Abstract
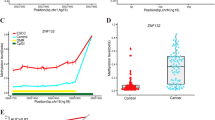
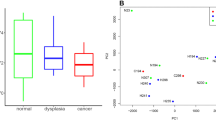
The growth arrest DNA damage-inducible gene (Gadd45) family, which is composed of Gadd45A, Gadd45B, and Gadd45G, is involved in DNA damage response and cell growth arrest. The present study was to detect the role of Gadd45 gene family in esophageal cancer and the relationship of Gadd45G methylation to a series of pathological parameters in a large esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) sample, in order to elucidate more information on the role of Gadd45 gene family with regard to the pathogenesis of ESCC. Frequent silencing of Gadd45G but not Gadd45A and Gadd45B were found in esophageal cancer cell lines and the silencing of Gadd45G may be reversed by 5-Aza-dC or TSA treatment in Eca109 cell line. The aberrant proximal promoter methylation of Gadd45G induces silencing of Gadd45G expression in Eca109 cell line. Gadd45A mRNA and protein expression in ESCC tumor tissues was significantly different compared to corresponding normal tissues. Decreased mRNA and protein expression of Gadd45G was observed in ESCC tumor tissues and was associated with Gadd45G proximal promoter methylation. Gadd45A or Gadd45B expression was not correlated with ESCC patients survival, while Gadd45G methylation status and protein expression were independently associated with ESCC patients’ survival. These data indicated that Gadd45G may be a functional tumor suppressor and its inactivation through proximal promoter methylation may play an important role in ESCC carcinogenesis and reactivation of Gadd45G gene may has therapeutic potential and may be used as a prognostic marker for ESCC patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamura RE, de Vasconcellos JF, Sarkar D, Libermann TA, Fisher PB, Zerbini LF (2012) GADD45 proteins: central players in tumorigenesis. Curr Mol Med 12:634–651
Fornace AJ Jr, Nebert DW, Hollander MC, Luethy JD, Papathanasiou M, Fargnoli J, Holbrook NJ (1989) Mammalian genes coordinately regulated by growth arrest signals and DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol 9:4196–4203
Rosemary Siafakas A, Richardson DR (2009) Growth arrest and DNA damage-45 alpha (GADD45alpha). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:986–989
Hollander MC, Sheikh MS, Bulavin DV, Lundgren K, Augeri-Henmueller L, Shehee R, Molinaro TA, Kim KE, Tolosa E, Ashwell JD, Rosenberg MP, Zhan Q, Fernández-Salguero PM, Morgan WF, Deng CX, Fornace AJ Jr (1999) Genomic instability in Gadd45a-deficient mice. Nat Genet 23:176–184
Vairapandi M, Balliet AG, Fornace AJ Jr, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (1996) The differentiation primary response gene MyD118, related to GADD45, encodes for a nuclear protein which interacts with PCNA and p21WAF1/CIP1. Oncogene 12:2579–2594
Zhang W, Bae I, Krishnaraju K, Azam N, Fan W, Smith K, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (1999) CR6: a third member in the MyD118 and Gadd45 gene family which functions in negative growth control. Oncogene 18:4899–4907
Cretu A, Sha X, Tront J, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2009) Stress sensor Gadd45 genes as therapeutic targets in cancer. Cancer Ther 7:268–276
Tront JS, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2006) Gadd45a suppresses Ras-driven mammary tumorigenesis by activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p38 stress signaling resulting in apoptosis and senescence. Cancer Res 66:8448–8454
Yang Z, Song L, Huang C (2009) Gadd45 proteins as critical signal transducers linking NF-kappaB to MAPK cascades. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9:915–930
Vairapandi M, Balliet AG, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2002) GADD45b and GADD45g are cdc2/cyclinB1 kinase inhibitors with a role in S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoints induced by genotoxic stress. J Cell Physiol 192:327–338
Liebermann DA, Tront JS, Sha X, Mukherjee K, Mohamed-Hadley A, Hoffman B (2011) Gadd45 stress sensors in malignancy and leukemia. Crit Rev Oncog 16:129–140
Yoo J, Ghiassi M, Jirmanova L, Balliet AG, Hoffman B, Fornace AJ Jr, Liebermann DA, Bottinger EP, Roberts AB (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis is mediated by Smad-dependent expression of GADD45b through p38 activation. J Biol Chem 278:43001–43007
Ying J, Srivastava G, Hsieh WS, Gao Z, Murray P, Liao SK, Ambinder R, Tao Q (2005) The stress-responsive gene GADD45G is a functional tumor suppressor, with its response to environmental stresses frequently disrupted epigenetically in multiple tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:6442–6449
Na YK, Lee SM, Hong HS, Kim JB, Park JY, Kim DS (2010) Hypermethylation of growth arrest DNA-damage-inducible gene 45 in non-small cell lung cancer and its relationship with clinicopathologic features. Mol Cells 30:89–92
Ramachandran K, Gopisetty G, Gordian E, Navarro L, Hader C, Reis IM, Schulz WA, Singal R (2009) Methylation-mediated repression of GADD45alpha in prostate cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Res 69:1527–1535
Qiu W, Zhou B, Zou H, Liu X, Chu PG, Lopez R, Shih J, Chung C, Yen Y (2004) Hypermethylation of growth arrest DNA damage-inducible gene 45 beta promoter in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol 165:1689–1699
Bahar A, Bicknell JE, Simpson DJ, Clayton RN, Farrell WE (2004) Loss of expression of the growth inhibitory gene GADD45gamma, in human pituitary adenomas, is associated with CpG island methylation. Oncogene 23:936–944
Ct Wu, Morris JR (2001) Genes, genetics, and epigenetics: a correspondence. Science 293:1103–1105
Jones PA, Baylin SB (2002) The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 3:415–428
Baylin SB, Herman JG (2000) DNA hypermethylation in tumorigenesis: epigenetics joins genetics. Trends Genet 16:168–174
Belinsky SA (2004) Gene-promoter hypermethylation as a biomarker in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4:707–717
Wang W, Huper G, Guo Y, Murphy SK, Olson JA Jr, Marks JR (2005) Analysis of methylation-sensitive transcriptome identifies GADD45a as a frequently methylated gene in breast cancer. Oncogene 24:2705–2714
Chung HK, Yi YW, Jung NC, Kim D, Suh JM, Kim H, Park KC, Kim DW, Hwang ES, Song JH, Ku BJ, Han HJ, Ro HK, Kim JM, Shong M (2003) Gadd45gamma expression is reduced in anaplastic thyroid cancer and its reexpression results in apoptosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3913–3920
Zhang W, Li T, Shao Y, Zhang C, Wu Q, Yang H, Zhang J, Guan M, Yu B, Wan J (2010) Semi-quantitative detection of GADD45-gamma methylation levels in gastric, colorectal and pancreatic cancers using methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:1267–1273
Zhang X, Sun H, Danila DC, Johnson SR, Zhou Y, Swearingen B, Klibanski A (2002) Loss of expression of GADD45 gamma, a growth inhibitory gene, in human pituitary adenomas: implications for tumorigenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:1262–1267
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:2241–2252
Shahbaz Sarwar CM, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ, Abbas G (2010) Esophageal cancer: an update. Int J Surg 8:417–422
Guo W, Zhou RM, Wan LL, Wang N, Li Y, Zhang XJ, Dong XJ (2008) Polymorphisms of the DNA repair gene xeroderma pigmentosum group A and C and risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a population of high incidence region of North China. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134:263–270
Dong Z, Guo W, Guo Y, Kuang G, Yang Z (2012) Concordant promoter methylation of transforming growth factor-beta receptor types I and II occurs early in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Med Sci 343:375–381
Heller G, Schmidt WM, Ziegler B, Holzer S, Müllauer L, Bilban M, Zielinski CC, Drach J, Zöchbauer-Müller S (2008) Genome-wide transcriptional response to 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine and trichostatina in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res 68:44–54
Das PM, Ramachandran K, vanWert J, Singal R (2004) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Biotechniques 37:961–969
Yu L, Liu C, Vandeusen J, Becknell B, Dai Z, Wu YZ, Raval A, Liu TH, Ding W, Mao C, Liu S, Smith LT, Lee S, Rassenti L, Marcucci G, Byrd J, Caligiuri MA, Plass C (2005) Global assessment of promoter methylation in a mouse model of cancer identifies ID4 as a putative tumor-suppressor gene in human leukemia. Nat Genet 37:265–274
Umemoto M, Yokoyama Y, Sato S, Tsuchida S, Al-Mulla F, Saito Y (2001) Carbonyl reductase as a significant predictor of survival and lymph node metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 85:1032–1036
Guo W, Dong Z, Chen Z, Yang Z, Wen D, Kuang G, Guo Y, Shan B (2009) Aberrant CpG Island hypermethylation of RASSF1A in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Cancer Invest 27:459–465
Sasaki M, Anast J, Bassett W, Kawakami T, Sakuragi N, Dahiya R (2003) Bisulfite conversion-specific and methylation-specific PCR: a sensitive technique for accurate evaluation of CpG methylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:305–309
Li LC, Dahiya R (2002) MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 18:1427–1431
Takai D, Jones PA (2003) The CpG island searcher: a new WWW resource. In Silico Biol 3:235–240
Mita H, TsutsuiJ Takekawa M, Witten E, Saito H (2002) Regulation of MTK1/MEKK4 kinase activity by its N-terminal autoinhibitory domain and GADD45 binding. Mol Cell Biol 22:4544–4555
Higashi H, Vallböhmer D, Warnecke-Eberz U, Hokita S, Xi H, Brabender J, Metzger R, Baldus SE, Natsugoe S, Aikou T, Hölscher AH, Schneider PM (2006) Down-regulation of Gadd45 expression is associated with tumor differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 26:2143–2147
Schneider G, Weber A, Zechner U, Oswald F, Friess HM, Schmid RM, Liptay S (2006) GADD45alpha is highly expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and required for tumor cell viability. Int J Cancer 118:2405–2411
Reddy SP, Britto R, Vinnakota K, Aparna H, Sreepathi HK, Thota B, Kumari A, Shilpa BM, Vrinda M, Umesh S, Samuel C, Shetty M, Tandon A, Pandey P, Hegde S, Hegde AS, Balasubramaniam A, Chandramouli BA, Santosh V, Kondaiah P, Somasundaram K, Rao MR (2008) Novel glioblastoma markers with diagnostic and prognostic value identified through transcriptome analysis. Clin Cancer Res 14:2978–2987
Bx Wang, Yin BL, He B, Chen C, Zhao M, Wx Zhang, Xia ZK, Yz Pan, Jq Tang, Xm Zhou, Yin N (2012) Overexpression of DNA damage-induced 45 α gene contributes to esophageal squamous cell cancer by promoter hypomethylation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31:11. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-31-11
Gao H, Jin S, Song Y, Fu M, Wang M, Liu Z, Wu M, Zhan Q (2005) B23 regulates GADD45a nuclear translocation and contributes to GADD45a-induced cell cycle G2-M arrest. J Biol Chem 280:10988–10996
Qiu W, David D, Zhou B, Chu PG, Zhang B, Wu M, Xiao J, Han T, Zhu Z, Wang T, Liu X, Lopez R, Frankel P, Jong A, Yen Y (2003) Down-regulation of growth arrest DNA damage-inducible gene 45beta expression is associated with human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol 162:1961–1974
Jiang C, Zhou B, Fan K, Heung E, Xue L, Liu X, Kirschbaum M, Yen Y (2007) A sequential treatment of depsipeptide followed by 5-azacytidine enhances Gadd45beta expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 27:3783–3789
Acknowledgments
This article was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81101854). We thank the patients and control individuals for taking part in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Zhu, T., Dong, Z. et al. Decreased expression and aberrant methylation of Gadd45G is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 30, 977–992 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9597-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9597-2