Abstract
Background
Little is known concerning the relationship of disease activity and sleep disturbances in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and specifically in patients with Crohn’s disease.
Aim
This study examined the prevalence of poor sleep quality in patients with active and inactive Crohn’s disease compared with healthy controls.
Methods
Participants included 108 patients with Crohn’s disease attending the IBD clinic of a tertiary medical center in 2009–2010 and 36 healthy volunteers. All prospectively completed a demographic questionnaire and the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI). Patients with Crohn’s disease completed the Crohn’s disease activity index (CDAI) and were divided into two groups accordingly: inactive disease (CDAI ≤150) and active disease (CDAI >150). Data on disease duration, medications, complications, and treatment were collected from the medical files.
Results
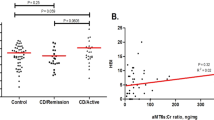
Seventy-one patients had inactive Crohn’s disease and 37 had active disease. All three groups were similar in mean age, sex distribution, and body mass index. Mean duration of Crohn’s disease was 10.22 ± 8.6 years; 40 patients (37 %) had ileal disease, 16 (15 %) colonic disease, and 56 (50 %) ileo-colonic disease. Patients with active disease had a significantly higher mean ± SD global score on the PSQI (8.6 ± 2.4; indicating poorer sleep quality) than patients with inactive disease (4.6 ± 1.9) or control subjects (5.1 ± 1.7) (p < 0.0001 for both), with no significant difference between the inactive-disease and control groups. The correlation between the CDAI and PSQI scores was statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Impaired sleep quality is associated with active Crohn’s disease, but not inactive disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoogerwerf WA. Role of biological rhythms in gastrointestinal health and disease. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2009;10:293–300.
Kumar D, Thompson PD, Wingate DL, Vesselinova-Jenkins CK, Libby G. Abnormal REM sleep in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:12–17.
Fass R, Fullerton S, Tung S, Mayer EA. Sleep disturbances in clinic patients with functional bowel disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:1195–1200.
Goldsmith G, Levin JS. Effect of sleep quality on symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:1809–1814.
Schey R, Dickman R, Parthasarathy S, et al. Sleep deprivation is hyperalgesic in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1787–1795.
Fass R. The relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2009;11:202–208.
Swanson RG, Burgess H, Keshavarzian A. Sleep disturbances and inflammatory bowel disease: a potential trigger for disease flare? Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2011;7:29–36.
Keefer L, Stepanski E, Ranjbaran Z, Benson LM, Keshavarzian A. An initial report of sleep disturbance in inactive inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Sleep Med. 2006;2:409–416.
Ali T, Madhoun MF, Orr WC, Rubin DT. Assessment of the relationship between quality of sleep and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:2440–2443.
Ranjbaran Z, Keefer L, Farhadi A, Stepanski E, Sedghi S, Keshanarzian A. Impact of sleep disturbances in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:1748–1753.
Tang Y, Preuss F, Turek WF, Jakate S, Keshavarzian A. Sleep deprivation worsens inflammation and delays recovery in a mouse model of colitis. Sleep Med. 2009;10:597–603.
Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn’s disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976;70:439–444.
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF III, Monk TH, Hoch CC, Yeager AL, Kupfer DJ. Quantification of subjective sleep quality in healthy elderly men and women using the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI). Sleep. 1991;14:331–338.
Smyth C. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index. Medsurg Nurs. 2003;12:261–262.
Morgan K, Dalloso H, Ebrahim S, Arie T, Fentem PH. Characteristics of subjective insomnia in the elderly living at home. Age Ageing. 1988;17:1–17.
Shochat T, Tzischinsky O, Oksenberg A, Peled R. Validation of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index Hebrew translation (PSQI-H) in a sleep clinic sample. Isr Med Assoc J. 2007;9:853–856.
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF III, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989;28:193–213.
Graff LA, Vincent N, Walker JR, et al. A population-based study of fatigue and sleep difficulties in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:1882–1889.
Ananthakrishnan AN, Long MD, Martin CF, Sandler RS, Kappelman MD. Sleep disturbance and risk of active disease in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:965–971. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.01.21.
Shoham S, Davenne D, Cady AB, Dinarello CA, Krueger JM. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 enhance slow-wave sleep. Am J Physiol. 1987;253:R142–R149.
Chandrasekhara PKS, Jayachandran NV, Rajasekhar L, Thomas J, Narsimula G. The prevalence and associations of sleep disturbances in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19:407–415.
Brass SD, Duquette P, Proulx-Therrien J, Auerbach S. Sleep disorders in patients with multiple sclerosis. Sleep Med Rev. 2010;14:121–129.
Abad VC, Sarinas PSA, Guilleminault C. Sleep and rheumatologic disorders. Sleep Med Rev. 2008;12:211–228.
Salahuddin N, Barroso J, Leserman J, Harmon JL, Pence BW. Daytime sleepiness, nighttime sleep quality, stressful life events, and HIV-related fatigue. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2009;20:6–13.
Wells G, Li T, Maxwell L, MacLean R, Tugwell P. Responsiveness of patient reported outcomes including fatigue, sleep quality, activity limitation, and quality of life following treatment with abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheumatol Dis. 2008;67:260–265.
Banovic I, Gilibert D, Cosnes J. Crohn’s disease and fatigue: constancy and co-variations of activity of the disease, depression, anxiety and subjective quality of life. Psychol Health Med. 2010;15:394–405.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Gloria Ginzach and Melanie Kawe of the Editorial Board of Rabin Medical Center for editing and preparing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gingold-Belfer, R., Peled, N., Levy, S. et al. Impaired Sleep Quality in Crohn’s Disease Depends on Disease Activity. Dig Dis Sci 59, 146–151 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2890-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2890-8