Abstract
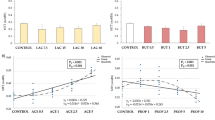
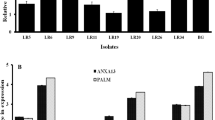
Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs) have been suggested as an alternative to the use of antibiotics in animal nutrition with promising results. First, we studied the sensitivity of Salmonella Enteritidis and an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain against caprylic (C8), capric (C10) and lauric (C12) acids. A porcine in vitro model using the porcine cell line IPEC-J2 was used to test the effects of MCFAs on structural and immunological traits without and with a concomitant challenge with E. coli or S. Enteritidis. The three MCFAs exerted an inhibitory effect on bacterial growth, stronger for C12 than C8 or C10, S. Enteritidis being more sensitive than the E. coli strain. Flow cytometry showed a numeric concentration dependent increase in the adhesion of E. coli or S. Enteritidis to IPEC-J2 cells. Measurement of transepithelial electrical resistance after bacterial challenge showed negative effects of all MCFAs on IPEC-J2 cells at the highest concentrations. Immune parameters were affected by C8, since a concentration dependent effect starting at 5 mM was observed for mRNA expression of IL-6 and TLR-4 (up-regulated) and IL-8 (down-regulated). TLR-4 was up-regulated with C10 at 2 and 5 mM. The three MCFAs affected also the epithelial morphology through down-regulation of Occludin and up-regulation of Claudin-4 expression. In conclusion, the three MCFAs under study influenced bacterial growth rates and modified the gene expression to a different degree in the cell line IPEC-J2 but the effect on the morphological structure and response of the cells after bacterial challenge could not be assessed. Although these tests show a prior estimation of MCFAs effects in intestinal epithelium, in vivo confirmation is still needed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen HK, Levine UY, Looft T, Bandrick M, Casey TA (2013) Treatment, promotion, commotion: antibiotic alternatives in food-producing animals. Trends Microbiol 21:114–119
Anderberg EK, Lindmark T, Artursson P (1993) Sodium caprate elicits dilatations in human intestinal tight junctions and enhances drug absorption by the paracellular route. Pharm Res 10:857–864
Andoh A, Takaya H, Araki Y, Tsujikawa T, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T (2000) Medium- and long-chain fatty acids differentially modulate interleukin-8 secretion in human fetal intestinal epithelial cells. J Nutr 130:2636–2640
Aungst BJ (2012) Absorption enhancers: applications and advances. AAPS J 14:10–18
Bergsson G, Steingrímsson O, Thormar H (2002) Bactericidal effects of fatty acids and monoglycerides on Helicobacter pylori. Int J Antimicrob Ag 20:258–262
Berschneider H (1989) Development of normal cultured small intestinal epithelial cell lines which transport Na and Cl. Gastroenterology 96:A41
Brayden DJ, Gleeson J, Walsh EG (2014) A head-to-head multi-parametric high content analysis of a series of medium chain fatty acid intestinal permeation enhancers in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 88:830–839
Breckenridge WC, Kuksis A (1967) Molecular weight distributions of milk fat triglycerides from seven species. J Lipid Res 8:473–478
Brosnahan AJ, Brown DR (2012) Porcine IPEC-J2 intestinal epithelial cells in microbiological investigations. Vet Microbiol 156:229–237
Chow CK (1992) Fatty acids in foods and their health implications. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York
Coyne CB, Ribeiro CMP, Boucher RC, Johnson LG (2003) Acute mechanism of medium chain fatty acid-induced enhancement of airway epithelial permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:440–450
Davies J, Davies D (2010) Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol R 74:417–433
Decuypere JA, Dierick NA (2003) The combined use of triacylglycerols containing medium-chain fatty acids and exogenous lipolytic enzymes as an alternative to in-feed antibiotics in piglets: concept, possibilities and limitations. An overview. Nutr Res Rev 16:193–209
Desbois AP, Smith VJ (2010) Antibacterial free fatty acids: activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1629–1642
Dierick NA, Decuypere JA, Molly K, Van Beek E, Vanderbeke E (2002a) The combined use of triacylglycerols containing medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs) and exogenous lipolytic enzymes as an alternative for nutritional antibiotics in piglet nutrition: I. In vitro screening of the release of MCFAs from selected fat sources by selected exogenous lipolytic enzymes under simulated pig gastric conditions and their effects on the gut flora of piglets. Lives Prod Sci 75:129–142
Dierick NA, Decuypere JA, Molly K, Van Beek E, Vanderbeke E (2002b) The combined use of triacylglycerols (TAGs) containing medium chain fatty acids (MCFAs) and exogenous lipolytic enzymes as an alternative to nutritional antibiotics in piglet nutrition: II. In vivo release of MCFAs in gastric cannulated and slaughtered piglets by endogenous and exogenous lipases; effects on the luminal gut flora and growth performance. Lives Prod Sci 76:1–16
Dierick NA, Decuypere JA, Degeyter I (2003) The combined use of whole Cuphea seeds containing medium chain fatty acids and an exogenous lipase in piglet nutrition. Arch Anim Nutr 57:49–63
Endo Y, Hanada K, Miyake M, Ogawara KI, Higaki K, Kimura T (2002) Mechanisms of cytoprotective effect of amino acids on local toxicity caused by sodium laurate, a drug absorption enhancer, in intestinal epithelium. J Pharm Sci 91:730–743
Georgiadi A, Kersten S (2012) Mechanisms of gene regulation by fatty acids. Adv Nutr 3:127–134
Glass CK, Olefsky JM (2012) Inflammation and lipid signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell Metab 15:635–645
González-Ortiz G, Pérez JF, Hermes RF, Molist F, Jiménez-Díaz R, Martín-Orúe SM (2014) Screening the ability of natural feed ingredients to interfere with the adherence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) K88 to the porcine intestinal mucus. Brit J Nutr 111:633–642
Graham SA, Knapp SJ (1989) Cuphea: a new plant source of medium-chain fatty acids. Crit Rev Food Sci 28:139–173
Heuer H, Schmitt H, Smalla K (2011) Antibiotic resistance gene spread due to manure application on agricultural fields. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:236–243
Hoshimoto A, Suzuki Y, Katsuno T, Nakajima H, Saito Y (2002) Caprylic acid and medium-chain triglycerides inhibit IL-8 gene transcription in Caco-2 cells: comparison with the potent histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin. Brit J Pharmacol 136:280–286
Kamm W, Jonczyk A, Jung T, Luckenbach G, Raddatz P, Kissel T (2000) Evaluation of absorption enhancement for a potent cyclopeptidic ανβ3-antagonist in a human intestinal cell line (Caco-2). Eur J Pharm Sci 10:205–214
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol Indic 8:1–13
Kono H, Fujii H, Ishii K, Hosomura N, Ogiku M (2009) Dietary medium-chain triglycerides prevent chemically induced experimental colitis in rats. Transl Res 155:131–141
Laroui H, Ingersoll SA, Liu HC, Baker MT, Ayyadurai S, Charania MA, Laroui F, Yan Y, Sitaraman SV, Merlin D (2012) Dextran Sodium Sulfate (DSS) induces colitis in mice by forming nano-lipocomplexes with medium-chain-length fatty acids in the colon. PLoS One 7:e32084
Lindmark T, Nikkilä T, Artursson P (1995) Mechanisms of absorption enhancement by medium chain fatty acids in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell monolayer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:958–964
Lindmark T, Kimura Y, Artursson P (1998) Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:362–369
Mariani V, Palermo S, Fiorentini S, Lanubile A (2009) Gene expression study of two widely used pig intestinal epithelial cell lines: IPEC-J2 and IPI-21. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 131:278–284
Marounek M, Skrinaková V, Savka O (2002) Effect of caprylic, capric and oleic acid on growth of rumen and rabbit caecal bacteria. J Anim Feed Sci 11:507–516
Marounek M, Skrinaková V, Rada V (2003) Susceptibility of Escherichia coli to C2-C18 fatty acids. Folia Microbiol 48:731–735
Marten B, Pfeuffer M, Schrezenmeir J (2006) Medium-chain triglycerides. Int Dairy J 16:1374–1382
Nagasaki H, Kondo T, Fuchigami M, Hashimoto H, Sugimura Y, Ozaki N, Arima H, Ota A, Oiso Y, Hamada Y (2012) Inflammatory changes in adipose tissue enhance expression of GPR84, a medium-chain fatty acid receptor TNFa enhances GPR84 expression in adipocytes. FEBS Lett 586:368–372
Petschow BW, Batema RP, Ford LL (1996) Susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to bactericidal properties of medium-chain monoglycerides and free fatty acids. Antimicrob Agents Ch 40:302–306
Pluske J (2013) Feed- and feed additives-related aspects of gut health and development in weanling pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 4:1
Rolfe MD, Rice CJ, Lucchini S, Pin C, Thompson A, Cameron ADS, Mark Alston M, Stringer MF, Betts RP, Baranyi J, Peck MW, Hinton JCD (2012) Lag phase is a distinct growth phase that prepares bacteria for exponential growth and involves transient metal accumulation. J Bacteriol 194:686–701
Roselli M, Finamore A, Britti MS, Bosi P, Oswald I, Mengheri E (2005) Alternatives to in-feed antibiotics in pigs: evaluation of probiotics, zinc or organic acids as protective agents for the intestinal mucosa. A comparison of in vitro and in vivo results. Anim Res 54:203–218
Schierack P, Nordhoff M, Pollmann M, Weyrauch KD, Amasheh S, Lodemann U, Jores J, Tachu B, Kleta S, Blikslager A, Tedin K, Wieler LH (2006) Characterization of a porcine intestinal epithelial cell line for in vitro studies of microbial pathogenesis in swine. Histochem Cell Biol 125:293–305
Seal BS, Lillehoj HS, Donovan DM, Gay CG (2013) Alternatives to antibiotics: a symposium on the challenges and solutions for animal production. Anim Health Res Rev 14:78–87
Shima M, Yohdoh K, Yamaguchi M, Kimura Y, Adachi S, Matsuno R (1997) Effects of medium-chain fatty acids and their acylglycerols on the transport of penicillin V across Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biosci Biotech Biochem 61:1150–1155
Spitzer F, Vahjen W, Pieper R, Martínez-Vallespín B, Zentek J (2014) A standardised challenge model with an enterotoxigenic F4 + Escherichia coli strain in piglets assessing clinical traits and faecal shedding of fae and est-II toxin genes. Arch Anim Nutr 68:448–459
Spitzer F, Speiser S, Vahjen W, Zentek J (2016) Effect of different feed ingredients and additives on IPEC-J2 cells challenged with an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain. Cytotechnology. 68:1463–1471
Støy ACF, Heegaard PMH, Sangild PT, Østergaard MV, Skovgaard K (2013) Gene expression analysis of the IPEC-J2 cell line: a simple model for the inflammation-sensitive preterm intestine. ISRN Genom Article ID 980651. doi:10.1155/2013/980651
Sun CQ, O´Connor CJ, Roberton AM (2003) Antibacterial actions of fatty acids and monoglycerides against Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Immunol Med Mic 36:9–17
Talukdar S, Olefsky JM, Osborn O (2011) Targeting GPR120 and other fatty acid-sensing GPCRs ameliorates insulin resistance and inflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32:543–550
Tanaka S, Saitoh O, Tabata K, Matsuse R, Kojima K, Sugi K, Nakagawa K, Kayazawa M, Teranishi T, Uchida K, Hirata I, Katsu KI (2001) Medium-chain fatty acids stimulate interleukin-8 production in Caco-2 cells with different mechanisms from long-chain fatty acids. J Gastroen Hepatol 16:748–754
Zentek J, Buchheit-Renko S, Ferrara F, Vahjen W, Van Kessel AG, Pieper R (2011) Nutritional and physiological role of medium-chain triglycerides and medium-chain fatty acids in piglets. Anim Health Res Rev 12:83–93
Zentek J, Buchheit-Renko S, Männer K, Pieper R, Vahjen W (2012) Intestinal concentrations of free and encapsulated dietary medium-chain fatty acids and effects on gastric microbial ecology and bacterial metabolic products in the digestive tract of piglets. Arch Anim Nutr 66:14–26
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Petra Huck for her invaluable assistance with IPEC-J2 cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Vallespín, B., Vahjen, W. & Zentek, J. Effects of medium-chain fatty acids on the structure and immune response of IPEC-J2 cells. Cytotechnology 68, 1925–1936 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-0003-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-0003-1