Abstract
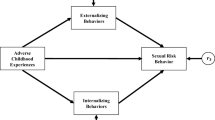
This longitudinal study examined psychopathology as an explanatory mechanism linking childhood violence exposure (CVE) to sexual risk in 177 African American girls recruited from mental health clinics serving low-income communities in Chicago. Beginning at average age 14, girls completed five interviews over 2 years and a sixth assessment including trauma history. CVE reflected sexual, physical, or witnessed violence before age 12. Latent growth modeling accounted for developmental change across the six time points. Externalizing, but not internalizing, symptoms mediated the pathway from CVE to number of partners (indirect effect = .16, 95 % CIBCBS = .04–.29) and inconsistent condom use (indirect effect = .11, CIBCBS = .004–.21). Externalizing problems associated with CVE may help to explain its relationship with sexual risk in low-income, treatment-seeking African American girls. Behavioral interventions addressing aggression, impulsivity, and general risk-taking may be most effective in reducing sexual risk in this population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donenberg GR, Pao M (2004) HIV/AIDS prevention and intervention: youths and psychiatric illness. Contemp Psychiatry 2:1–8
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2008) HIV/AIDS among women
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2012) Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2011
Forhan SE, Gottlieb SL, Sternberg MR, Xu F, Datta SD, Mcquillan GM et al (2009) Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections among female adolescents aged 14 to 19 in the United States. Pediatrics 124:1505–1512
Quinn TC, Overbaugh J (2005) HIV/AIDS in women: an expanding epidemic. Science 308:1582–1583
Pearlin L, Schieman S, Fazio EM, Meersman SC (2005) Stress, health, and the life course: some conceptual perspectives. J Health Soc Behav 46:205–219
Berman SL, Silverman WK, Kurtines WM (2002) The effects of community violence on children and adolescents: Intervention and social policy. In: Bottoms BL, Kovera MB, Mcauliff BDs (eds) Children, social science, and the law. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 301–321
Dube SR, Felitti VJ, Dong M, Giles WH, Anda RF (2003) The impact of adverse childhood experiences on health problems: evidence from four birth cohorts dating back to 1900. Prev Med 37:268–277
Repetti RL, Taylor SE, Seeman TE (2002) Risky families: family social environments and the mental and physical health of offspring. Psychol Bull 128:330–366
Ickovics JR, Beren SE, Grigorenko EL, Morrill AC, Druley JA, Rodin J (2002) Pathways of risk: race, social class, stress, and coping as factors predicting heterosexual risk behaviors for HIV among women. AIDS Behav 6:339–350
Voisin DR, Neilands TB (2010) Community violence and health risk factors among adolescents among adolescents on Chicago’s Southside: does gender matter? J Adolesc Health 46:600–602
Wyatt GE, Myers HF, Williams JK, Kitchen CR, Loeb T, Carmona JV et al (2002) Does a history of trauma contribute to HIV risk for women of color? Implications for prevention and policy. Am J Public Health 92:660–665
Wilson HW, Widom CS (2008) An examination of risky sexual behavior and HIV among victims of child abuse and neglect: a thirty-year follow-up. Health Psychol 27:49–158
Senn TE, Carey MP, Vanable PA (2008) Childhood and adolescent sexual abuse and subsequent sexual risk behavior: evidence from controlled studies, methodological critique, and suggestions for research. Clin Psychol Rev 28:711–735
Wilson HW, Woods BA, Emerson E, Donenberg GR (2012) Patterns of violence exposure and sexual risk in low-income, urban African American girls. Psychol Violence 2:194–207
Sroufe LA, Rutter M (1984) The domain of developmental psychopathology. Child Dev 55:17–29
Margolin G, Gordis EB (2000) The effects of family and community violence on children. Ann Rev Psychol 51:445–479
Mcdonald CC, Richmond TR (2008) The relationship between community violence exposure and mental health symptoms in urban adolescents. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs 15(10):833–849
Elkington KS, Bauermeister JA, Zimmerman MA (2010) Psychological distress, substance use, and HIV/STI risk behaviors among youth. J Youth Adolesc 39:514–527
Ramrakha S, Bell ML, Paul C, Dickson N, Moffitt TE, Caspi A (2007) Childhood behavior problems linked to sexual risk taking in young adulthood: a birth cohort study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:1272–1279
Fernandez VV, Kramer TT, Fong GG, Doig AA, Garralda ME (2009) Depressive symptoms and behavioral health risks in young women attending an urban sexual health clinic. Child Health Care Dev 35(6):799–806
Donenberg GR, Emerson E, Mackesy-Amiti ME (2011) Sexual risk among African American girls: psychopathology and mother-daughter relationships. J Consult Clin Psychol 79(2):153–158
Udell W, Donenberg GR, Emerson E (2011) The impact of mental health problems and religiosity on African-American girls’ HIV-risk. Cultural Divers Ethnic Minority Psychol 17(2):217–224
Shaffer D, Fisher P, Lucas CP, Dulcan MK, Schwabstone ME (2000) NIMH diagnostic interview schedule for children version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): description, difference from previous versions and reliability of some common diagnoses. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39:28–38
Brown LK, Hadley W, Stewart A, Lescano C, Whiteley L, Donenberg G et al (2010) Psychiatric disorders and sexual risk among adolescents in mental health treatment. J Consult Clin Psychol 78:590–597
Hollingshead AB (1975) Four-factor index of social status. Yale University, New Haven
Widom CS, Dutton MA, Czaja SJ, Dumont KA (2005) Development and validation of a new instrument to assess lifetime trauma and victimization history. J Trauma Stress 18(5):519–531
Donenberg GR, Emerson E, Bryant FB, Wilson H, Weber-Shifrin E (2001) Understanding AIDS-risk behavior among adolescents in psychiatric care: links to psychopathology and peer relationships. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:642–653
Achenbach TM (1991) Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL/4-18. University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry, Burlington, VT, YSR and TRF profiles
Bollen KA, Curran PJ (2006) Latent growth curve models: a structural equation perspective. Wiley series in probability and statistics. Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Mackinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Hoffman JM, West SG, Sheets V (2002) A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychol Methods 7(1):83–104
Mackinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Williams J (2004) Confidence limits for the indirect effect: distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivar Behav Res 39:99–128
Allison PD (2003) Missing data techniques for structural equation modeling. J Abnorm Psychol 117:545–557
Schlomer GL, Bauman S, Card NA (2010) Best practices for missing data management in counseling psychology. J Couns Psychol 57:1–10
Barrett P (2007) Structural equation modelling: adjudging model fit. Personal Individ Differ 42:815–824
Wilson HW, Donenberg GR, Emerson E (2014) Violence exposure and the development of sexual risk in low-income African American girls. Journal of Behavioral Medicine epub ahead of print
Hutton HE, Lyketsos CG, Zenilman JM, Thompson RE, Erbelding EJ (2004) Depression and HIV risk behaviors among patients in a sexually transmitted disease clinic. Am J Psychiatry 161:912–914
Jessor R (1998) New perspectives on adolescent risk behavior. In: Jessor Rs (ed) New perspectives on adolescent risk behavior. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–12
Ehrensaft MK, Cohen P, Brown J, Smailes E, Chen H, Johnson JG (2003) Intergenerational transmission of partner violence: a 20-year prospective study. J Consult Clin Psychol 71:741–753
Wingood GM, Diclemente RJ (1997) The effects of an abusive primary partner on the condom use and sexual negotiation practices of African American women. Am J Public Health 87:1016–1018
De Bellis MD (2001) Developmental traumatology: the psychobiological development of maltreated children and its implications for research, treatment, and policy. Dev Psychopathol 13:539–564
Lupien SJ, Mcewen BS, Gunnar MR, Heim C (2009) Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behavior, and cognition. Nature 10:434–445
Widom CS, Czaja SJ (2012) Childhood trauma, psychopathology, and violence: Disentangling causes, consequences, and correlates. In: Widom CSs (ed) Trauma, psychopathology, and violence: causes, correlates, or consequences?. Oxford University Press, New York
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funding from the National Institute of Mental Health and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Health and Human Development (R03MH086361; R01MH065155; R01HD067511). We thank the mothers and daughters who participated in the study and gratefully acknowledge the administrators and clinical staff at the outpatient mental health clinics who identified eligible families. We also thank Gloria Coleman, the study recruiter at UIC, and for their invaluable assistance in conducting interviews and entering data, graduate students at RFUMS Bola Animashaun, Tiffany Brakefield, Neha Darji, and Mary Beth Tull, and an undergraduate intern, Paige Saltzberg. These data reflect self-reported behaviors that place girls at risk for sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS, and may not represent girls’ willingness to engage in the behavior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, H.W., Pettineo, L., Edmonds, A. et al. From Violence Exposure to Development of Sexual Risk in Low-Income Urban Girls: The Role of Psychopathology. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 46, 270–280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-014-0466-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-014-0466-2