Abstract
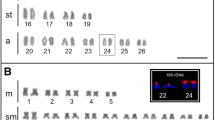
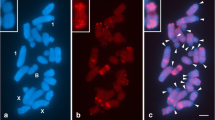
A novel family of repetitive DNA sequences was molecularly cloned from ApaI-digested genomic DNA of two Galliformes species, Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) and guinea fowl (Numida meleagris), and characterized by chromosome in-situ hybridization and filter hybridization. Both the repeated sequence elements produced intensely painted signals on the W chromosomes, whereas they weakly hybridized to whole chromosomal regions as interspersed-type repetitive sequences. The repeated elements of the two species had high similarity of nucleotide sequences, and cross-hybridized to chromosomes of two other Galliformes species, chicken (Gallus gallus) and blue-breasted quail (Coturnix chinensis). The nucleotide sequences were conserved in three other orders of Neognathous birds, the Strigiformes, Gruiformes and Falconiformes, but not in Palaeognathous birds, the Struthioniformes and Tinamiformes, indicating that the repeated sequence elements were amplified on the W chromosomes in the lineage of Neognathous birds after the common ancestor diverged into the Palaeognathae and Neognathae. They are components of the W heterochromatin in Neognathous birds, and a good molecular cytogenetic marker for estimating the phylogenetic relationships and for clarifying the origin of the sex chromosome heterochromatin and the process of sex chromosome differentiation in birds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari HA, Takagi N, Sasaki M (1988) Morphological differentiation of sex chromosomes in three species of ratite birds. Cytogenet Cell Genet 47: 185–188.
Charlesworth B (1991) The evolution of sex chromosomes. Science 251: 1030–1033.
Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D (2000) The degeneration of Y chromosomes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 355: 1563–1572.
Cracraft J (2001) Avian evolution, Gondwana biogeography and the Cretaceous–Tertiary mass extinction event. Proc R Soc Lond B 268: 459–469.
de Boer LEM (1980) Do the chromosomes of the kiwi provide evidence for a monophyletic origin of the ratites? Nature 287: 84–85.
de Kloet RS, de Kloet SR (2003) Evolution of the spindlin gene in birds: independent cessation of the recombination of sex chromosomes at the spindlin locus in neognathous birds and tinamous, a palaeognathous avian family. Genetica 119: 333–342.
García-Moreno J, Mindell DP (2000) Rooting a phylogeny with homologous genes on opposite sex chromosomes (gametologs): a case study using avian CHD. Mol Biol Evol 17: 1826–1832.
Haddrath O, Baker AJ (2001) Complete mitochondrial DNA genome sequences of extinct birds: ratite phylogenetics and the vicariance biogeography hypothesis. Proc R Soc Lond B 268: 939–945.
Handley L-JL, Ceplitis H, Ellegren H (2004) Evolutionary strata on the chicken Z chromosome: implications for sex chromosome evolution. Genetics 167: 367–376.
Itoh Y, Mizuno S (2002) Molecular and cytological characterization of SspI-family repetitive sequence on the chicken W chromosome. Chromosome Res 10: 499–511.
Kodama H, Saitoh H, Tone M, Kuhara S, Sakaki Y, Mizuno S (1987) Nucleotide sequences and unusual electrophoretic behavior of the W chromosome-specific repeating DNA units of the domestic fowl, Gallus gallus domesticus. Chromosoma 96: 18–25.
Matsuda Y, Chapman VM (1995) Application of fluorescence in situ hybridization in genome analysis of the mouse. Electrophoresis 16: 261–272.
Nishida-Umehara C, Fujiwara A, Ogawa A, Mizuno S, Abe S, Yoshida MC (1999) Differentiation of Z and W chromosomes revealed by replication banding and FISH mapping of sex-chromosome-linked DNA markers in the cassowary (Aves, Ratitae). Chromosome Res 7: 635–640.
Ogawa A, Murata K, Mizuno S (1998) The location of Z- and W-linked marker genes and sequence on the homomorphic sex chromosomes of the ostrich and the emu. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 4415–4418.
Ohno S (1967) Sex Chromosomes and Sex-linked Genes. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Pigozzi MI, Solari AJ (1997) Extreme axial equalization and wide distribution of recombination nodules in the primitive ZW pair of Rhea americana (Aves, Ratitae). Chromosome Res 5: 421–428.
Pigozzi MI, Solari AJ (1999) The ZW pairs of two paleognath birds from two orders show transitional stage of sex chromosome differentiation. Chromosome Res 7: 541–551.
Pigozzi MI, Solari AJ (2005) Meiotic recombination in the ZW pair of a tinamid birds shows a differential pattern compared with neognaths. Genome 48: 286–290.
Saitoh H, Harata M, Mizuno S (1989) Presence of female-specific bent-repetitive DNA sequences in the genomes of turkey and pheasant and their interactions with W-protein of chicken. Chromosoma 98: 250–258.
Saitoh Y, Saitoh H, Ohtomo K, Mizuno S (1991) Occupancy of the majority of DNA in the chicken W chromosome by bent-repetitive sequences. Chromosoma 101: 32–40.
Saitoh Y, Mizuno S (1992) Distribtion of XhoI and EcoRI family repetitive DNA sequences into separate domains in the chicken W chromosome. Chromosoma 101: 474–477.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sasaki M, Nishida C, Takagi N, Hori H (1980) Sex-chromosomes of the elegant crested tinamou, Eudromia elegans (Aves: Tinamiformes: Tinamidae). Chromosome Info Serv 29: 19–21.
Schmid M, Enderle E, Schindler D, Schempp W (1989) Chromosome banding and DNA replication patterns in bird karyotypes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 52: 139–146.
Shetty S, Griffin DK, Graves JAM (1999) Comparative painting reveals strong chromosome homology over 80 million years of bird evolution. Chromosome Res 7: 289–295.
Sibley CG, Ahlquist JE (1990) Phylogeny and Classification of Birds: A Study in Molecular Evolution. New Haven: Yale University Press.
Suzuki T, Kurosaki, T, Shimada K et al. (1999) Cytogenetic mapping of 31 functional genes on chicken chromosomes by direct R-banding FISH. Cytogenet Cell Genet 87: 32–40.
Takagi N (1972) A comparative study of the chromosome replication in 6 species of birds. Jpn J Genet 47: 115–123.
Takagi N, Sasaki M (1974) A phylogenetic study of bird karyotypes. Chromosoma 46: 91–120.
Takagi N, Itoh M, Sasaki M (1972) Chromosome studies in four species of Ratitae (Aves). Chromosoma 36: 281–291.
Tone M, Nakano N, Takao E, Narisawa S, Mizuno S (1982) Demonstration of W chromosome-specific repetitive DNA sequences in the domestic fowl, Gallus g. domesticus. Chromosoma 86: 551–569.
Tone M, Sakaki Y, Hashiguchi T, Mizuno S (1984) Genus specificity and extensive methylation of the W chromosome-specific repetitive DNA sequences from the domestic fowl, Gallus gallus domesticus. Chromosoma 89: 228–237.
van Tuinen M, Hedges SB (2001) Calibration of avian molecular clocks. Mol Biol Evol 18: 206–213.
van Tuinen M, Sibley CG, Hedges SB (1998) Phylogeny and biogeography of ratite birds inferred from DNA sequences of the mitochondrial ribosomal genes. Mol Biol Evol 15: 370–376.
van Tuinen M, Sibley CG, Hedges SB (2000) The early history of modern birds inferred from DNA sequences of nuclear and mitochondrial ribosomal genes. Mol Biol Evol 17: 451–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, K., Nishida-Umehara, C., Ishijima, J. et al. A novel family of repetitive DNA sequences amplified site-specifically on the W chromosomes in Neognathous birds. Chromosome Res 14, 613–627 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-006-1071-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-006-1071-4