Abstract
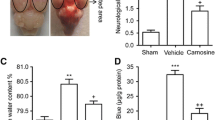
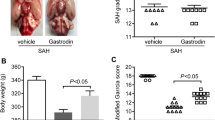
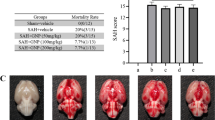
Oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of early brain injury (EBI) following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The aim of this study was to assess whether cysteamine prevents post-SAH oxidative stress injury via its antioxidative and anti-apoptotic effects. It was observed that intraperitoneal administration of cysteamine (20 mg/kg/day) could significantly alleviate EBI (including neurobehavioral deficits, brain edema, blood–brain barrier permeability, and cortical neuron apoptosis) after SAH in rats. Meanwhile, cysteamine treatment reduced post-SAH elevated the reactive oxygen species level, the concentration of malondialdehyde, 3-nitrotyrosine, and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and increased the glutathione peroxidase enzymatic activity, the concentration of glutathione and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain cortex at 48 h after SAH. These results indicated that administration of cysteamine may ameliorate EBI and provide neuroprotection after SAH in rat models.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayer RE, Zhang JH (2008) Oxidative stress in subarachnoid haemorrhage: significance in acute brain injury and vasospasm. Acta Neurochir Suppl 104:33–41
Barry C, Turner RJ, Corrigan F, Vink R (2012) New therapeutic approaches to subarachnoid hemorrhage. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21(6):845–859. doi:10.1517/13543784.2012.683113
Besouw M, Masereeuw R, van den Heuvel L, Levtchenko E (2013) Cysteamine: an old drug with new potential. Drug Discov Today 18(15–16):785–792. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2013.02.003
Borrell-Pages M, Canals JM, Cordelieres FP, Parker JA, Pineda JR, Grange G, Bryson EA, Guillermier M, Hirsch E, Hantraye P, Cheetham ME, Neri C, Alberch J, Brouillet E, Saudou F, Humbert S (2006) Cystamine and cysteamine increase brain levels of BDNF in Huntington disease via HSJ1b and transglutaminase. J Clin Investig 116(5):1410–1424. doi:10.1172/JCI27607
Dubinsky R, Gray C (2006) CYTE-I-HD: phase I dose finding and tolerability study of cysteamine (Cystagon) in Huntington’s disease. Mov Disord 21(4):530–533. doi:10.1002/mds.20756
Friedrich V, Flores R, Sehba FA (2012) Cell death starts early after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosci Lett 512(1):6–11. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.01.036
Goggi J, Pullar IA, Carney SL, Bradford HF (2003) Signalling pathways involved in the short-term potentiation of dopamine release by BDNF. Brain Res 968(1):156–161
Gomis P, Graftieaux JP, Sercombe R, Hettler D, Scherpereel B, Rousseaux P (2010) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 112(3):681–688. doi:10.3171/2009.4.JNS081377
Hunyady B, Palkovits M, Mozsik G, Molnar J, Feher K, Toth Z, Zolyomi A, Szalayova I, Key S, Sibley DR, Mezey E (2001) Susceptibility of dopamine D5 receptor targeted mice to cysteamine. J Physiol Paris 95(1–6):147–151
Kessler A, Biasibetti M, Da Silva Melo DA, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho CS, De Souza Wyse AT, Wannmacher CM (2008a) Antioxidant effect of cysteamine in brain cortex of young rats. Neurochem Res 33(5):737–744. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9486-7
Kessler A, Biasibetti M, Feksa LR, Rech VC, Melo DA, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse AT, Wannmacher CM (2008b) Effects of cysteamine on oxidative status in cerebral cortex of rats. Metab Brain Dis 23(1):81–93. doi:10.1007/s11011-007-9078-x
Kutiyanawalla A, Terry AV Jr, Pillai A (2011) Cysteamine attenuates the decreases in TrkB protein levels and the anxiety/depression-like behaviors in mice induced by corticosterone treatment. PLoS One 6(10):e26153. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026153
Pillai A, Veeranan-Karmegam R, Dhandapani KM, Mahadik SP (2008) Cystamine prevents haloperidol-induced decrease of BDNF/TrkB signaling in mouse frontal cortex. J Neurochem 107(4):941–951. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05665.x
Pinto JT, Khomenko T, Szabo S, McLaren GD, Denton TT, Krasnikov BF, Jeitner TM, Cooper AJ (2009) Measurement of sulfur-containing compounds involved in the metabolism and transport of cysteamine and cystamine. Regional differences in cerebral metabolism. J Chromatogr B 877(28):3434–3441. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.05.041
Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM, Zhang JH (2012) The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol 97(1):14–37. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.02.003
Shieh CH, Hong CJ, Huang YH, Tsai SJ (2008) Potential antidepressant properties of cysteamine on hippocampal BDNF levels and behavioral despair in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(6):1590–1594. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.06.003
Sun BL, Shen FP, Wu QJ, Chi SM, Yang MF, Yuan H, Xie FM, Zhang YB, Chen J, Zhang F (2010a) Intranasal delivery of calcitonin gene-related peptide reduces cerebral vasospasm in rats. Front Biosci 2:1502–1513
Sun L, Xu S, Zhou M, Wang C, Wu Y, Chan P (2010b) Effects of cysteamine on MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Brain Res 1335:74–82. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.079
van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJ (2007) Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 369(9558):306–318. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60153-6
Zhang S, Wang L, Liu M, Wu B (2010) Tirilazad for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD006778. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006778.pub2
Zhang ZY, Sun BL, Yang MF, Li DW, Fang J, Zhang S (2014) Carnosine attenuates early brain injury through its antioxidative and anti-apoptotic effects in a rat experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Cell Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s10571-014-0106-1
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 81301018 for Z.Z. and No. 81471212 for B.S.).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zong-yong Zhang, Ming-feng Yang, and Tao Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Zy., Yang, Mf., Wang, T. et al. Cysteamine Alleviates Early Brain Injury Via Reducing Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in a Rat Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Model. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 543–553 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0150-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0150-x