yang W, Liu XM. Effect of nf-kappab and p38 mapk in activated monocytes/macrophages on pro-inflammatory cytokines of rats with acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2513–2518.
Wei S, Huang Q, Li J, et al. Taurine attenuates liver injury by downregulating phosphorylated p38 mapk of kupffer cells in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation. 2012;35:690–701.
Cao MH, Xu J, Cai HD, et al. P38 mapk inhibition alleviates experimental acute pancreatitis in mice. Hepatobil Pancreat Dis Int: HBPD INT. 2015;14:101–106.
Yang SI, Yuan Y, Jiao S, Luo QI, Yu J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide protects rats from cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via a mechanism of action in the mapk pathway. Biomed Rep. 2016;4:699–703.
Bayne K. Revised guide for the care and use of laboratory animals available. Am Physiol Soc Physiol. 1996;39:208–211.
Shi LL, Liu MD, Chen M, Zou XP. Involvement of interstitial cells of cajal in experimental severe acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:2179–2186.
Wang XY, Tang QQ, Zhang JL, Fang MY, Li YX. Effect of sb203580 on pathologic change of pancreatic tissue and expression of tnf-alpha and il-1beta in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:338–343.
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, et al. A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 1992;215:44–56.
Ji CH, Tang CW, Feng WM, Bao Y, Yao LQ. A Chinese herbal decoction, huoxue qingyi decoction, promotes rehabilitation of patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med: eCAM. 2016;2016:3456510.
Kumaravel A, Stevens T, Papachristou GI, et al. A model to predict the severity of acute pancreatitis based on serum level of amylase and body mass index. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:1496–1501.
Bierma MJ, Coffey MJ, Nightingale S, van Rheenen PF, Ooi CY. Predicting severe acute pancreatitis in children based on serum lipase and calcium: A multicentre retrospective cohort study. Pancreatology. 2016;16:529–534.
Pooran N, Indaram A, Singh P, Bank S. Cytokines (il-6, il-8, tnf): Early and reliable predictors of severe acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;37:263–266.
Feng C, Li B, Wang LL, et al. Effect of peritoneal lavage with ulinastatin on the expression of nf-kappab and tnf-alpha in multiple organs of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10:2029–2034.
Zhou M, Chen B, Sun H, Deng Z, Andersson R, Zhang Q. The protective effects of lipoxin a4 during the early phase of severe acute pancreatitis in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:211–219.
Samuel I, Yuan Z, Meyerholz DK, Twait E, Williard DE, Kempuraj D. A novel model of severe gallstone pancreatitis: Murine pancreatic duct ligation results in systemic inflammation and substantial mortality. Pancreatology. 2010;10:536–544.
Dambrauskas Z, Giese N, Gulbinas A, et al. Different profiles of cytokine expression during mild and severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1845–1853.
Tam LS, Li EK, Leung VY, et al. Effects of vitamins c and e on oxidative stress markers and endothelial function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a double blind, placebo controlled pilot study. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:275–282.
Mousavi Jazi M, Pour Rodsari HR, Mirmiran F. Level of oxidative stress markers in peri-implant crevicular fluid and their correlation with clinical parameters. J Dent. 2015;12:340–346.
Schmitt B, Vicenzi M, Garrel C, Denis FM. Effects of n-acetylcysteine, oral glutathione (gsh) and a novel sublingual form of gsh on oxidative stress markers: a comparative crossover study. Redox Biol. 2015;6:198–205.
Chooklin S, Pereyaslov A, Bihalskyy I. Pathogenic role of myeloperoxidase in acute pancreatitis. Hepatobil Pancreat Dis Int HBPD INT. 2009;8:627–631.
Lassen LH, Jacobsen VB, Haderslev PA, et al. Involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide in migraine: Regional cerebral blood flow and blood flow velocity in migraine patients. J Headache Pain. 2008;9:151–157.
Holzer P, Wachter C, Jocic M, Heinemann A. Vascular bed-dependent roles of the peptide cgrp and nitric oxide in acid-evoked hyperaemia of the rat stomach. J Physiol. 1994;480:575–585.
Wu Y, Hao GM, He J, et al. Lentivirus mediated over expression of cgrp inhibited oxidative stress in schwann cell line. Neurosci Lett. 2015;598:52–58.
Warzecha Z, Dembinski A, Ceranowicz P, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide can attenuate or augment pancreatic damage in caerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999;50:49–62.
Chen P, Zhang Y, Qiao M, Yuan Y. Activated protein c, an anticoagulant polypeptide, ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis via regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:887–896.
Boilan E, Winant V, Dumortier E, et al. Role of p38mapk and oxidative stress in copper-induced senescence. Age. 2013;35:2255–2271.
Al-Lahham R, Deford JH, Papaconstantinou J. Mitochondrial-generated ros down regulates insulin signaling via activation of the p38mapk stress response pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;419:1–11.
Olson CM, Hedrick MN, Izadi H, Bates TC, Olivera ER, Anguita J. P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase controls nf-kappab transcriptional activation and tumor necrosis factor alpha production through rela phosphorylation mediated by mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 in response to borrelia burgdorferi antigens. Infect Immun. 2007;75:270–277.
Huang BP, Lin CH, Chen HM, Lin JT, Cheng YF, Kao SH. Ampk activation inhibits expression of proinflammatory mediators through downregulation of pi3 k/p38 mapk and nf-kappab signaling in murine macrophages. DNA Cell Biol. 2015;34:133–141.
Stjernberg-Salmela S, Ranki A, Karenko L, et al. Low tnf-induced nf-kappab and p38 phosphorylation levels in leucocytes in tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Rheumatology. 2010;49:382–390.
Li YJ, Peng J. The cardioprotection of calcitonin gene-related peptide-mediated preconditioning. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;442:173–177.
Hong-Min F, Chun-Rong H, Rui Z, Li-Na S, Ya-Jun W, Li L. Cgrp 8-37 enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and regulating aquaporin 1 and 5 expressions in rats. J Physiol Biochem. 2016;73:381–386.
Samuel I, Zaheer A, Fisher RA. In vitro evidence for role of erk, p38, and jnk in exocrine pancreatic cytokine production. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:1376–1383.
Umoh NA, Walker RK, Millis RM, Al-Rubaiee M, Gangula PR, Haddad GE. Calcitonin gene-related peptide regulates cardiomyocyte survival through regulation of oxidative stress by pi3 k/akt and mapk signaling pathways. Ann Clin Exp Hypertens. 2014;2:1007.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the reviewers for their useful comments in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, SH., Guang, Y. & Wang, WX. Protective Effects of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Mediated p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway on Severe Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 64, 447–455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5345-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5345-4