Abstract
Background
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) has a poor prognosis due to its high frequency of metastasis and invasion. Recent studies have suggested glucose-regulated protein 78KD (GRP78) may play important roles in progression and development of malignant tumors. However, the mechanisms of invasion and metastasis of ESCC in relation to GRP78 still remain obscure.
Aim
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of GRP78 on invasion and metastasis of ESCC and to explore its potential mechanism.
Methods
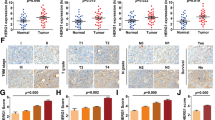
GRP78 expression levels in ESCC tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry. RT-PCR and western blot were used to test the relative expression of GRP78 in non-metastatic and high-metastatic ESCC cells. In vitro and in vivo studies were both performed to investigate the role of GRP78 in invasion and metastasis of ESCC cells. The expression of metastasis-related proteins was examined by western blot in GRP78-depleted cells.
Results
The expression of GRP78 is correlated with invasion, metastasis and poor prognosis in ESCC patients. GRP78 expression was significantly higher in highly metastatic cells compared with ESCC non-metastatic cells. In addition, down-regulation of GRP78 significantly inhibited the metastatic potential of ESCC cells in both in vitro and in vivo studies. The expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were down-regulated in GRP78-depleted ESCC cells.
Conclusions
The present study demonstrated that GRP78 plays important roles in invasion and metastasis of ESCC, indicating that GRP78 might be used as a potential prognostic and therapeutic marker in patients with ESCC by modulating the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- NC:
-
Negative control
- GRP78:
-
Glucose-regulated protein 78KD
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Eloubeidi MA, Desmond R, Arguedas MR, Reed CE, Wilcox CM. Prognostic factors for the survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma in the US: the importance of tumor length and lymph node status. Cancer. 2002;95:1434–1443.
Lin DC, Du XL, Wang MR. Protein alterations in ESCC and clinical implications: a review. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:9–20.
Kwong KF. Molecular biology of esophageal cancer in the genomics era. Surg Clin N Am. 2005;85:539–553.
Ye Q, Yan Z, Liao X, et al. Muc1 induces metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by upregulating matrix metalloproteinase 13. Lab Invest. 2011;91:778–787.
Koyama H, Iwata H, Kuwabara Y, Iwase H, Kobayashi S, Fujii Y. Gelatinolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in oesophageal carcinoma. A study using in situ zymography. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:2164–2170.
Uchikado Y, Natsugoe S, Okumura H, et al. Slug expression in the e-cadherin preserved tumors is related to prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1174–1180.
Cao J, Chiarelli C, Richman O, Zarrabi K, Kozarekar P, Zucker S. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:6232–6240.
Su R, Li Z, Li H, et al. GRP78 promotes the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:20.
Xing X, Lai M, Wang Y, Xu E, Huang Q. Overexpression of glucose-regulated protein 78 in colon cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;364:308–315.
Uramoto H, Sugio K, Oyama T, et al. Expression of endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone GRP78 in human lung cancer and its clinical significance. Lung Cancer. 2005;49:55–62.
Zhang J, Jiang Y, Jia Z, et al. Association of elevated GRP78 expression with increased lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2006;23:401–410.
Daneshmand S, Quek ML, Lin E, et al. Glucose-regulated protein GRP78 is up-regulated in prostate cancer and correlates with recurrence and survival. Hum Pathol. 2007;38:1547–1552.
Du XL, Hu H, Lin DC, et al. Proteomic profiling of proteins dysregulted in chinese esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007;85:863–875.
Dong D, Stapleton C, Luo B, et al. A critical role for GRP78/bip in the tumor microenvironment for neovascularization during tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2848–2857.
Li H, Song H, Luo J, Liang J, Zhao S, Su R. Knockdown of glucose-regulated protein 78 decreases the invasion, metalloproteinase expression and ECM degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31:39.
Kraljevic PS, Sedic M, Bosnjak H, Spaventi S, Pavelic K. Metastasis: new perspectives on an old problem. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:22.
Li Z, Li Z. Glucose regulated protein 78: a critical link between tumor microenvironment and cancer hallmarks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1826:13–22.
Dong D, Ni M, Li J, et al. Critical role of the stress chaperone GRP78/bip in tumor proliferation, survival, and tumor angiogenesis in transgene-induced mammary tumor development. Cancer Res. 2008;68:498–505.
Baumeister P, Dong D, Fu Y, Lee AS. Transcriptional induction of GRP78/bip by histone deacetylase inhibitors and resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:1086–1094.
Zhang LC, Wang JR, Zhao L, et al. GRP78 upregulation-induced increase in cisplatin sensitivity of spca1 lung cancer cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124:3341–3346.
Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904.
Zucker S, Vacirca J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPS) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:101–117.
Pellikainen JM, Ropponen KM, Kataja VV, Kellokoski JK, Eskelinen MJ, Kosma VM. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer with a special reference to activator protein-2, her2, and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7621–7628.
Li Y, Ma J, Guo Q, et al. Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:664–667.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Qingchuan Zhao for his help in collection of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma specimens and Prof. Zengshan Li for his help in analyzing the results of HE staining of paraffin sections.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guohong Zhao, Jianqin Kang, Kai Jiao and Guanghui Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Kang, J., Jiao, K. et al. High Expression of GRP78 Promotes Invasion and Metastases in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 60, 2690–2699 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3689-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3689-6