Abstract
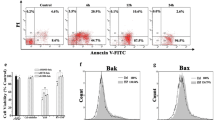
Our previous study reported that the saponin-rich fraction from Clematis chinensis Osbeck roots (SFC) could effectively alleviate experimental osteoarthritis induced by monosodium iodoacetate in rats through protecting articular cartilage and inhibiting local inflammation. The present study was performed to investigate the preventive effects of SFC on articular chondrocyte, and explore the underlying mechanisms. Primary rabbit chondrocytes were cultured and exposed to sodium nitroprusside (SNP), a NO donor. After treatment with different concentrations of SFC (30, 100, 300, 1,000 μg/ml) for 24 h, nucleic morphology, apoptotic rate, mitochondrial function and caspase-3 activity of chondrocytes were examined. The results showed that SNP induced remarkable apoptosis of rabbit chondrocytes evidenced by Hoechst 33258 staining and flow cytometry analysis, and SFC prevented the apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner. Further studies indicated that SFC could prevent the depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential (∆ψm) in SNP-treated chondrocytes and suppress the activation of caspase-3. It can be concluded that the protection of SFC on articular chondrocytes is associated with the anti-apoptosis effects via inhibiting the mitochondrion impairment and caspase-3 activation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson S, Krasnokutsky S (2006) Biomarkers in osteoarthritis. Bull NYU Hosp Joint Dis 64:77–81
Ahmed S, Wang N, Lalonde M, Goldberg VM, Haqqi TM (2004) Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) differentially inhibits interleukin-1 beta induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 an -13 in human chondrocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:767–773
Aigner T (2002) Apoptosis, necrosis, or whatever: how to find out what really happens? J Pathol 198:1–4
Aigner T, Kim HA (2002) Apoptosis and cellular vitality: issues in osteoarthritic cartilage degeneration. Arthr Rheum 46:1986–1996
Beak YH, Hun JE, Lee JD, Choi DY, Park DS (2006) Effect of Aralia cordata extracts on cartilage protection and apoptosis inhibition. Biol Pharm Bull 29:1423–1430
Beltrán B, Mathur A, Duchen MR, Erusalimsky JD, Moncada S (2000) The effect of nitric oxide on cell respiration: a key to understanding its role in cell survival or death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14602–14607
Blanco FJ, Ochs RL, Schwarz H, Lotz M (1995) Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am J Pathol 146:75–85
Blanco FJ, Guitian R, Vázquez-Martul E, de Toro FJ, Galdo F (1998) Osteoarthritis chondrocytes die by apoptosis. A possible pathway for osteoarthritis pathology. Arthr Rheum 41:284–289
Blanco FJ, López-Armada MJ, Maneiro E (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction in osteoarthritis. Mitochondrion 4:715–728
Böhm B, Hess S, Krause K, Schirner A, Ewald W, Aigner T, Burkhardt H (2010) ADAM15 exerts an antiapoptotic effect on osteoarthritic chondrocytes via up-regulation of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis. Arthr Rheum 62:1372–1382
Chen Q, Liu SQ, Du YM, Peng H, Sun LP (2006) Carboxymethyl-chitosan protects rabbit chondrocytes from interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 541:1–8
Chen S, Liu J, Liu X, Fu Y, Zhang M, Lin Q, Zhu J, Mai L, Shan Z, Yu X, Yang M, Lin S (2011) Panax notoginseng saponins inhibit ischemia-induced apoptosis by activating PI3 K/Akt pathway in cardiomyocytes. J Ethnopharmacol 137:263–270
Choi JH, Choi JH, Kim DY, Yoon JH, Youn HY, Yi JB, Rhee HI, Ryu KH, Jung K, Han CK, Kwak WJ, Cho YB (2002) Effects of SKI 360X, a new herbal agent, on proteoglycan degradation in cartilage explant culture and collagenase-induced rabbit osteoarthritis model. Osteoarthr Cartil 10:471–478
Csaki C, Keshishzadeh N, Fischer K, Shakibaei M (2008) Regulation of inflammation signaling by resveratrol in human chondrocytes in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 75:677–687
Felson DT (2006) Clinical practice. Ostearthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med 354:841–848
Goldring MB, Goldring SR (2007) Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol 213:626–634
Greisbery J, Bliss M, Terek R (2002) The prevalence of nitric oxide in apoptotic chondrocytes of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 10:207–211
Hashimoto S, Takahashi K, Amiel D, Coutts RD, Lotz M (1998) Chondrocyte apoptosis and nitric oxide production during experimentally induced osteoarthritis. Arthr Rheum 41:1266–1274
Hooshmand S, Soung do Y, Lucas EA, Madihally SV, Levenson CW, Arjmandi BH (2007) Genistein reduces the production of proinflammatory molecules in human chondrocytes. J Nutr Biochem 18:609–614
Ju XD, Deng M, Deng M, Ao YF, Yu CL, Wang JQ, Yu JK, Cui GQ, Hu YL (2010) Protective effect of sinomenine on cartilage degradation and chondrocytes apoptosis. Yakugaku Zasshi 130:1053–1060
Kim SJ, Hwang SG, Shin DY, Kang SS, Chun JS (2002a) p38 kinase regulates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of articular chondrocytes by accumulating p53 via NFkappa B-dependent transcription and stabilization by serine 15 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 227:33501–33508
Kim SJ, Ju JW, Oh CD, Yoon YM, Song WK, Kim JH, Yoo YJ, Bang OS, Kang SS, Chun JS (2002b) ERK-1/2 and p38 kinase oppositely regulate nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes in association with p53, caspase-3, and differentiation status. J Biol Chem 277:1332–1339
Kim JH, Ryu KH, Jung KW, Han CK, Kwak WJ, Cho YB (2005a) Effects of SKI306X on arachidonate metabolism and other inflammatory mediators. Biol Pharm Bull 28:1615–1620
Kim JH, Ryu KH, Jung KW, Han CK, Kwak WJ, Cho YB (2005b) SKI360X suppresses cartilage destruction and inhibits the production of matrix metalloproteinase in rabbit joint cartilage explant culture. J Pharmacol Sci 98:298–306
Krasnokutsky S, Samuels J, Abramson SB (2007) Osteoarthritis in 2007. Bull NYU Hosp Joint Dis 65:222–228
Kühn K, D’Lima DD, Hashimoto S, Lotz M (2004) Cell death in cartilage. Osteoarthr Cartil 12:1–16
Lee SW, Chung WT, Choi SM, Kim KT, Yoo KS, Yoo YH (2005) Clematis mandshurica protected to apoptosis of rat chondrocytes. J Ethnopharmacol 101:294–298
Li RW, Lin GD, Leach DN, Waterman PG, Myers SP (2006) Inhibition of COXs and 5-LOX and activation of PPARs by Australian Clematis species (Ranunculaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 104:138–143
Liu LF, Ma XL, Wang YX, Li FW, Li YM, Wan ZQ, Tang QL (2009) Triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Clematis chinensis Osbeck. J Asian Nat Prod Res 11:389–396
Lohmander LS (2000) What can we do about osteoarhritis? Arthr Res 2:95–100
López-Armada MJ, Caramés B, Martín MA, Cillero-Pastor B, Lires-Dean M, Fuentes-Boquete I, Arenas J, Blanco FJ (2006) Mitochondrial activity is modulated by TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in normal human chondrocyte cells. Osteoarthr Cartil 14:1011–1022
Lotz M, Hashimoto S, Kühn K (1999) Mechanisms of chondrocyte apoptosis. Osteoarthr Cartil 7:389–391
Maneiro E, López-Armada MJ, de Andres MC, Caramés B, Martín MA, Bonilla A, Del Hoyo P, Galdo F, Arenas J, Blanco FJ (2005) Effect of nitric oxide on mitochondrial respiratory activity of human articular chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 64:388–395
Mimaki Y, Yokosuka A, Hmanaka M, Sakuma C, Yamori T, Sashida Y (2004) Triterpene saponins from the roots of Clematis chinensis. J Nat Prod 67:1511–1516
Panico AM, Cardile V, Garufi F, Puglia C, Bonina F, Ronsisvalle G (2005) Protective effect of Capparis spinosa on chondrocytes. Life Sci 77:2479–2488
Park EK, Ryu MH, Kim YH, Lee YA, Lee SH, Woo DH, Hong SJ, Han JS, Yoo MC, Yang HI, Kim KS (2006) Anti-inflammatory effects of an ethanolic extract from Clematis mandshurica Rupr. J Ethnopharmacol 108:142–147
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Rong C, Chen F, Jiang S, Hu W, Wu F, Chen T (2011) Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels by amiloride protects rat articular chondrocytes from acid-induced apoptosis via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Cell Biol Int (Epub ahead of print)
Shakibaei M, John T, Schulze-Tanzil G, Lehmann I, Mobasheri A (2007) Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by curcumin leads to inhibition of expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human articular chondrocytes: implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol 73:1434–1445
Shang L, Qu Z, Sun L, Wang Y, Liu F, Wang S, Gao H, Jiang F (2011) Astragaloside IV inhibits adenovirus replication and apoptosis in A549 cells in vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:688–694
Shao B, Qin G, Xu R, Wu H, Ma K (1995) Triterpenoid saponins from Clematis chinensis. Phytochemistry 38:1473–1479
Shi S, Jiang D, Dong C, Tu P (2006) Triterpene saponins from clematis mandshurica. J Nat Prod 69:1591–1595
Terauchi R, Takahashi KA, Arai Y, Ikeda T, Ohashi S, Imanishi J, Mazda O, Kubo T (2003) Hsp70 prevents nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in articular chondrocytes. Arthr Rheum 48:1562–1568
Wu GJ, Chen TG, Chang HC, Chiu WT, Chang CC, Chen RM (2007) Nitric oxide from both exogenous and endogenous sources activates mitochondria-dependent events and induces insults to human chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem 101:1520–1531
Wu WJ, Xu XX, Dai Y, Xia LZ (2010) Therapeutic effect of saponin fraction from Clematis chienesis Osbeck roots on osteoarthritis induced by monosodium iodoacetate through inhibiting local inflammation and protecting articular cartilage. Phytother Res 24:538–546
Xu XX, Xia LZ (2006) Study on separation and purification of total saponins from Radix Clematidis with macroporous absorptive resin. Zhong Yao Xing Yao Yu Lin Chuang Yao Li 17:57–59
Zhang G, Liu A, Zhou Y, San X, Jin T, Jin Y (2008) Panax ginseng ginsenoside-Rg2 protects memory impairment via anti-apoptosis in a rat model with vascular dementia. J Ethnopharmacol 115:441–448
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Wenjun Wu and Xinghua Gao equally contributed to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Gao, X., Xu, X. et al. Saponin-rich fraction from Clematis chinensis Osbeck roots protects rabbit chondrocytes against nitric oxide-induced apoptosis via preventing mitochondria impairment and caspase-3 activation. Cytotechnology 65, 287–295 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9485-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9485-7