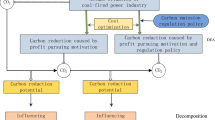
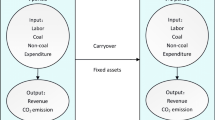
Abstract
The rapid economic development in China has intensified the country’s many problems, such as environmental pollution. Coal-fired power plants are a major source of environmental pollution. In order to effectively reduce environmental pollution, it is particularly important that China’s coal-fired power plants reach the best performance standards. In this paper, data envelopment analysis is used to evaluate the environmental efficiency of 27 coal-fired power plants in China. First, we develop a range adjusted measurement (RAM) efficiency measure based on farthest target which considers undesirable output to measure the environmental efficiency. Then, based on the fact that benchmarking information can offer a pivotal pathway for inefficient DMUs to achieve efficiency, another RAM environmental efficiency measure, based on closest target, is built to analyze the efficiency and give the closest benchmarking information. The empirical study shows that closest targets are more easily attainable and provide the most relevant solution to remove inefficiency.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirteimoori, A., & Kordrostami, S. (2010). A Euclidean distance-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Optimization, 59(7), 985–996.
Ando, K., Kai, A., Maeda, Y., & Sekitani, K. (2012). Least distance based inefficiency measures on the Pareto-efficient frontier in DEA. Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan, 55(1), 73–91.
An, Q., Chen, H., Wu, J., & Liang, L. (2015). Measuring slacks-based efficiency for commercial banks in China by using a two-stage DEA model with undesirable output. Annals of Operations Research, 235(1), 13–35.
Aparicio, J., Borras, F., Ortiz, L., & Pastor, J. T. (2014). Benchmarking in healthcare: An approach based on closest targets. In Managing service productivity (pp. 67–91). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer
Aparicio, J., & Pastor, J. T. (2013). A well-defined efficiency measure for dealing with closest targets in DEA. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 219(17), 9142–9154.
Aparicio, J., & Pastor, J. T. (2014). Closest targets and strong monotonicity on the strongly efficient frontier in DEA. Omega, 44, 51–57.
Aparicio, J., Ruiz, J. L., & Sirvent, I. (2007). Closest targets and minimum distance to the Pareto-efficient frontier in DEA. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 28(3), 209–218.
Baek, C., & Lee, J. D. (2009). The relevance of DEA benchmarking information and the least-distance measure. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 49(1), 265–275.
Barba-Gutiérrez, Y., Adenso-Díaz, B., & Lozano, S. (2009). Eco-efficiency of electric and electronic appliances: A data envelopment analysis (DEA). Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 14(4), 439–447.
Bi, G., Luo, Y., Ding, J., & Liang, L. (2012). Environmental performance analysis of Chinese industry from a slacks-based perspective. Annals of Operations Research, 228(1), 65–80.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research, 2(6), 429–444.
Chen, C. M., & Delmas, M. A. (2012). Measuring eco-inefficiency: A new frontier approach. Operations Research, 60(5), 1064–1079.
Coelli, T. J., Rao, D. S. P., O’Donnell, C. J., & Battese, G. E. (2005). An introduction to efficiency and productivity analysis. New York: Springer Science & Business Media.
Cook, W. D., & Seiford, L. M. (2009). Data envelopment analysis (DEA)-Thirty years on. European Journal of Operational Research, 192(1), 1–17.
Cooper, W. W., Park, K. S., & Pastor, J. T. (1999). RAM: A range adjusted measure of inefficiency for use with additive models, and relations to other models and measures in DEA. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 11(1), 5–42.
Du, J., Wang, J., Chen, Y., Chou, S. Y., & Zhu, J. (2014). Incorporating health outcomes in Pennsylvania hospital efficiency: An additive super-efficiency DEA approach. Annals of Operations Research, 221(1), 161–172.
Fandel, G. (2007). On the performance of universities in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany: Government’s redistribution of funds judged using DEA efficiency measures. European Journal of Operational Research, 176(1), 521–533.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., Lovell, C. K., & Pasurka, C. (1989). Multilateral productivity comparisons when some outputs are undesirable: A nonparametric approach. The Review of Economics and Statistics, 71(1), 90–98.
Fukuyama, H., Maeda, Y., Sekitani, K., & Shi, J. (2014). Input-output substitutability and strongly monotonic p-norm least distance DEA measures. European Journal of Operational Research, 237(3), 997–1007.
González, E., & Álvarez, A. (2001). From efficiency measurement to efficiency improvement: The choice of a relevant benchmark. European Journal of Operational Research, 133(3), 512–520.
Hailu, A., & Veeman, T. S. (2001). Non-parametric productivity analysis with undesirable outputs: An application to the Canadian pulp and paper industry. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 83(3), 605–616.
Huang, J., Yang, X., Cheng, G., & Wang, S. (2014). A comprehensive eco-efficiency model and dynamics of regional eco-efficiency in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 67, 228–238.
Hu, H. H., Qi, Q., & Yang, C. H. (2012). Evaluation of China’s regional hospital efficiency: DEA approach with undesirable output. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 63(6), 715–725.
Korhonen, P. J., & Luptacik, M. (2004). Eco-efficiency analysis of power plants: An extension of data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 154(2), 437–446.
Kuah, C. T., & Wong, K. Y. (2011). Efficiency assessment of universities through data envelopment analysis. Procedia Computer Science, 3, 499–506.
Li, H., & Shi, J. F. (2014). Energy efficiency analysis on Chinese industrial sectors: An improved super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. Journal of Cleaner Production, 65, 97–107.
Portela, M. C. A. S., Borges, P. C., & Thanassoulis, E. (2003). Finding closest targets in non-oriented DEA models: The case of convex and non-convex technologies. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 19(2–3), 251–269.
Seiford, L. M., & Zhu, J. (2002). Modeling undesirable factors in efficiency evaluation. European Journal of Operational Research, 142(1), 16–20.
Shi, G. M., Bi, J., & Wang, J. N. (2010). Chinese regional industrial energy efficiency evaluation based on a DEA model of fixing non-energy inputs. Energy Policy, 38(10), 6172–6179.
Song, M., An, Q., Zhang, W., Wang, Z., & Wu, J. (2012). Environmental efficiency evaluation based on data envelopment analysis: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16(7), 4465–4469.
Song, M. L., & Wang, S. H. (2014). DEA decomposition of China’s environmental efficiency based on search algorithm. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 247, 562–572.
Sueyoshi, T., & Goto, M. (2012). DEA environmental assessment of coal fired power plants: Methodological comparison between radial and non-radial models. Energy Economics, 34(6), 1854–1863.
Sueyoshi, T., Goto, M., & Ueno, T. (2010). Performance analysis of US coal-fired power plants by measuring three DEA efficiencies. Energy Policy, 38(4), 1675–1688.
Wang, K., Huang, W., Wu, J., & Liu, Y. N. (2014). Efficiency measures of the Chinese commercial banking system using an additive two-stage DEA. Omega, 44, 5–20.
Wang, K., Yu, S., & Zhang, W. (2007). China’s regional energy and environmental efficiency: A DEA window analysis based dynamic evaluation. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 58, 1117–1127.
Wang, K., Yu, S., & Zhang, W. (2013). China’s regional energy and environmental efficiency: A DEA window analysis based dynamic evaluation. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 58(5), 1117–1127.
Wu, J., Liang, L., & Yang, F. (2009). Achievement and benchmarking of countries at the Summer Olympics using cross efficiency evaluation method. European Journal of Operational Research, 197(2), 722–730.
Wu, J., Zhu, Q., Chu, J., & Liang, L. (2015a). Two-stage network structures with undesirable intermediate outputs reused: A DEA based approach. Computational Economics, 46(3), 455–477.
Wu, J., Zhu, Q., Chu, J., Liu, H., & Liang, L. (2015b). Measuring energy and environmental efficiency of transportation systems in China based on a parallel DEA approach. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2015.08.001
Wu, J., Zhu, Q., Yin, P., & Song, M. (2015c). Measuring energy and environmental performance for regions in China by using DEA-based Malmquist indices. Operational Research. doi:10.1007/s12351-015-0203-z.
Xie, B. C., Shang, L. F., Yang, S. B., & Yi, B. W. (2014). Dynamic environmental efficiency evaluation of electric power industries: Evidence from OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) and BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India and China) countries. Energy, 74, 147–157.
Yang, H., & Pollitt, M. (2009). Incorporating both undesirable outputs and uncontrollable variables into DEA: The performance of Chinese coal-fired power plants. European Journal of Operational Research, 197(3), 1095–1105.
Yang, H., & Pollitt, M. (2010). The necessity of distinguishing weak and strong disposability among undesirable outputs in DEA: Environmental performance of Chinese coal-fired power plants. Energy Policy, 38(8), 4440–4444.
Yang, L., Ouyang, H., Fang, K., Ye, L., & Zhang, J. (2015). Evaluation of regional environmental efficiencies in China based on super-efficiency-DEA. Ecological Indicators, 51, 13–19.
Zhang, B., Bi, J., Fan, Z., Yu an, Z., & Ge, J. (2008). Eco-efficiency evaluation of industrial system in China: A data envelopment analysis approach. Ecological Economics, 68(1–2), 306–316.
Zhang, W., & Yang, S. Y. (2013). The influence of energy consumption of China on its real GDP from aggregated and disaggregated viewpoints. Energy Policy, 57, 76–81.
Zhou, P., Ang, B. W., & Poh, K. L. (2008). Measuring environmental performance under different environmental DEA technologies. Energy Economics, 30(1), 1–14.
Zhou, P., Poh, K. L., & Ang, B. W. (2007). A non-radial DEA approach to measuring environmental performance. European Journal of Operational Research, 178(1), 1–9.
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by National Natural Science Funds of China (Nos. 71222106 and 71110107024), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20133402110028), Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of P. R. China (No. 201279) and The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. WK2040160008) and Top-Notch Young Talents Program of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhu, Q., Chu, J. et al. Environmental Performance and Benchmarking Information for Coal-Fired Power Plants in China: A DEA Approach. Comput Econ 54, 1287–1302 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-015-9560-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-015-9560-1