Abstract
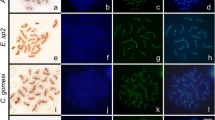
Bivalent 1 of the synaptonemal complex (SC) in XY male Oreochromis niloticus shows an unpaired terminal region in early pachytene. This appears to be related to recombination suppression around a sex determination locus. To allow more detailed analysis of this, and unpaired regions in the karyotype of other Oreochromis species, we developed techniques for FISH on SC preparations, combined with DAPI staining. DAPI staining identified presumptive centromeres in SC bivalents, which appeared to correspond to the positions observed in the mitotic karyotype (the kinetochores could be identified only sporadically in silver-stained EM SC images). Furthermore, two BAC clones containing Dmo (dmrt4) and OniY227 markers that hybridize to known positions in chromosome pair 1 in mitotic spreads (near the centromere, Flpter 0.25, and the putative sex-determination locus, Flpter 0.57, respectively) were used as FISH probes on SCs to verify that the presumptive centromere identified by DAPI staining was located in the expected position. Visualization of both the centromere and FISH signals on bivalent 1 allowed the unpaired region to be positioned at Flpter 0.80 to 1.00, demonstrating that the unpaired region is located in the distal part of the long arm(s). Finally, differences between mitotic and meiotic measurements are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenyloindole
- FISH:
-
fluorescence in-situ hybridization
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- LG:
-
linkage group
- SC:
-
synaptonemal complex
- TEM:
-
transmission electron microscopy
References
Anderson LK, Reeves A, Webb LM, Ashley T (1999) Distribution of crossing over on mouse synaptonemal complexes using immunofluorescent localization of MLH1 protein. Genetics 151:1569–1579
Belonogova NM, Karamysheva TV, Biltueva L et al (2006) Identification of all pachytene bivalents in the common shrew using DAPI-staining of synaptonemal complex spreads. Chromosome Res 14:673–679
Campos-Ramos R, Harvey SC, Masabanda JS et al (2001) Identification of putative sex chromosomes in the blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus, through synaptonemal complex and FISH analysis. Genetica 111:143–153
Campos-Ramos R, Harvey SC, McAndrew BJ, Penman DJ (2003) An investigation of sex determination in the Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, using synaptonemal complex analysis, FISH, sex reversal and gynogenesis. Aquaculture 221:125–140
Carrasco LAP, Penman DJ, Bromage N (1999) Evidence for the presence of sex chromosomes in the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from synaptonemal complex analysis of XX, XY and YY genotypes. Aquaculture 173:207–218
Cnaani A, Lee BY, Zilberman N, Ozouf-Costaz C et al (2008) Genetics of sex determination in tilapiine species. Sex Dev 2:43–54
Ezaz MT, Harvey SC, Boonphakdee C, Teale AJ, McAndrew BJ, Penman DJ (2004) Isolation and physical mapping of sex-linked AFLP markers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 6:435–445
Ferreira IA, Martins C (2008) Physical chromosome mapping of repetitive DNA sequences in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus: evidences for a differential distribution of repetitive elements in the sex chromosomes. Micron 39:411–418
Fischer C, Ozouf-Costaz C, Roest Crollius H et al (2000) Karyotype and chromosome location of characteristic tandem repeat in the pufferfish Tetraodon nigroviridis. Cytogenet Cell Genet 88:50–55
Foresti F, Oliveira C, Galetti PM, de Almeida-Toledo LF (1993) Synaptonemal complex analysis-analysis in spermatocytes of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces, Cichlidae). Genome 36:1124–1128
Froenicke L, Anderson LK, Wienberg J, Ashley T (2002) Male mouse recombination maps for each autosome identified by chromosome painting. Am J Hum Genet 71:1353–1368
Griffin DK, Harvey SC, Campos-Ramos R et al (2002) Early origins of the X and Y chromosomes: Lessons from tilapia. Cytogenet Genome Res 99:157–163
Harvey SC, Masabanda J, Carrasco LAP, Bromage NR, Penman DJ, Griffin DK (2002) Molecular-cytogenetic analysis reveals sequence differences between the sex chromosomes in Oreochromis niloticus: evidence for an early stage of sex chromosome differentiation. Cytogenet Genome Res 97:76–80
Harvey SC, Boonphakdee C, Campos-Ramos R et al (2003) Analysis of repetitive DNA sequences in the sex chromosomes of Oreochromis niloticus. Cytogenet Genome Res 101:314–319
Hurtado NS, Pasantes JJ (2005) Surface spreading of synaptonemal complexes in the clam Dosinia exolata (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Chromosome Res 13:575–580
Kapuscinski J (1995) DAPI: a DNA-specific fluorescent probe. Biotech Histochem 70:220–233
Lee BY, Penman DJ, Kocher TD (2003) Identification of a sex-determining region in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) using bulked segregant analysis. Anim Genet 34:379–383
Lee BY, Hulata G, Kocher TD (2004) Two unlinked loci controlling the sex of blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus). Heredity 92:543–549
Lee BY, Lee WJ, Streelman JT et al (2005) A second-generation genetic linkage map of tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Genetics 170:237–244
Majumdar KC, McAndrew BJ (1986) Relative DNA content of somatic nuclei and chromosomal studies in three genera, Tilapia, Sarotherodon, and Oreochromis of the tribe Tilapinii (Pisces Cichlidae). Genetica 68:175–188
Nagl S, Tichy H, Mayer WE, Samonte IE, McAndrew BJ, Klein J (2001) Classification and phylogenetic relationships of African tilapiine fishes inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 20:361–374
Ocalewicz K (2005) Identification of early and late replicating heterochromatic regions on platyfish (Xiphophorus maculatus) chromosomes. Folia Biol (Krakow) 53:149–153
Ocalewicz K, Babiak I, Dobosz S, Nowaczyk J, Goryczko K (2004) The stability of telomereless chromosome fragments in adult androgenetic rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 207:2229–2236
Ocalewicz K, Hliwa P, Krol J, Rabova M, Stabinski R, Rab P (2007) Karyotype and chromosomal characteristics of Ag-NOR sites and 5S rDNA in European smelt (Osmerus eperlanus L.). Genetica 131:29–35
Oliveira C, Chew K, Porto-Foresti F, Dobson M, Wright M (1999) A LINE2 repetitive DNA sequence from the cichlid fish, Oreochromis niloticus: sequence analysis and chromosomal distribution. Chromosoma 108:457–468
Penman DJ, Piferrer F (2008) Fish gonadogenesis. Part I: genetic and environmental mechanisms of sex determination. Rev Fisheries Sci 16(S1):14–32
Peterson G, Lapitan V, Stack M (1999) Localization of single- and low-copy sequences on tomato synaptonemal complex spreads using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Genetics 152:427–439
Solari AJ (1994) Sex chromosomes and sex determination in vertebrates. CRC, Boca Raton
Solari AJ, Dresser ME (1995) High-resolution cytological localization of the Xho I and EcoR I repeat sequence in the pachytene ZW bivalent of the chicken. Chromosome Res 3:87–93
Acknowledgement
J.C. Mota-Velasco was supported by a PhD grant from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia (CONACYT), Mexico. K. Ocalewicz and R. Campos-Ramos were supported by a grant from the Research Council of Norway.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Walther Traut.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ocalewicz, K., Mota-Velasco, J.C., Campos-Ramos, R. et al. FISH and DAPI staining of the synaptonemal complex of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) allow orientation of the unpaired region of bivalent 1 observed during early pachytene. Chromosome Res 17, 773–782 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9071-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9071-9