Abstract
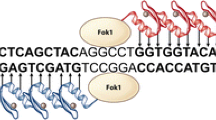
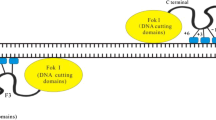
Genome editing tools (GET), including zinc-finger nucleases (ZFN), transcription activator-like endonucleases (TALENS), and meganucleases possess long recognition sites and are thus capable of cutting DNA in a very specific manner. These genome editing tools mediate targeted genetic alterations by enhancing DNA mutation frequency via induction of double-strand breaks at a predetermined genomic site. Compared to conventional homologous recombination based gene targeting, GETs can increase gene targeting and gene disruption via mutagenic DNA repair more than 10,000-fold. Recently, a novel class of genome editing tools was described that uses RNAs to target a specific genomic site. The CRISPR/Cas9 system is capable of targeting even multiple genomic sites in one shot and thus could be superior to ZFNs or TALEN. Current results indicate that these tools can be successfully employed in a broad range of organisms which renders them useful for improving the understanding of complex physiological systems, producing transgenic animals, including creating large animal models for human diseases, creating specific cell lines, and plants, and even for treating human genetic diseases. This review provides an update on the use of ZFNs to modify the genome of farm animals, summarizes current knowledge on the underlying mechanism, and discusses new opportunities for generating genetically modified farm animals.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRISPR:
-
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- DSB:
-
Double-strand break
- EGFP:
-
Enhanced green fluorescent protein
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- GET:
-
Genome editing tools
- HR:
-
Homologous recombination
- HDR:
-
Homology-directed repair
- IPS:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- NHEJ:
-
Nonhomologous end joining
- SCNT:
-
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
- SSB:
-
Single-strand break
- TALEN:
-
Transcription activator-like effector endonuclease
- ZF:
-
Zinc-finger
- ZFN:
-
Zinc-finger nuclease
References
Bao L, Chen H, Jong U, Rim C, Li W, Lin X, Zhang D, Luo Q, Cui C, Huang H, Zhang Y, Xiao L, Fu Z (2014) Generation of GGTA1 biallelic knockout pigs via zinc-finger nucleases and somatic cell nuclear transfer. Sci Chin Life sci 57(2):263–268. doi:10.1007/s11427-013-4601-2
Bedell VM, Wang Y, Campbell JM, Poshusta TL, Starker CG, Krug RG 2nd, Tan W, Penheiter SG, Ma AC, Leung AY, Fahrenkrug SC, Carlson DF, Voytas DF, Clark KJ, Essner JJ, Ekker SC (2012) In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature 491(7422):114–118. doi:10.1038/nature11537
Bibikova M, Golic M, Golic KG, Carroll D (2002) Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 161(3):1169–1175
Chen F, Pruett-Miller SM, Huang Y, Gjoka M, Duda K, Taunton J, Collingwood TN, Frodin M, Davis GD (2011) High-frequency genome editing using ssDNA oligonucleotides with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Methods 8(9):753–755. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1653
Choulika A, Perrin A, Dujon B, Nicolas JF (1995) Induction of homologous recombination in mammalian chromosomes by using the I-SceI system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 15(4):1968–1973
Cooper DK, Ayares D (2011) The immense potential of xenotransplantation in surgery. Int J Surg 9(2):122–129. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.11.002
Deng C, Capecchi MR (1992) Reexamination of gene targeting frequency as a function of the extent of homology between the targeting vector and the target locus. Mol Cell Biol 12(8):3365–3371
Donoho G, Jasin M, Berg P (1998) Analysis of gene targeting and intrachromosomal homologous recombination stimulated by genomic double-strand breaks in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 18(7):4070–4078
Doyon Y, Choi VM, Xia DF, Vo TD, Gregory PD, Holmes MC (2010) Transient cold shock enhances zinc-finger nuclease-mediated gene disruption. Nat Methods 7(6):459–460
Epinat JC, Arnould S, Chames P, Rochaix P, Desfontaines D, Puzin C, Patin A, Zanghellini A, Paques F, Lacroix E (2003) A novel engineered meganuclease induces homologous recombination in yeast and mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 31(11):2952–2962
Ezzelarab M, Ayares D, Cooper DK (2005) Carbohydrates in xenotransplantation. Immunol Cell Biol 83(4):396–404. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1711.2005.01344.x
Flisikowska T, Thorey IS, Offner S, Ros F, Lifke V, Zeitler B, Rottmann O, Vincent A, Zhang L, Jenkins S, Niersbach H, Kind AJ, Gregory PD, Schnieke AE, Platzer J (2011) Efficient immunoglobulin gene disruption and targeted replacement in rabbit using zinc finger nucleases. PLoS One 6(6):e21045. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021045
Flisikowska T, Kind A, Schnieke A (2014) Genetically modified pigs to model human diseases. J Appl Genet 55(1):53–64. doi:10.1007/s13353-013-0182-9
Geurts AM, Cost GJ, Freyvert Y, Zeitler B, Miller JC, Choi VM, Jenkins SS, Wood A, Cui X, Meng X, Vincent A, Lam S, Michalkiewicz M, Schilling R, Foeckler J, Kalloway S, Weiler H, Menoret S, Anegon I, Davis GD, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Jacob HJ, Buelow R (2009) Knockout rats via embryo microinjection of zinc-finger nucleases. Science 325(5939):433. doi:10.1126/science.1172447
Guilinger JP, Thompson DB, Liu DR (2014) Fusion of catalytically inactive Cas9 to FokI nuclease improves the specificity of genome modification. Nat Biotechnol. doi:10.1038/nbt.2909
Hauschild J, Petersen B, Santiago Y, Queisser AL, Carnwath JW, Lucas-Hahn A, Zhang L, Meng X, Gregory PD, Schwinzer R, Cost GJ, Niemann H (2011) Efficient generation of a biallelic knockout in pigs using zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(29):12013–12017. doi:10.1073/pnas.1106422108
Hauschild-Quintern J, Petersen B, Cost GJ, Niemann H (2013a) Gene knockout and knockin by zinc-finger nucleases: current status and perspectives. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 70(16):2969–2983. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1204-1
Hauschild-Quintern J, Petersen B, Queisser AL, Lucas-Hahn A, Schwinzer R, Niemann H (2013b) Gender non-specific efficacy of ZFN mediated gene targeting in pigs. Transgenic Res 22(1):1–3. doi:10.1007/s11248-012-9647-6
Kim YG, Cha J, Chandrasegaran S (1996) Hybrid restriction enzymes: zinc finger fusions to Fok I cleavage domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(3):1156–1160
Kwon DN, Lee K, Kang MJ, Choi YJ, Park C, Whyte JJ, Brown AN, Kim JH, Samuel M, Mao J, Park KW, Murphy CN, Prather RS, Kim JH (2013) Production of biallelic CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase knock-out pigs. Sci rep 3:1981. doi:10.1038/srep01981
Li P, Estrada JL, Burlak C, Tector AJ (2012) Biallelic knockout of the alpha-1,3 galactosyltransferase gene in porcine liver-derived cells using zinc finger nucleases. Journal of surgical research, The. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2012.06.035
Lillico SG, Proudfoot C, Carlson DF, Stverakova D, Neil C, Blain C, King TJ, Ritchie WA, Tan W, Mileham AJ, McLaren DG, Fahrenkrug SC, Whitelaw CB (2013) Live pigs produced from genome edited zygotes. Sci rep 3:2847. doi:10.1038/srep02847
Liu X, Wang Y, Guo W, Chang B, Liu J, Guo Z, Quan F, Zhang Y (2013) Zinc-finger nickase-mediated insertion of the lysostaphin gene into the beta-casein locus in cloned cows. Nat Commun 4:2565. doi:10.1038/ncomms3565
Liu X, Wang Y, Tian Y, Yu Y, Gao M, Hu G, Su F, Pan S, Luo Y, Guo Z, Quan F, Zhang Y (2014) Generation of mastitis resistance in cows by targeting human lysozyme gene to beta-casein locus using zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Biol sci / The Royal Society 281(1780):20133368. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.3368
Meselson MS, Radding CM (1975) A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72(1):358–361
Miller J, McLachlan AD, Klug A (1985) Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J 4(6):1609–1614
Moehle EA, Rock JM, Lee YL, Jouvenot Y, DeKelver RC, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Holmes MC (2007) Targeted gene addition into a specified location in the human genome using designed zinc finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(9):3055–3060. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611478104
Nowak-Imialek M, Niemann H (2012) Pluripotent cells in farm animals: state of the art and future perspectives. Reprod Fertil Dev 25(1):103–128. doi:10.1071/RD12265
Orlando SJ, Santiago Y, DeKelver RC, Freyvert Y, Boydston EA, Moehle EA, Choi VM, Gopalan SM, Lou JF, Li J, Miller JC, Holmes MC, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Cost GJ (2010) Zinc-finger nuclease-driven targeted integration into mammalian genomes using donors with limited chromosomal homology. Nucleic Acids Res 38(15):e152. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq512
Pabo CO, Peisach E, Grant RA (2001) Design and selection of novel Cys2His2 zinc finger proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 70:313–340. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.313
Pavletich NP, Pabo CO (1991) Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science 252(5007):809–817
Petersen B, Lucas-Hahn A, Oropeza M, Hornen N, Lemme E, Hassel P, Queisser AL, Niemann H (2008) Development and validation of a highly efficient protocol of porcine somatic cloning using preovulatory embryo transfer in peripubertal gilts. Cloning Stem Cells 10(3):355–362. doi:10.1089/clo.2008.0026
Petersen B, Carnwath JW, Niemann H (2009) The perspectives for porcine-to-human xenografts. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 32(2):91–105. doi:10.1016/j.cimid.2007.11.014
Radding CM (1982) Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet 16:405–437. doi:10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201
Rouet P, Smih F, Jasin M (1994) Expression of a site-specific endonuclease stimulates homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(13):6064–6068
Smith J, Bibikova M, Whitby FG, Reddy AR, Chandrasegaran S, Carroll D (2000) Requirements for double-strand cleavage by chimeric restriction enzymes with zinc finger DNA-recognition domains. Nucleic Acids Res 28(17):3361–3369
Szczepek M, Brondani V, Buchel J, Serrano L, Segal DJ, Cathomen T (2007) Structure-based redesign of the dimerization interface reduces the toxicity of zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 25(7):786–793. doi:10.1038/nbt1317
Tsai SQ, Wyvekens N, Khayter C, Foden JA, Thapar V, Reyon D, Goodwin MJ, Aryee MJ, Joung JK (2014) Dimeric CRISPR RNA-guided FokI nucleases for highly specific genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 32(6):569–576. doi:10.1038/nbt.2908
Vasquez KM, Marburger K, Intody Z, Wilson JH (2001) Manipulating the mammalian genome by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(15):8403–8410. doi:10.1073/pnas.111009698
Wang J, Friedman G, Doyon Y, Wang NS, Li CJ, Miller JC, Hua KL, Yan JJ, Babiarz JE, Gregory PD, Holmes MC (2012) Targeted gene addition to a predetermined site in the human genome using a ZFN-based nicking enzyme. Genome Res 22(7):1316–1326. doi:10.1101/gr.122879.111
Watanabe M, Umeyama K, Matsunari H, Takayanagi S, Haruyama E, Nakano K, Fujiwara T, Ikezawa Y, Nakauchi H, Nagashima H (2010) Knockout of exogenous EGFP gene in porcine somatic cells using zinc-finger nucleases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402(1):14–18
Watanabe M, Nakano K, Matsunari H, Matsuda T, Maehara M, Kanai T, Kobayashi M, Matsumura Y, Sakai R, Kuramoto M, Hayashida G, Asano Y, Takayanagi S, Arai Y, Umeyama K, Nagaya M, Hanazono Y, Nagashima H (2013) Generation of interleukin-2 receptor gamma gene knockout pigs from somatic cells genetically modified by zinc finger nuclease-encoding mRNA. PLoS One 8(10):e76478. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076478
Whyte JJ, Prather RS (2012) CELL BIOLOGY SYMPOSIUM: Zinc finger nucleases to create custom-designed modifications in the swine (Sus scrofa) genome. J Anim Sci 90(4):1111–U1159. doi:10.2527/jas. 2011-4546
Whyte JJ, Zhao J, Wells KD, Samuel MS, Whitworth KM, Walters EM, Laughlin MH, Prather RS (2011) Gene targeting with zinc finger nucleases to produce cloned eGFP knockout pigs. Mol Reprod Dev 78(1):2. doi:10.1002/mrd.21271
Yang D, Yang H, Li W, Zhao B, Ouyang Z, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Fan N, Song J, Tian J, Li F, Zhang J, Chang L, Pei D, Chen YE, Lai L (2011a) Generation of PPARgamma mono-allelic knockout pigs via zinc-finger nucleases and nuclear transfer cloning. Cell Res 21(6):979–982. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.70
Yang D, Yang H, Li W, Zhao B, Ouyang Z, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Fan N, Song J, Tian J, Li F, Zhang J, Chang L, Pei D, Chen YE, Lai L (2011b) Generation of PPARgamma mono-allelic knockout pigs via zinc-finger nucleases and nuclear transfer cloning. Cell Res. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.70
Yu S, Luo J, Song Z, Ding F, Dai Y, Li N (2011) Highly efficient modification of beta-lactoglobulin (BLG) gene via zinc-finger nucleases in cattle. Cell Res 21(11):1638–1640. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.153
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editors: Natalay Kouprina and Vladimir Larionov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petersen, B., Niemann, H. Advances in genetic modification of farm animals using zinc-finger nucleases (ZFN). Chromosome Res 23, 7–15 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9451-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9451-7