Abstract
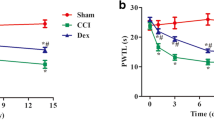
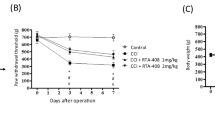
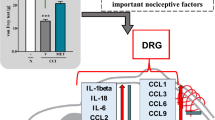
We investigate the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal and intraperitoneal tempol administration in a rat model of chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain and explore the underlying antinociceptive mechanisms of tempol. Rats were randomly assigned to four groups (n = 8 per group): sham group, CCI group, Tem1 group (intrathecal injection of tempol), and Tem2 group (intraperitoneal injection of tempol). Neuropathic pain was induced by CCI of the sciatic nerve. Tempol was intrathecally or intraperitoneally administered daily for 7 days beginning on postoperative day one. The mechanical withdrawal threshold and thermal withdrawal latency were tested on preoperative day 3 and postoperative days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, and 21. Structural changes were examined by hematoxylin and eosin staining, toluidine blue staining, and electron microscopy. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels were determined using the thiobarbituric acid and nitroblue tetrazolium methods, respectively. Nerve growth factor (NGF) expression levels were determined by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Intrathecal, but not intraperitoneal, injection of tempol produced a persistent antinociceptive effect. Intraperitoneal injection of tempol did not result in high enough concentration of tempol in the cerebrospinal fluid. Intrathecal, but not intraperitoneal, injection of tempol inhibited CCI-induced structural damage in the spinal cord reduced MDA levels, and increased SOD activities in the spinal cord. Furthermore, intrathecal, but not intraperitoneal, injection of tempol further downregulated the expression of NGF in the spinal cord following CCI, and this effect was blocked by p38MAPK inhibitor. Intrathecal injection of tempol produces antinociceptive effects and reduces CCI-induced structural damage in the spinal cord by increasing SOD activities and downregulating the expression of NGF via the p38MAPK pathway. Intraperitoneal administration of tempol does not exhibit antinociceptive effects.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attal N, Lanteri-Minet M, Laurent B, Fermanian J, Bouhassira D (2011) The specific disease burden of neuropathic pain: results of a French nationwide survey. Pain 152:2836–2843. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2011.09.014
Beaudry F, Girard C, Vachon P (2007) Early dexamethasone treatment after implantation of a sciatic-nerve cuff decreases the concentration of substance P in the lumbar spinal cord of rats with neuropathic pain. Can J Vet Res 71:90–97
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Blonder JM, McCalden TA, Hsia CJ, Billings RE (2000) Polynitroxyl albumin plus tempol attenuates liver injury and inflammation after hepatic ischemia and reperfusion. Life Sci 67:3231–3239
Bouhassira D, Lanteri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C (2008) Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 136:380–387. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.08.013
Cahill CM, Dray A, Coderre TJ (2003) Intrathecal nerve growth factor restores opioid effectiveness in an animal model of neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 45:543–552
Cao YY, Ding XD, Meng LX, Zhao BS (2014) Effects of tempol preconditioning on the expression level of HIF-α and VEGF after brain injure induced by cardiac arrest in rats. Guandong Med J 35:497–500
Chatterjee PK, Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Zacharowski K, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, Thiemermann C (2000) Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces oxidant stress-mediated renal dysfunction and injury in the rat. Kidney Int 58:658–673. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00212.x
Choi DC, Lee JY, Lim EJ, Baik HH, Oh TH, Yune TY (2012) Inhibition of ROS-induced p38MAPK and ERK activation in microglia by acupuncture relieves neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol 236:268–282. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.05.014
Clark AK et al (2007) Inhibition of spinal microglial cathepsin S for the reversal of neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10655–10660. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610811104
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Doth AH, Hansson PT, Jensen MP, Taylor RS (2010) The burden of neuropathic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of health utilities. Pain 149:338–344. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.02.034
Dray A (2008) Neuropathic pain: emerging treatments. Br J Anaesth 101:48–58. doi:10.1093/bja/aen107
Dworkin RH et al (2010) Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain: an overview and literature update. Mayo Clin Proc 85:S3–S14. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0649
Fang X, Djouhri L, McMullan S, Berry C, Okuse K, Waxman SG, Lawson SN (2005) trkA is expressed in nociceptive neurons and influences electrophysiological properties via Nav1.8 expression in rapidly conducting nociceptors. J Neurosci 25:4868–4878. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0249-05.2005
Gao X, Kim HK, Chung JM, Chung K (2007) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are involved in enhancement of NMDA-receptor phosphorylation in animal models of pain. Pain 131:262–271. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.01.011
Gwak YS, Hulsebosch CE (2007) Inhibition of neuronal p38-mapk activation attenuates below-level central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 24:1259
Gwak YS, Kang J, Unabia GC, Hulsebosch CE (2012) Spatial and temporal activation of spinal glial cells: role of gliopathy in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol 234:362–372. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.10.010
Gwak YS, Hassler SE, Hulsebosch CE (2013) Reactive oxygen species contribute to neuropathic pain and locomotor dysfunction via activation of CamKII in remote segments following spinal cord contusion injury in rats. Pain 154:1699–1708. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.05.018
Hahn SM et al (1992) Tempol, a stable free radical, is a novel murine radiation protector. Cancer Res 52:1750–1753
Hains BC, Waxman SG (2006) Activated microglia contribute to the maintenance of chronic pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 26:4308–4317. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0003-06.2006
Hayashida K, Eisenach JC (2010) Spinal alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated analgesia in neuropathic pain reflects brain-derived nerve growth factor and changes in spinal cholinergic neuronal function. Anesthesiology 113:406–412. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181de6d2c
Janes K, Neumann WL, Salvemini D (2012) Anti-superoxide and anti-peroxynitrite strategies in pain suppression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:815–821. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.12.008
Ji RR, Samad TA, Jin SX, Schmoll R, Woolf CJ (2002) p38 MAPK activation by NGF in primary sensory neurons after inflammation increases TRPV1 levels and maintains heat hyperalgesia. Neuron 36:57–68
Julius D, Basbaum AI (2001) Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature 413:203–210. doi:10.1038/35093019
Kallenborn-Gerhardt W et al (2013a) Antioxidant activity of sestrin 2 controls neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:2013–2023. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4958
Kallenborn-Gerhardt W, Schroder K, Geisslinger G, Schmidtko A (2013b) NOXious signaling in pain processing. Pharmacol Ther 137:309–317. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.11.001
Kato N, Yanaka K, Hyodo K, Homma K, Nagase S, Nose T (2003) Stable nitroxide Tempol ameliorates brain injury by inhibiting lipid peroxidation in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 979:188–193
Khalil Z, Liu T, Helme RD (1999) Free radicals contribute to the reduction in peripheral vascular responses and the maintenance of thermal hyperalgesia in rats with chronic constriction injury. Pain 79:31–37
Lindsay RM, Harmar AJ (1989) Nerve growth factor regulates expression of neuropeptide genes in adult sensory neurons. Nature 337:362–364. doi:10.1038/337362a0
Liu HX, Zhang JJ, Zhang L, Liu H (2013) Effects of tempol on white matter lesions and cognitive impairment in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 93:1330–1334
Liu X et al (2014) Early repeated administration of progesterone improves the recovery of neuropathic pain and modulates spinal 18 kDa-translocator protein (TSPO) expression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 143:130–140. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.02.017
Matsuo H et al (2014) Early transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces hyperalgesia and decreases activation of spinal glial cells in mice with neuropathic pain. Pain 155:1888–1901. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2014.06.022
Mitchell JB et al (1991) Inhibition of oxygen-dependent radiation-induced damage by the nitroxide superoxide dismutase mimic, tempol. Arch Biochem Biophys 289:62–70
Ohayon MM, Stingl JC (2012) Prevalence and comorbidity of chronic pain in the German general population. J Psychiatr Res 46:444–450. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.01.001
Ohsawa I et al (2007) Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 13:688–694. doi:10.1038/nm1577
Patel SP, Sullivan PG, Pandya JD, Rabchevsky AG (2009) Differential effects of the mitochondrial uncoupling agent, 2,4-dinitrophenol, or the nitroxide antioxidant, Tempol, on synaptic or nonsynaptic mitochondria after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci Res 87:130–140. doi:10.1002/jnr.21814
Pathak NN et al (2013) Antihyperalgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Inflammation 36:1468–1478. doi:10.1007/s10753-013-9688-x
Petty BG et al (1994) The effect of systemically administered recombinant human nerve growth factor in healthy human subjects. Ann Neurol 36:244–246. doi:10.1002/ana.410360221
Sakura S, Kirihara Y, Muguruma T, Kishimoto T, Saito Y (2005) The comparative neurotoxicity of intrathecal lidocaine and bupivacaine in rats. Anesth Analg 101:541–547. doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000155960.61157.12
Schwartz ES, Lee I, Chung K, Chung JM (2008) Oxidative stress in the spinal cord is an important contributor in capsaicin-induced mechanical secondary hyperalgesia in mice. Pain 138:514–524. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2008.01.029
Siniscalco D, Giordano C, Rossi F, Maione S, de Novellis V (2011) Role of neurotrophins in neuropathic pain. Curr Neuropharmacol 9:523–529. doi:10.2174/157015911798376208
Smith BH, Torrance N (2012) Epidemiology of neuropathic pain and its impact on quality of life. Curr Pain Headache Rep 16:191–198. doi:10.1007/s11916-012-0256-0
Smith BH, Torrance N, Bennett MI, Lee AJ (2007) Health and quality of life associated with chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin in the community. Clin J Pain 23:143–149. doi:10.1097/01.ajp.0000210956.31997.89
Tal M (1996) A novel antioxidant alleviates heat hyperalgesia in rats with an experimental painful peripheral neuropathy. Neuroreport 7:1382–1384
Torrance N, Smith BH, Bennett MI, Lee AJ (2006) The epidemiology of chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Results from a general population survey. J Pain 7:281–289. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2005.11.008
Wen YR et al (2007) Nerve conduction blockade in the sciatic nerve prevents but does not reverse the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in spinal microglia in the rat spared nerve injury model. Anesthesiology 107:312–321. doi:10.1097/01.anes.0000270759.11086.e7
Wilcox CS (2010) Effects of tempol and redox-cycling nitroxides in models of oxidative stress. Pharmacol Ther 126:119–145. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.01.003
Xiong Y, Hall ED (2009) Pharmacological evidence for a role of peroxynitrite in the pathophysiology of spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 216:105–114. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.11.025
Xiong Y, Singh IN, Hall ED (2009) Tempol protection of spinal cord mitochondria from peroxynitrite-induced oxidative damage. Free Radic Res 43:604–612. doi:10.1080/10715760902977432
Zhao BS, Ding YY, Wang H, Han G, Meng LX (2013) Effects of hyperbaric oxygen postconditioning of microglia on activation in rats model of neuropathic pain. Int J Anesth Resus 34:546–548
Zhao BS, Meng LX, Ding YY, Cao YY (2014a) Hyperbaric oxygen treatment produces an antinociceptive response phase and inhibits astrocyte activation and inflammatory response in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Mol Neurosci 53:251–261. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0213-3
Zhao BS, Meng LX, Tan YH, Song XR (2014b) Effects hyperbaric oxygen treatment on expression of nerve growth factor in spinal cord of rats with neuropathic pain. Chin J Anesthesiol 34:800–803
Zhao BS, Song XR, Hu PY, Meng LX, Tan YH, She YJ, Ding YY (2015) Hyperbaric oxygen treatment at various stages following chronic constriction injury produces different antinociceptive effects via regulation of P2X4R expression and apoptosis. PLoS One 10:e0120122. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120122
Zhu W, Oxford GS (2007) Phosphoinositide-3-kinase and mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathways mediate acute NGF sensitization of TRPV1. Mol Cell Neurosci 34:689–700. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2007.01.005
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Medjaden Academy & Research Foundation for Young Scientists and BBraun Anesthesia Scientific Research Fund (Grant Nos. MJR20150037 and BBF 2012-012).We thank Dr. Lingxin Meng for supporting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Pan, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Intrathecal Administration of Tempol Reduces Chronic Constriction Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats by Increasing SOD Activity and Inhibiting NGF Expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36, 893–906 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0274-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0274-7